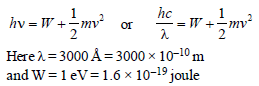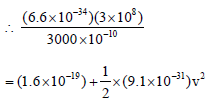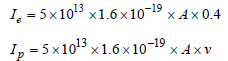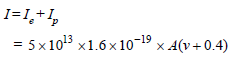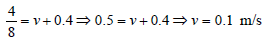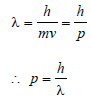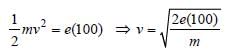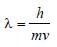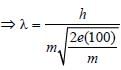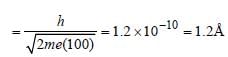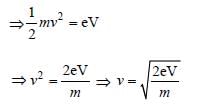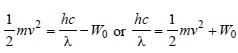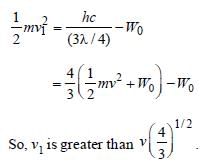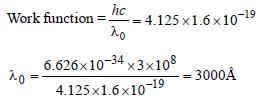31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Dual Nature of Radiation & Matter - 2 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - 31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Dual Nature of Radiation & Matter - 2
The energy of a photon of wavelength λ is [1988]
The threshold frequency for photoelectric effecton sodium corresponds to a wavelength of5000 Å. Its work function is [1988]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The de -Broglie wave corresponding to a particle of mass m and velocity v has a wavelength associated with it [1989]
Energy levels A, B, C of a certain atom correspond to increasing values of energy i.e., EA < EB < EC. If λ1, λ2, λ3 are the wavelengths of radiation corresponding to the transitions C to B, B to A and C to A respectively, which of the following relation is correct? [1990, 2005]
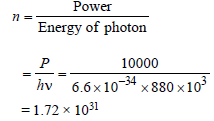
A radio transmitter operates at a freqency 880kHz and a power of 10 kW. The number ofphotons emitted per second is [1990]
The momentum of a photon of an electromagneticradiation is 3.3 × 10–29 kgms–1. What is thefrequency of the associated waves ? [h = 6.6 × 10–34 Js; c = 3 × 108 ms–1) [1990]
Consider an electron in the nth orbit of ahydrogen atom in the Bohr model. Thecircumference of the orbit can be expressed interms of de-Broglie wavelength λ of that electronas [1990]
The wavelength of a 1 keV photon is 1.24 × 10–9 m. What is the frequency of 1 MeV photon ? [1991]
Photoelectric work function of a metal is 1eV.Light of wavelength λ�� = 3000 Å falls on it. Thephoto electrons come out with velocity [1991]
The cathode of a photoelectric cell is changedsuch that the work function changes from W1 toW2 (W2 > W1). If the current before and afterchanges are I1 and I2, all other conditionsremaining unchanged, then (assuming hν > W2)[1992]
An ionization chamber with parallel conductingplates as anode and cathode has 5 × 107 electronsand the same number of singly charged positiveions per cm3. The electrons are moving towards the anode with velocity 0.4 m/s. The currentdensity from anode to cathode is 4μA/m2. Thevelocity of positive ions moving towardscathode is [1992]
When light of wavelength 300 nm (nanometer) falls on a photoelectric emitter, photoelectronsare liberated. For another emitter, however, light of 600 nm wavelength is sufficient for creatingphotoemission. What is the ratio of the work functions of the two emitters? [1993]
Number of ejected photoelectron increases withincrease [1993]
Momentum of a photon of wavelength λ is
In photoelectric effect the work function of ametal is 3.5 eV. The emitted electrons can bestopped by applying a potential of –1.2 V. Then[1994]
Doubly ionised helium atoms and hydrogen ions are accelerated from rest through the same potential drop. The ratio of the final velocities of the helium and the hydrogen ion is [1994]
Gases begin to conduct electricity at low pressurebecause [1994]
Kinetic energy of an electron, which isaccelerated in a potential difference of 100 V is[1995]
The wavelength associated with an electron,accelerated through a potential difference of 100V, is of the order of [1996]
An electron of mass m and charge e is accelerated from rest through a potential difference of V volt in vacuum. Its final speed will be [1996]
Which of the following statement is correct? [1997]
Cosmic rays are [1997]
The X-rays cannot be diffracted by means of anordinary grating because of [1997]
In a photo-emissive cell, with exciting wavelength λ, the fastest electron has speed v. If the exciting wavelength is changed to 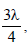 the speed of the fastest emitted electron will be [1998]
the speed of the fastest emitted electron will be [1998]
The 21 cm radio wave emitted by hydrogen ininterstellar space is due to the interaction called the hyperfine interaction in atomic hydrogen.The energy of the emitted wave is nearly [1998]
Light of wavelength 5000 Å falls on a sensitiveplate with photo-electric work function of 1.9 eV.The kinetic energy of the photo-electronsemitted will be [1998]
As the intensity of incident light increases [1999]
The photoelectric work function for a metalsurface is 4.125 eV. The cut off wavelength forthis surface is [1999]
Einstein work on the photoelectric effect provided support for the equation [2000]
Which of the following moving particles (movingwith same velocity) has largest wavelength ofmatter waves? [2002]


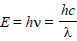
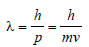
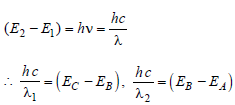
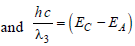
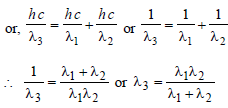 )
)