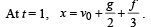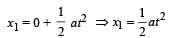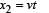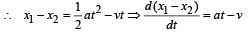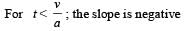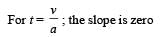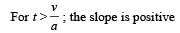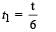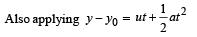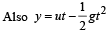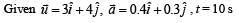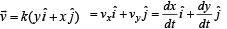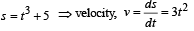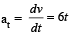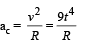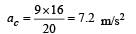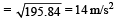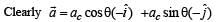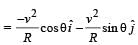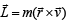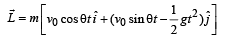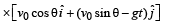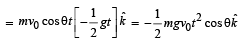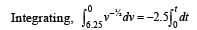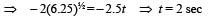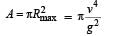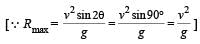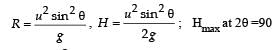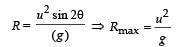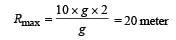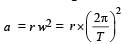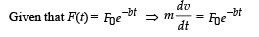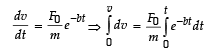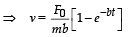Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- Motion - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- Motion
STATEMENT-1 : For an observer looking out through the window of a fast moving train, the nearby objects appear to move in the opposite direction to the train, while the distant objects appear to be stationary.
STATEMENT-2 : If the observer and the object are moving at velocities 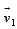 and
and 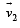 respectively with reference to a laboratory frame, the velocity of the object with respect to the observer is
respectively with reference to a laboratory frame, the velocity of the object with respect to the observer is 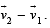 .
.
STATEMENT-2 : If the observer and the object are moving at velocities
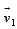 and
and 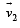 respectively with reference to a laboratory frame, the velocity of the object with respect to the observer is
respectively with reference to a laboratory frame, the velocity of the object with respect to the observer is 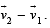 .
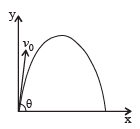
.A ball whose kinetic energy is E, is projected at an angle of 45° to the horizontal. The kinetic energy of the ball at the highest point of its flight will be
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
From a building two balls A and B are thrown such that A is thrown upwards and B downwards (both vertically with the same speed). If vA and vB are their respective velocities on reaching the ground, then
A car, moving with a speed of 50 km/hr, can be stopped by brakes after at least 6 m. If the same car is moving at a speed of 100 km/hr, the minimum stopping distance is
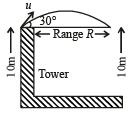
A boy playing on the roof of a 10 m high building throws a ball with a speed of 10m/s at an angle of 30º with the horizontal. How far from the throwing point will the ball be at the height of 10 m from the ground ?
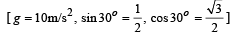
The co-ordinates of a moving particle at any time ‘t’are given by x =at 3 and y =bt 3 . The speed of the particle at time ‘t’ is given by
A ball is released from the top of a tower of height h meters. It takes T seconds to reach the ground. What is the position of the ball at t/3 second?
A projectile can have the same range ‘R’ for two angles of projection. If ‘T1’ and ‘T2’ to be time of flights in the two cases, then the product of the two time of flights is directly proportional to.
Which of the following statements is FALSE for a particle moving in a circle with a constant angular speed ?
An automobile travelling with a speed of 60 km/h, can brake to stop within a distance of 20m. If the car is going twice as fast i.e., 120 km/h, the stopping distance will be
A ball is thrown from a point with a speed ' v0' at an elevation angle of q. From the same point and at the same instant, a person starts running with a constant speed ' 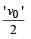
to catch the ball. Will the person be able to catch the ball? If yes, what should be the angle of projection θ?
A car, starting from rest, accelerates at the rate f through a distance S, then continues at constant speed for time t and then decelerates at the rate f/2 to come to rest. If the total distance traversed is 15 S , then
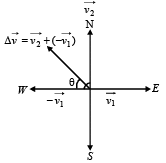
A particle is moving eastwards with a velocity of 5 ms -1 . In 10 seconds the velocity changes to 5 ms-1 northwards.
The average acceleration in this time is
The relation between time t and distance x is t = ax 2 + bx where a and b are constants. The acceleration is
A particle located at x = 0 at time t = 0, starts moving along with the positive x-direction with a velocity 'v' that varies as v = a√ x . The displacement of the particle varies with time as
A particle is projected at 60o to the horizontal with a kinetic energy K. The kinetic energy at the highest point is
The velocity of a particle is v = v0 + gt + ft2. If its position is x = 0 at t = 0, then its displacement after unit time (t = 1) is
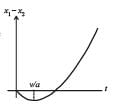
A body is at rest at x = 0. At t = 0, it starts moving in the positive x-direction with a constant acceleration. At the same instant another body passes through x = 0 moving in the positive x-direction with a constant speed. The position of the first body is given by x1(t) after time ‘t’; and that of the second body by x2(t) after the same time interval. Which of the following graphs correctly describes (x1 – x2) as a function of time ‘t’?
Consider a rubber ball freely falling from a height h = 4.9 m onto a horizontal elastic plate. Assume that the duration of collision is negligible and the collision with the plate is totally elastic.
Then the velocity as a function of time and the height as a function of time will be :
A par t icle h as an in i tial vel ocit y of 3iˆ +4ˆj an d an acceleration of 0.4iˆ + 0.3ˆj . Its speed after 10 s is :
A particle is moving with velocity  , where k is a constant. The general equation for its path is
, where k is a constant. The general equation for its path is
A point P moves in counter-clockwise direction on a circular path as shown in the figure. The movement of 'P' is such that it sweeps out a length s = t3 + 5, where s is in metres and t is in seconds. The radius of the path is 20 m. The acceleration of 'P' when t = 2 s is nearly.
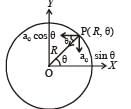
For a particle in uniform circular motion, the acceleration ar at a point P(R,θ) on the circle of radius R is (Here θ is measured from the x-axis )
A small particle of mass m is projected at an angle q with the x-axis with an initial velocity v0 in the x-y plane as shown in the figure. At a time the angular momentum of the particle is
where iˆ,ˆj and kˆ are unit vectors along x, y and z-axis respectively.
An object, moving with a speed of 6.25 m/s, is decelerated at a rate given by: dv/dt =-2.5√v
where v is the instantaneous speed. The timetaken by the object, to come to rest, would be:
A water fountain on the ground sprinkles water all around it. If the speed of water coming out of the fountain is v, the total area around the fountain that gets wet is :
A boy can throw a stone up to a maximum height of 10 m.
The maximum horizontal distance that the boy can throw the same stone up to will be :
Two cars of mass m1 and m2 are moving in circles of radii r1 and r2, respectively. Their speeds are such that they make complete circles in the same time t. The ratio of their centripetal acceleration is :
A particle of mass m is at r est at th e or igin at time t = 0. It is subjected to a force F(t) = F0e–bt in the x direction.
Its speed v(t) is depicted by which of the following curves?




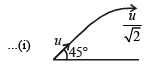
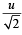 (Remember that the horizontal component of velocity does not change during a projectile motion).
(Remember that the horizontal component of velocity does not change during a projectile motion).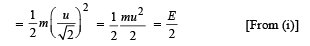

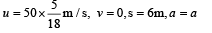
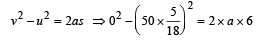
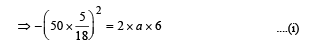
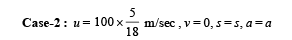
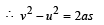
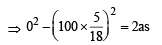
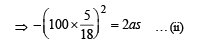
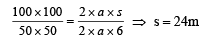
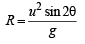
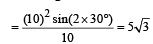
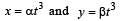
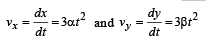
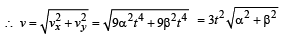
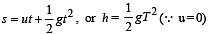 distance moved is given by
distance moved is given by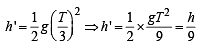
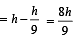
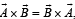 then the angle between A and B is
then the angle between A and B is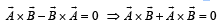


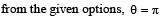

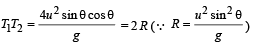 .Hence it is proportional to R.
.Hence it is proportional to R.


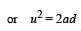
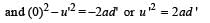
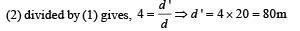
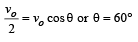
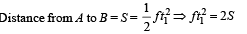

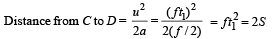

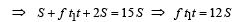

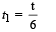
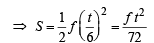
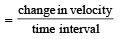
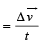

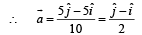
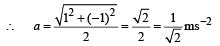
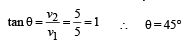
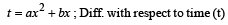
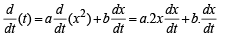

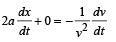
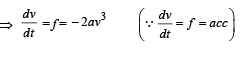
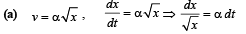
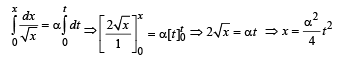
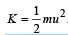
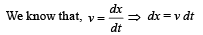
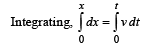
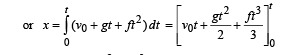 .
.