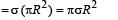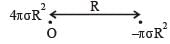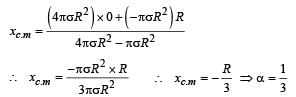Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- Rotational Motion - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- Rotational Motion
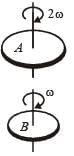
Two discs A and B are mounted coaxially on a vertical axle. The discs have moments of inertia I and 2 I respectively about the common axis. Disc A is imparted an initial angular velocity 2 ω using the entire potential energy of a spring compressed by a distance xl. Disc B is imparted an angular velocity ω by a spring having the same spring constant and compressed by a distance x2 .Both the discs rotate in the clockwise direction.
Q1.The ratio x1/x2 is
Two discs A and B are mounted coaxially on a vertical axle. The discs have moments of inertia I and 2 I respectively about the common axis. Disc A is imparted an initial angular velocity 2 ω using the entire potential energy of a spring compressed by a distance xl. Disc B is imparted an angular velocity ω by a spring having the same spring constant and compressed by a distance x2 .Both the discs rotate in the clockwise direction.
Q.2. When disc B is brought in contact with disc A, they acquire a common angular velocity in time t . The average frictional torque on one disc by the other during this period is
Two discs A and B are mounted coaxially on a vertical axle. The discs have moments of inertia I and 2 I respectively about the common axis. Disc A is imparted an initial angular velocity 2 ω using the entire potential energy of a spring compressed by a distance xl. Disc B is imparted an angular velocity ω by a spring having the same spring constant and compressed by a distance x2 .Both the discs rotate in the clockwise direction.
Q.3. The loss of kinetic energy in the above process is
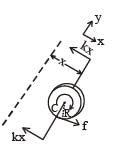
A uniform thin cylindrical disk of mass M and radius R is attached to two identical massless springs of spring constant k which are fixed to the wall as shown in the figure. The springs are attached to the axle of the disk symmetrically on either side at a distance d from its centre. The axle is massless and both the springs and the axle are in horizontal plane.
The unstretched length of each spring is L. The disk is initially at its equilibrium position with its centre of mass (CM) at a distance L from the wall. The disk rolls without slipping T he coefficient of friction is µ.
Q.4. The net external force acting on the disk when its centre of mass is at displacement x with respect to its equilibrium position is
A uniform thin cylindrical disk of mass M and radius R is attached to two identical massless springs of spring constant k which are fixed to the wall as shown in the figure. The springs are attached to the axle of the disk symmetrically on either side at a distance d from its centre. The axle is massless and both the springs and the axle are in horizontal plane.
The unstretched length of each spring is L. The disk is initially at its equilibrium position with its centre of mass (CM) at a distance L from the wall. The disk rolls without slipping T he coefficient of friction is µ.
Q.5.The centre of mass of the disk undergoes simple harmonic motion with angular frequency w equal to –
A uniform thin cylindrical disk of mass M and radius R is attached to two identical massless springs of spring constant k which are fixed to the wall as shown in the figure. The springs are attached to the axle of the disk symmetrically on either side at a distance d from its centre. The axle is massless and both the springs and the axle are in horizontal plane.
The unstretched length of each spring is L. The disk is initially at its equilibrium position with its centre of mass (CM) at a distance L from the wall. The disk rolls without slipping T he coefficient of friction is µ.
The maximum value of V0 for which the disk will roll without slipping is –
The general motion of a rigid body can be considered to be a combination of (i) a motion of its centre of mass about an axis, and (ii) its motion about an instantaneous axis passing through the centre of mass.
These axes need not be stationary. Consider, for example, a thin uniform disc welded (rigidly fixed) horizontally at its rim to a massless, stick, as shown in the figure. When the disc-stick system is rotated about the origin on a horizontal frictionless plane with angular speedω, the motion at any instant can be taken as a combination of (i) a rotation of the centre of mass of the disc about the z-axis and (ii) a rotation of the disc through an instantaneous vertical axis passing through its centre of mass (as is seen from the changed orientation of points P and Q). Both these motions have the same angular speed w in this case
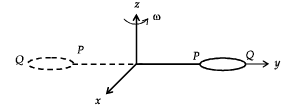
Now consider two similar systems as shown in the figure: Case (a) the disc with its face vertical and parallel to x-z plane; Case (b) the disc with its face making an angle of 45° with x-y plane and its horizontal diameter parallel to x-axis. In both the cases, the disc is welded at point P, and the systems are rotated with constant angular speed ω about the z-axis.
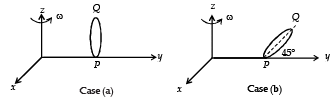
Q.7. Which of the following statements about the instantaneous axis (passing through the centre of mass) is correct?
The general motion of a rigid body can be considered to be a combination of (i) a motion of its centre of mass about an axis, and (ii) its motion about an instantaneous axis passing through the centre of mass.
These axes need not be stationary. Consider, for example, a thin uniform disc welded (rigidly fixed) horizontally at its rim to a massless, stick, as shown in the figure. When the disc-stick system is rotated about the origin on a horizontal frictionless plane with angular speedω, the motion at any instant can be taken as a combination of (i) a rotation of the centre of mass of the disc about the z-axis and (ii) a rotation of the disc through an instantaneous vertical axis passing through its centre of mass (as is seen from the changed orientation of points P and Q). Both these motions have the same angular speed w in this case

Now consider two similar systems as shown in the figure: Case (a) the disc with its face vertical and parallel to x-z plane; Case (b) the disc with its face making an angle of 45° with x-y plane and its horizontal diameter parallel to x-axis. In both the cases, the disc is welded at point P, and the systems are rotated with constant angular speed ω about the z-axis.

Q.8.Which of the following statements regarding the angular speed about the instantaneous axis (passing through the centre of mass) is correct?
STATEMENT-1: If there is no external torque on a body about its center of mass, then the velocity of the center of mass remains constant.
STATEMENT-2: The linear momentum of an isolated system remains constant.
STATEMENT-1 : Two cylinders, one hollow (metal) and the other solid (wood) with the same mass and identical dimensions are simultaneously allowed to roll without slipping down an inclined plane from the same height. The hollow cylinder will reach the bottom of the inclined plane first.
STATEMENT-2 : By the principle of conservation of energy, the total kinetic energies of both the cylinders are identical when they reach the bottom of the incline.
Initial angular velocity of a circular disc of mass M is ω 1.
Then two small spheres of mass m are attached gently to diametrically opposite points on the edge of the disc. What is the final angular velocity of the disc?
The minimum velocity (in ms–1) with which a car driver must traverse a flat curve of radius 150 m and coefficient of friction 0.6 to avoid skidding is
A cylinder of height 20 m is completely filled with water. The velocity of efflux of water (in ms–1) through a small hole on the side wall of the cylinder near its bottom is
Two identical particles move towards each other with velocity 2v and v respectively. The velocity of centre of mass is
A solid sphere, a hollow sphere and a ring are released from top of an inclined plane (frictionless) so that they slide down the plane. Then maximum acceleration down the plane is for (no rolling)
Moment of inertia of a circular wire of mass M and radius R about its diameter is
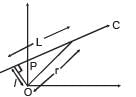
A particle of mass m moves along line PC with velocity v as shown. What is the angular momentum of the particle about P?
A circular disc X of radius R is made from an iron plate of thickness t, and another disc Y of radius 4R is made from an iron plate of thickness 4
t . Then the relation between the moment of inertia IX and IY is
A particle performing uniform circular motion has angular frequency is doubled & its kinetic energy halved, then the new angular momentum is
 be the force acting on a particle having position vector
be the force acting on a particle having position vector 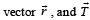 be the torque of this force about the origin.
be the torque of this force about the origin.
Then
A solid sphere is rotating in free space. If the radius of the sphere is increased keeping mass same which one of the following will not be affected ?
One solid sphere A and another hollow sphere B are of same mass and same outer radii. Their moment of inertia about their diameters are respectively I A and I B Such that
A body A of mass M while falling vertically downwards under gravity breaks into two parts; a body B of mass 1/3 M and a body C of mass 2/3 M. The centre of mass of bodies B and C taken together shifts compared to that of body A towards
The moment of inertia of a uniform semicircular disc of mass M and radius r about a line perpendicular to the plane of the disc through the centre is
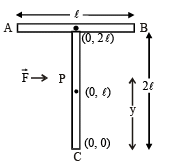
A ‘ T’ shaped object with dimensions shown in the figure, is lying on a smooth floor. 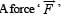 is applied at the point P parallel to AB, such that the object has only the translational motion without rotation. Find the location of P with respect to C.
is applied at the point P parallel to AB, such that the object has only the translational motion without rotation. Find the location of P with respect to C.
Consider a two particle system with particles having masses m1 and m2. If the first particle is pushed towards the centre of mass through a distance d, by what distance should the second particle is moved, so as to keep the centre of mass at the same position?
Four point masses, each of value m, are placed at the corners of a square ABCD of side l. The moment of inertia of this system about an axis passing through A and parallel to BD is
A force of  ˆ acts on O, the origin of the coordinate system. The torque about the point (1, –1) is
ˆ acts on O, the origin of the coordinate system. The torque about the point (1, –1) is
A thin circular ring of mass m and radius R is rotating about its axis with a constant angular velocity ω. Two objects each of mass M are attached gently to the opposite ends of a diameter of the ring. The ring now rotates with an angular velocity ω' =
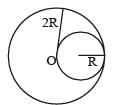
A circular disc of radius R is removed from a bigger circular disc of radius 2R such that the circumferences of the discs coincide. The centre of mass of the new disc is α / R form the centre of the bigger disc. The value of α is


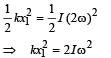
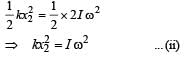
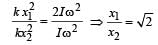
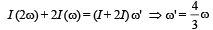
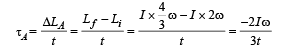

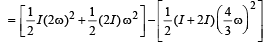
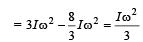
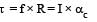
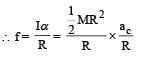
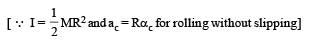

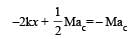
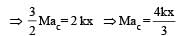

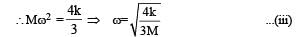
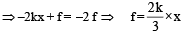
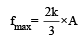
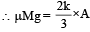
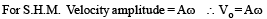
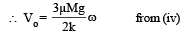
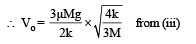
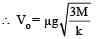


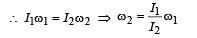
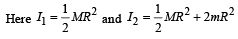
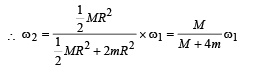
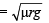
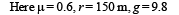
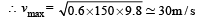
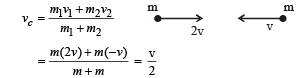
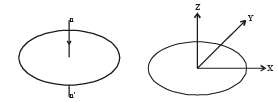
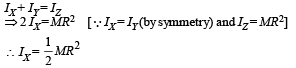
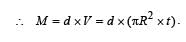

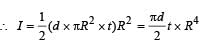
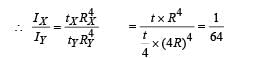
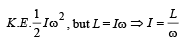
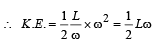
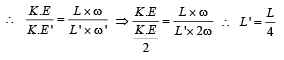
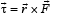 The angle between tr and rr is 90° and the angle between tr and
The angle between tr and rr is 90° and the angle between tr and 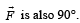 We also know that the dot product of two vectors which have an angle of 90° between them is zero. Therefore (d) is the correct option
We also know that the dot product of two vectors which have an angle of 90° between them is zero. Therefore (d) is the correct option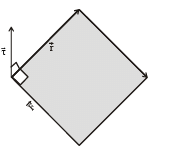
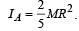
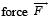 has to be applied
has to be applied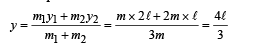
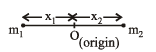
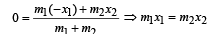
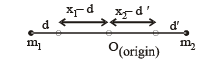
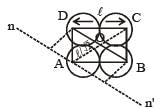
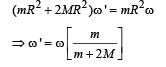
 Let us consider the above situation to be a complete disc of radius 2R on which a disc of radius R of negative mass is superimposed. Let O be the origin. Then the above figure can be redrawn keeping in mind the concept of centre of mass as :
Let us consider the above situation to be a complete disc of radius 2R on which a disc of radius R of negative mass is superimposed. Let O be the origin. Then the above figure can be redrawn keeping in mind the concept of centre of mass as :