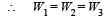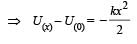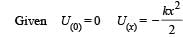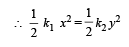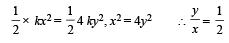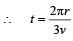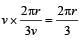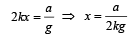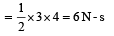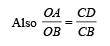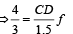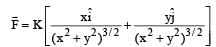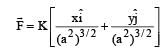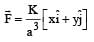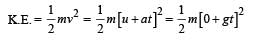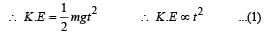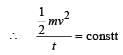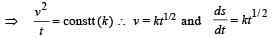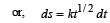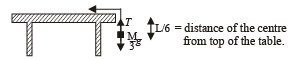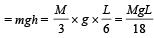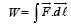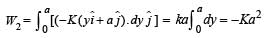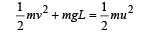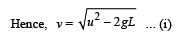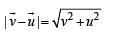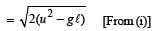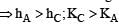JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Work, Energy and Power - JEE MCQ
21 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Work, Energy and Power
If a machine is lubricated with oil (1980)
Two masses of 1 gm and 4 gm are moving with equal kinetic energies. The ratio of the magnitudes of their linear momenta is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A particle of mass m is moving in a circular path of constant radius r such that its centripetal acceleration ac is varying with time t as ac = k2rt2 where k is a constant. The power delivered to the particles by the force acting on it is:
A spring of force-constant k is cut into two pieces such that one piece is double the length of the other. Then the long piece will have a force-constant of
A wind-powered generator converts wind energy into electrical energy. Assume that the generator converts a fixed fraction of the wind energy intercepted by its blades into electrical energy. For wind speed v, the electrical power output will be proportional to
A particle, which is constrained to move along the x-axis, is subjected to a force in the same direction which varies with the distance x of the particle from the origin as F(x) = –kx + ax3. Here k and a are positive constants. For x≥ 0 , the functional form of the potential energy U(x) of the particle is
An ideal spring with spring-constant k is hung from the ceiling and a block of mass M is attached to its lower end.
The mass is released with the spring initially unstretched.
Then the maximum extension in the spring is
If W1, W2 and W3 represent the work done in moving a particle from A to B along three different paths 1,2 and 3 respectively (as shown) in the gravitational field of a point mass m, find the correct relation between W1, W2 and W3
A particle is acted by a force F = kx, where k is a +ve constant. Its potential energy at x = 0 is zero. Which curve correctly represents the variation of potential energy of the block with respect t o x
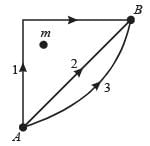
A block (B) is attached to two unstretched springs S1 and S2 with spring constants k and 4k, respectively (see fig. I).
The other ends are attached to identical supports M1 and M2 not attached to the walls. The springs and supports have negligible mass. There is no friction anywhere. The block B is displaced towards wall 1 by a small distance x (figure II) and released. The block returns and moves a maximum distance y towards wall 2. Displacements x and y are measured with respect to the equilibrium position of the block B. The ratio y/x is –
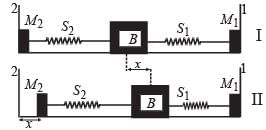
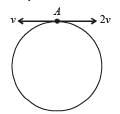
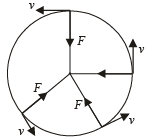
Two small particles of equal masses start moving in opposite directions from a point A in a horizontal circular orbit. Their tangential velocities are v and 2v, respectively, as shown in the figure. Between collisions, the particles move with constant speeds. After making how many elastic collisions, other than that at A, these two particles will again reach the point A?
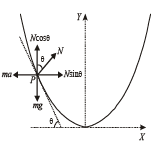
A piece of wire is bent in the shape of a parabola y = kx2 (y-axis vertical) with a bead of mass m on it. The bead can slide on the wire without friction. It stays at the lowest point of the parabola when the wire is at rest. The wire is now accelerated parallel to the x-axis with a constant acceleration a. The distance of the new equilibrium position of the bead, where the bead can stay at rest with respect to the wire, from the y-axis is
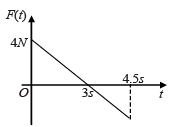
A block of mass 2 kg is free to move along the x-axis. It is at rest and from t = 0 onwards it is subjected to a time-dependent force F(t) in the x direction. The force F(t) varies with t as shown in the figure. The kinetic energy of the block after 4.5 seconds is
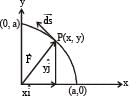
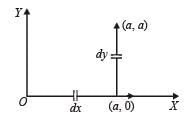
The work done on a particle of mass m by a force,
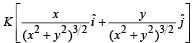
(K being a constant of appropriate dimensions), when the particle is taken from the point (a, 0) to the point (0, a) along a circular path of radius a about the origin in the x – y plane is
A tennis ball is dropped on a horizontal smooth surface. It bounces back to its original position after hitting the surface.
The force on the ball during the collision is proportional to the length of compression of the ball. Which one of the following sketches describes the variation of its kinetic energy K with time t most appropriately? The figure are only illustrative and not to the scale.
A body is moved along a straight line by a machine delivering constant power. The distance moved by the body in time t is proportional to
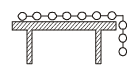
A uniform chain of length L and mass M is lying on a smooth table and one third of its length is hanging vertically down over the edge of the table. If g is acceleration due to gravity, the work required to pull the hanging part on to the table is
A particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude which is always perpendicular to the velocity of the particle.
The motion of the particle takes place in a plane. It follows that :
A force F = - K (where K is a positive constant) acts on a particle moving in the xy plane. Starting from the origin, the particle is taken along the positive x axis to the point (a, 0), and then parallel to the y axis to the point (a, a), The total work done by the force F on the particle is
A stone tied to a string of length L is whirled in a vertical circle with the other end of the string at the centre. At a certain instant of time, the stone is at its lowest position, and has a speed u. The magnitude of the change in its velocity as it reaches a position where the string is horizontal is
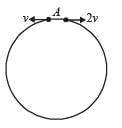
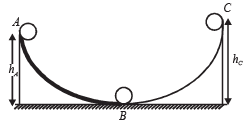
A small ball starts moving from A over a fixed track as shown in the figure. Surface AB has friction. From A to B the ball rolls without slipping. Surface BC is frictionless. KA, KB and KC are kinetic energies of the ball at A, B and C, respectively.
Then


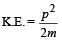
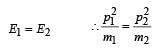
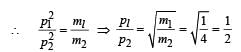
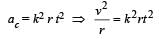
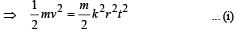

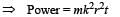
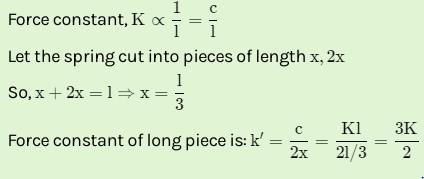

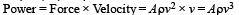
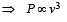
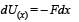
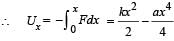
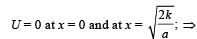 we have potential energy zero twice (out of which one is at origin).
we have potential energy zero twice (out of which one is at origin).
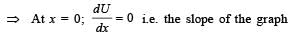 should be zero. These characteristics are represented by (d).
should be zero. These characteristics are represented by (d).