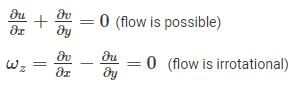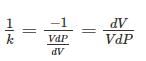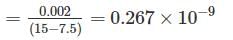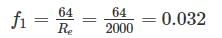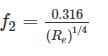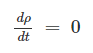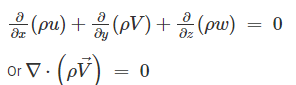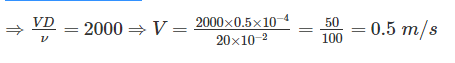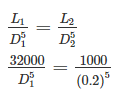Fluid Machinery - 1 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Fluid Machinery - 1
Equation of continuity results from the principal of conservation of _____.
Which of the following conditions will be satisfied by steady irrotational flow?
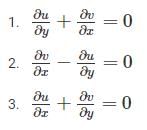
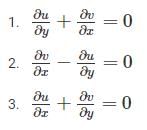
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
An object weighs 60 gm in air, 50 gm in water and 40 gm in oil. Then the specific gravity of the oil will be _____.
The mechanical efficiency of an impulse turbine is generally between:
An increase in pressure of a liquid from 7.5 MPa to 15 MPa results into 0.2 percent decrease in its volume. The coefficient of compressibility of the liquid in m2/N is
Which one of the following statement is CORRECT about the centre of buoyancy?
Property of a fluid by which molecules of different kinds of fluids are attracted to each other is called _____.
While representing the energy equation, the difference between the total head line and Hydaullic gradient line is:
Which one of the following equations represents the continuity equation for steady compressible fluid flow?
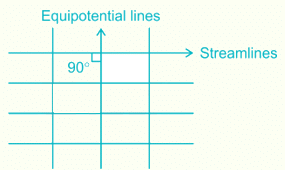
What is the value of the angle (degree) between stream lines and equipotential lines at the point of intersection in the flow net?
An oil of kinematic viscosity of 0.5 stokes flow through a pipe of 20 cm diameter. What is the velocity if the flow is critical?
For very high discharge at low pressure such as for flood control and irrigation applications, which of the following types of pump is preferred?
Calculate the diameter of a pipe of 32000 m long, if it is equivalent to another pipe of 0.2 m diameter and 1000 m long.
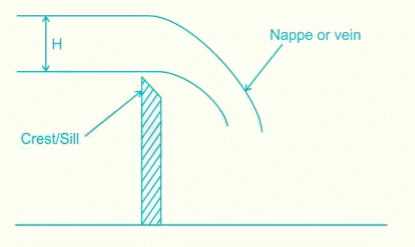
The upper surface of a weir over which water flows is known as
The fluid forces considered in the Navier-Strokes equation are ______.
Which of the following instrument is used for measuring the discharge?
For measuring flow by a Venturimeter, it should be installed in _______.