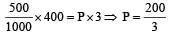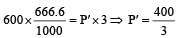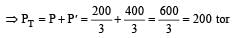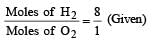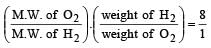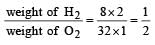31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: States of Matter - 2 (Old NCERT) - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - 31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: States of Matter - 2 (Old NCERT)
If P, V, M, T and R are pressure, Volume, molar mass, temperature and gas constant respectively, then for an ideal gas, the density is given by
Pressure remaining the same, the volume of a given mass of an ideal gas increases for every degree centigrade rise in temperature by definite fraction of its volume at [1989]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Correct gas equation is : [1989]
Root mean square velocity of a gas molecule is proportional to [1990]
Absolute zero is defined as the temperature
In vander Waal's equation of state for a non-ideal gas, the term that accounts for intermolecular forces is : [1990]
A gas is said to behave like an ideal gas when the relation PV/T = constant. When do you expect a real gas to behave like an ideal gas ? [1991]
In a closed flask of 5 litres, 1.0 g of H2 is heated from 300 to 600 K. Which statement is not correct?
At constant temperature, for a given mass of an ideal gas [1991]
The root mean square speeds at STP for the gases H2, N2, O2 and HBr are in the order : [1991]
A closed flask contains water in all its three states solid, liquid and vapour at 0°C. In this situation, the average kinetic energy of water molecules will be[1992]
Which is not true in case of an ideal gas ? [1992]
The correct value of the gas constant ‘R’ is close to :[1992]
An ideal gas can’t be liquefied because [1992]
Select one correct statement. In the gas equation, PV = nRT [1992]
At STP, 0.50 mol H2 gas and 1.0 mol He gas
Under what conditions will a pure sample of an ideal gas not only exhibit a pressure of 1 atm but also a concentration of 1 mole litre–1 ? (R = 0.082 litre atm mol–1deg–1) [1993]
Internal energy and pressure of a gas per unit volume are related as : [1993]
The ratio among most probable velocity, mean velocity and root mean square velocity is given by
[1993]
When is deviation more in the behaviour of a gas from the ideal gas equation PV = nRT ? [1993]
The temperature of the gas is raised from 27°C to 927°C, the root mean square velocity is [1994]
In a pair of immiscible liquids, a common solute dissolves in both and the equilibrium is reached.Then the concentration of the solute in upper layer is[1994]
A liquid can exist only : [1994]
500 ml of nitrogen at 27°C is cooled to –5°C at the same pressure. The new volume becomes
600 c.c. of a gas at a pressure of 750 mm is compressed to 500 c.c. Taking the temperature to remain constant, the increase in pressure, is
Cyclopropane and oxygen at partial pressures 170 torr and 570 torr respectively are mixed in a gas cylinder. What is the ratio of the number of moles of cyclopropane to the number of moles of oxygen (nC3H6/nO2)? [1996]
At which one of the following temperatur e -pressure conditions the deviation of a gas from ideal behaviour is expected to be minimum? [1996]
From a heated mixture of nitrogen, oxygen and carbon, two compounds (out of the many obtained) are isolated. The rates of diffusion of the two isolated compounds are almost identical.The two compounds are [1999]
If 500 ml of gas A at 400 torr and 666.6 ml of B at 600 torr are placed in a 3 litre flask, the pressure of the system will be [1999]
A gaseous mixture contains H2 and O2 in the molar ratio 8 : 1. The ratio of H2 : O2 by weight in this mixture would be [1999]


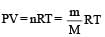
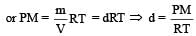
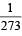 of its volume at 0°C for each degree rise or fall of temperature at constant pressure.
of its volume at 0°C for each degree rise or fall of temperature at constant pressure.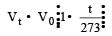 at constt. Pressure
at constt. Pressure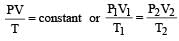
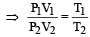
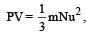 u = root mean square velocity
u = root mean square velocity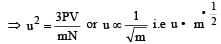
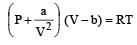
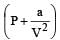 represent the intermolecularforces. (V – b) is the corrected volume.
represent the intermolecularforces. (V – b) is the corrected volume.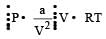
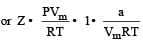
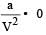
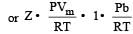
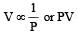 = constant
= constant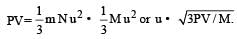

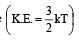
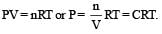
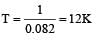
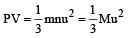
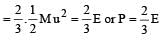 per unit vol.
per unit vol.
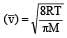
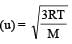
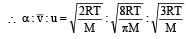
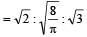
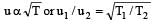
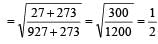
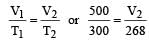
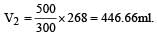
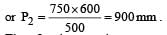
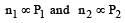
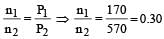
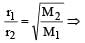 r1 = r2 if M1 = M2
r1 = r2 if M1 = M2