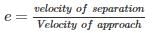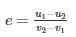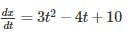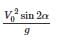Engineering Mechanics - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Engineering Mechanics - 2
On a ladder resting on a smooth ground and leaning against vertical wall, the force of friction will be:
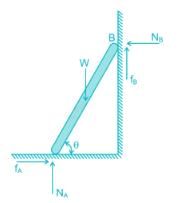
A body moves with a speed of 10 m/s in the curved path of 25 m radius of curvature. If the tangential acceleration is 3 m/s2, then total acceleration for the body will be:
A person who weighs 800 N steps onto a scale that is on the floor of an elevator car. If the elevator accelerates upward at a rate of 5 m/s2, what will the scale read?
Two forces of 30 N and 40 N are acting at 90° to each other, the resultant force is
A fan consumes 20 W of electric power and discharges air from a ventilated room at 0.25 kg/s. The maximum air outlet velocity is nearly
Which of the following forces have zero value of resultant?
A man stands on weighing scale in a lift which carries him upwards with acceleration. The reading on the weighing scale will be
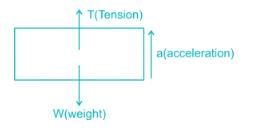
An elevator weighing 1000 kg attains an upward velocity of 4 m/sec in two seconds with uniform acceleration. The tension in the supporting cables will be:-
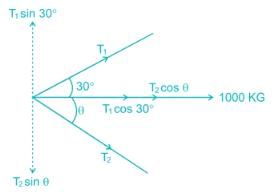
A barge is pulled by two tugboats as shown in the figure below. The resultant of forces exerted by the tugboats is 1000 kg force. What will be the value of θ so that tension in rope 2 is minimum?
The Force applied on a body of mass 100 kg to produce an acceleration of 5 m/s2, is
A rubber ball is dropped from a height of 2 m. If there is not loss of velocity after rebounding the ball will rise to a height of
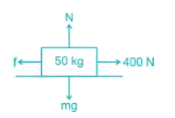
A 50 - kg box rests on horizontal floor for which coefficient of friction is 0.3. If the box is subjected to a horizontal towing force of 400 N, what is its velocity after 5 sec from rest? (Take g = 10 m/s2)
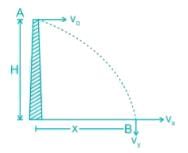
A cannonball is fired from a tower 80 m above the ground with a horizontal velocity of 100 m/s. Determine the horizontal distance at which the ball will hit the ground. (Take g = 10 m/s2)
A bucket of water weighing 10 kg is pulled up from a 20 m deep well by a rope weighing 1 kg/m length, then the work done is _____.
The sum of kinetic and potential energy of a falling body _____.
If v1 and v2 are the initial velocities of two bodies making direct collision and if u1 and u2 are their respective velocities after collision then the coefficient of restitution is given by:
The position of a particle in rectilinear motion is given by the equation (x = t3 - 2t2 + 10t - 4), where x is in meters and t is in seconds. What will be the velocity of the particle at 3s?
The angular velocity (in radians /sec) of a body rotating at N rpm is:
For maximum horizontal range, the angle of projection of a projectile should be


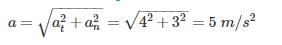

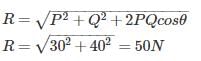
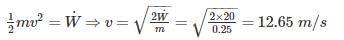
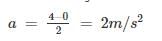
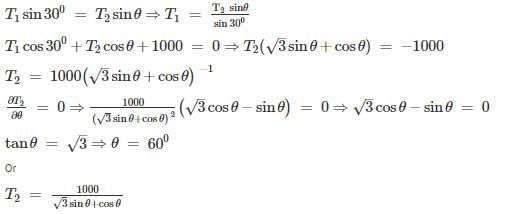
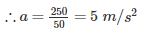
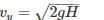
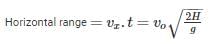
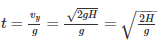
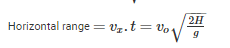
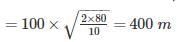
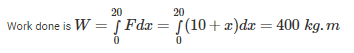
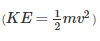 represents energy the mass possesses by virtue of its motion. Likewise, potential energy (PE=mgh) represents energy the mass possesses by virtue of its position.
represents energy the mass possesses by virtue of its motion. Likewise, potential energy (PE=mgh) represents energy the mass possesses by virtue of its position.