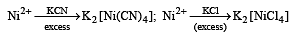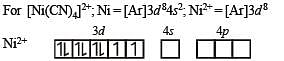Test: Comprehension Based Questions: The d- and f-Block Elements & Coordination Compounds - JEE MCQ
13 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Comprehension Based Questions: The d- and f-Block Elements & Coordination Compounds
PASSAGE 1
The coordination number of Ni2+ is 4.
NiCl2 + KCN (excess) → A (cyano complex)
NiCl2 + Conc . HCl (excess) → B (chloro complex)
Q.The IUPAC name of A and B are
PASSAGE 1
The coordination number of Ni2+ is 4.
NiCl2 + KCN (excess) → A (cyano complex)
NiCl2 + Conc . HCl (excess) → B (chloro complex)
Q. Predict the magnetic nature of A and B
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
PASSAGE 1
The coordination number of Ni2+ is 4.
NiCl2 + KCN (excess) → A (cyano complex)
NiCl2 + Conc . HCl (excess) → B (chloro complex)
Q. The hybridization of A and B are
PASSAGE 2
Copper is the most noble of the first row transition metals and occurs in small deposits in several countries. Ores of copper include chalcanthite (CuSO4.5H2O), atacamite (Cu2Cl(OH)3), cuprite (Cu2O), copper glance (Cu2S) and malachite (Cu2(OH)2CO3). However, 80% of the world copper production comes from the ore chalcopyrite (CuFeS2). The extraction of copper from chalcopyrite involves partial roasting, removal of iron and self-reduction.
Q. Partial roasting of chalcopyrite produces
PASSAGE 2
Copper is the most noble of the first row transition metals and occurs in small deposits in several countries. Ores of copper include chalcanthite (CuSO4.5H2O), atacamite (Cu2Cl(OH)3), cuprite (Cu2O), copper glance (Cu2S) and malachite (Cu2(OH)2CO3). However, 80% of the world copper production comes from the ore chalcopyrite (CuFeS2). The extraction of copper from chalcopyrite involves partial roasting, removal of iron and self-reduction.
Q. Iron is removed from chalcopyrite as
PASSAGE 2
Copper is the most noble of the first row transition metals and occurs in small deposits in several countries. Ores of copper include chalcanthite (CuSO4.5H2O), atacamite (Cu2Cl(OH)3), cuprite (Cu2O), copper glance (Cu2S) and malachite (Cu2(OH)2CO3). However, 80% of the world copper production comes from the ore chalcopyrite (CuFeS2). The extraction of copper from chalcopyrite involves partial roasting, removal of iron and self-reduction.
Q. In self-reduction, the reducing species is
PASSAGE 3
When a metal rod M is dipped in to an aqueous colour less concentrated solution of compound N, the solution turns light blue. Addition of aqueous NaCl to the blue solution gives a white precipitate O. Addition of aqueous NH3 dissolves O and gives an intense blue solution.
Q. The metal rod M is
PASSAGE 3
When a metal rod M is dipped in to an aqueous colour less concentrated solution of compound N, the solution turns light blue. Addition of aqueous NaCl to the blue solution gives a white precipitate O. Addition of aqueous NH3 dissolves O and gives an intense blue solution.
Q. The final solution contains
PASSAGE 3
When a metal rod M is dipped in to an aqueous colour less concentrated solution of compound N, the solution turns light blue. Addition of aqueous NaCl to the blue solution gives a white precipitate O. Addition of aqueous NH3 dissolves O and gives an intense blue solution.
Q. The compound N is
Read the following statement-1(Asseration/Statement) and Statement -2 (Reason/Explanation) and answer as per the options given below :
Q.
Statement-1 : To a solution of potassium chromate if a strong acid is added it changes its colour from yellow to orange.
Statement-2 : The colour change is due to the oxidation of potassium chromate.
Statement-1 : Zn2+ is diamagnetic.
Statement-2 : Two electrons are lost from 4s orbital to form Zn2+.
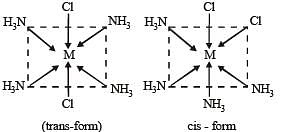
Statement-1 : The geometrical isomers of the complex [M(NH3)4Cl2] are optically inactive. and
Statement-2 : Both geometrical isomers of the complex [M(NH3)4Cl2] possess axis of symmetry.
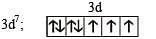
Statement-1 : [Fe(H2O)5NO]SO4 is paramagnetic. and
Statement-2 : The Fe in [Fe(H2O)5NO]SO4 has three unpaired electrons.