31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Thermodynamics - 1 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - 31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Thermodynamics - 1
What is the entropy change (in JK–1 mol–1) when one mole of ice is converted into water at 0º C? (The enthalpy change for the conversion of ice to liquid water is 6.0 kJ mol–1 at 0ºC) [2003]
The densities of graphite and diamond at 298 K are 2.25 and 3.31g cm–3, respectively. If the standard free energy difference (ΔGº) is equal to 1895 J mol–1, the pressure at which graphite will be transformed into diamond at 298 K is: [2003]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
For which one of the following equations is ΔHºreact equal to ΔHfº for the product? [2003]
For the reaction C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) → 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(l) at constant temperature, ΔH – ΔE is: [2003]
If the bond energies of H-H, Br-Br, and HBr are 433, 192 and 364 kJ mol–1 respectively, the ΔH° for the reaction H2(g) + Br2(g) → 2HBr(g) is: [2004]
The standard enthalpy and standard entropy changes for the oxidation of ammonia at 298 K are -382.64 kJ mol–1 and -145.6 JK–1 mol–1, respectively.
Standard Gibb's energy change for the same reaction at 298 K is: [2004]
Considering entropy(S) as a thermodynamic parameter, the criterion for the spontaneity of any process is: [2004]
The work done during the expansion of a gas from a volume of 4 dm3 to 6 dm3 against a constant external pressure of 3 atm is: (1L atm = 101.32 J) [2004]
The absolute enthalpy of neutralisation of the reaction: MgO (s) + 2HCl (aq) —→ MgCl2(aq) + H2O (l) will be:[2005]
A reaction occurs spontaneously if: [2005]
Which of the following pairs of a chemical reaction is certain to result in a spontaneous reaction? [2005]
The enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene is –119.5 kJ mol–1. If the resonance energy of benzene is –150.4 kJ mol–1, its enthalpy of hydrogenation would be: [2006]
The enthalpy and entropy change for the reaction Br2(l) + Cl2(g) → 2BrCl(g) are 30kJ mol–1 and 105 JK–1 mol–1 respectively.The temperature at which the reaction will be in equilibrium is: [2006]
Identify the correct statement for change of Gibbs energy for a system (ΔGsystem) at constant temperature and pressure: [2006]
Assume each reaction is carried out in an open container. For which reaction will ΔH = ΔE? [2006]
Consider the following reactions: [2007]
(i) 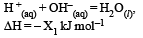
(ii) 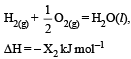
(iii) 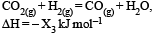
(iv) 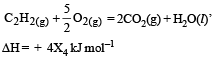
Enthalpy of formation of H2O (l) is
Given that bond energy of H–H and Cl–Cl is 430 kJ mol–1 and 240 kJ mol–1 respectively and ΔHf for HCl is - 90 kJ mol–1, bond enthalpy of HCl is: [2007]
Which of the following are not state functions? [2008]
(I) q + w
(II) q
(III) w
(IV) H - TS
For the gas phase reaction, which of the following conditions is correct? [2008]
PCl5(g) ⇌ PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
Bond dissociation enthalpy of H2, Cl2, and HCl are 434, 242, and 431 kJ mol–1 respectively. Enthalpy of formation of HCl is: [2008]
The values of ΔH and ΔS for the reaction, C(graphite) + CO2 (g) → 2CO(g) are 170 kJ and 170 JK–1, respectively. This reaction will be spontaneous at: [2009]
From the following bond energies: [2009]
H – H bond energy: 431.37 kJ mol–1
C = C bond energy: 606.10 kJ mol–1
C – C bond energy: 336.49 kJ mol–1
C – H bond energy: 410.50 kJ mol–1
Enthalpy for the reaction, will be:
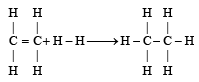
Standard entropies of X2 , Y2 and XY3 are 60, 40 and 50 JK–1mol–1 respectively. For the reaction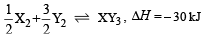
to be at equilibrium, the temperature should be: [2010]
For vapor ization of water at 1 atmospheric pressure, the values of ΔH and ΔS are 40.63 kJmol–1 and 108.8 JK–1 mol–1, respectively. The temperature when Gibbs energy change (ΔG) for this transformation will be zero, is: [2010]
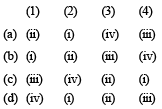
Match List -I (Equations) with List-II (Type of processes) and select the correct option. [2010]

Options:
The following two reactions are known : [2010]
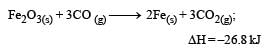
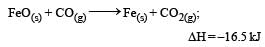
The value of ΔH for the following reaction
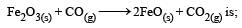
If the enthalpy change for the transition of liquid water to steam is 30 kJ mol–1 at 27ºC, the entropy change for the process would be: [2011]
Enthalpy change for the reaction, 4H(g) → 2H2 (g) is - 869.6 kJ. The dissociation energy of H–H bond is: [2011]
Consider the following processes :
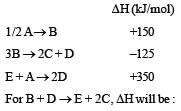 [2011M]
[2011M]
In which of the following reactions, standard entropy change (ΔS°) is positive and standard Gibb’s energy change (ΔG°) decreases sharply with increasing temperature? [2012]


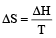
 = 21.98 JK -1mol-1
= 21.98 JK -1mol-1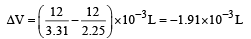
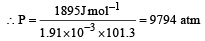
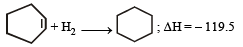
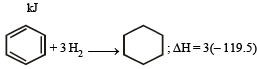 = – 348.5 kJ
= – 348.5 kJ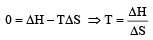
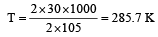
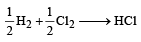
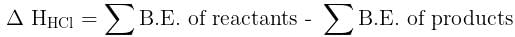
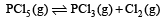
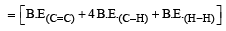
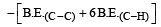
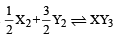
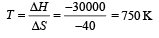
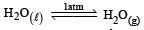
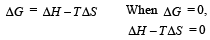
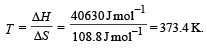
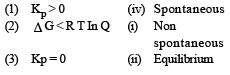
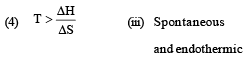
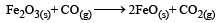
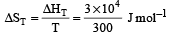 = 100J mol–1 K–1
= 100J mol–1 K–1










