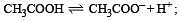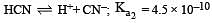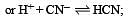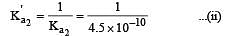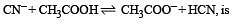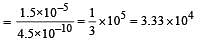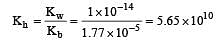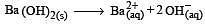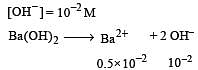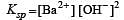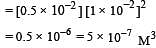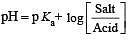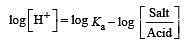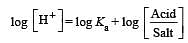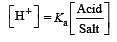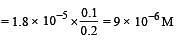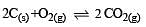31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Equilibrium - 2 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - 31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Equilibrium - 2
Solubility of MX2-type eletrolytes is 0.5 × 10–4 mole/lit, then find out Ksp of electrolytes [2002]
Which has the highest value of pH? [2002]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Solution of 0.1 N NH4OH and 0.1 N NH4Cl has pH 9.25. Then find out pKb of NH4OH [2002]
The reaction quotient (Q) for the reaction
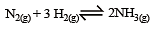
is given by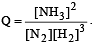
The reaction will proceed from right to left if [2003]
where Kc is the equilibrium constant
Which one of the following orders of acid strength is correct? [2003]
Which one of the following compounds is not a protonic acid? [2003]
The solubility product of AgI at 25ºC is 1.0 × 10–16 mol2 L–2. The solubiliy of AgI in 10–4 N solution of KI at 25ºC is approximately(in mol L–1) [2003]
The solubility product of a sparingly soluble salt AX2 is 3.2 x 10-11 . Its solubility ( in moles/litre) is
[2004]
The rapid change of pH near the stoichiometric point of an acid-base titration is the basis of indicator detection. pH of the solution is related to ratio of the concentrations of the conjugate acid (HIn) and base (In–) forms of the indicator by the expression [2004]
H2S gas when passed through a solution of cations containing HCl precipitates the cations of second group of qualitative analysis but not those belonging to the fourth group. It is be cau se [2005]
What is the correct relation ship between the pHs of isomolar solutions of sodium oxide (pH1), sodium sulphide (pH2), sodium selenide (pH3) and sodium telluride (pH4)? [2 00 5]
At 25°C, the dissociation con stant of a base, BOH, is 1. 0 x 10-12. The concentration of hydroxyl ions in 0.01 M aqueous solution of the base would be [2005]
For the reaction [2006]
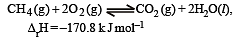
Which of the following statements is not true ?
The hydrogen ion concentration of a 10–8 M HCl aqueous solution at 298 K (Kw = 10–14) is [2006]
Which of the following pairs constitutes a buffer?
A weak acid, HA, has a Ka of 1.00 × 10–5. If 0.100 mole of this acid dissolved in one litre of water, the percentage of acid dissociated at equilbrium is closest to [2007]
The following equilibrium constants are given:
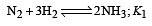
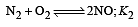
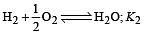
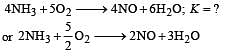
The equilibrium constant for the oxidation of NH3 by oxygen to give NO is
Calculate the pOH of a solution at 25°C that contains 1× 10–10 M of hydronium ions, i.e. H3O+.
Equal volumes of three acid solutions of pH 3, 4 and 5 are mixed in a vessel. What will be the H+ ion concentration in the mixture ? [2008]
If the concentration of OH– ions in the reaction decreased by
decreased by 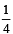 times, then equilibriumconcentration of Fe3+ will increase by : [2008]
times, then equilibriumconcentration of Fe3+ will increase by : [2008]
Equimolar solutions of the following were prepared in water separately. Which one of the solutions will record the highest pH ? [2008]
The dissociation equilibrium of a gas AB2 can be represented as : [2008]
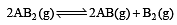
The degree of dissociation is ‘x’ and is small compared to 1. The expression relating the degree of dissociation (x) with equilibrium constant Kp and total pressure P is :
The values of Kp1 and Kp2 for the reactions
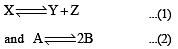
are in the ratio of 9 : 1. If degree of dissociation of X and A be equal, then total pressure at equilibrium (1) and (2) are in the ratio :
The value of equilibrium constant of the reaction
 [2008]
[2008]
The equilibrium constant of the reaction 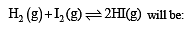
The dissociation constants for acetic acid and HCN at 25°C are 1.5 × 10–5 and 4.5 × 10–10 respectively. The equilibrium constant for the equilibrium [2009] 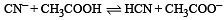 would be:
would be:
Which of the following molecules acts as a Lewis acid ?[2009]
The ionization constant of ammonium hydroxide is 1.77 × 10–5 at 298 K. Hydrolysis constant of ammonium chloride is: [2009]
If pH of a saturated solution of Ba (OH)2 is 12, the value of its K(sp) is : [2010]
What is [H+] in mol/L of a solution that is 0.20 M in CH3COONa and 0.10 M in CH3COOH?Ka for CH3COOH = 1.8 × 10-5 . [2010]
In which of the following equilibrium Kc and Kp are not equal? [2010]


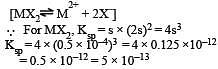
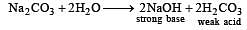
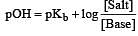

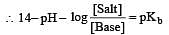
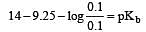
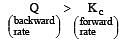 i.e the reaction will be fast in backward direction i.e rb > rf.
i.e the reaction will be fast in backward direction i.e rb > rf.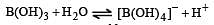
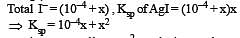
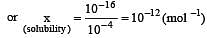
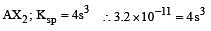
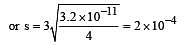
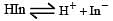
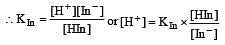
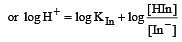
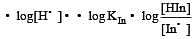
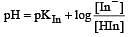
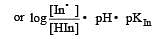
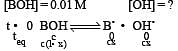

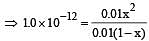
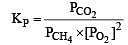
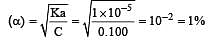
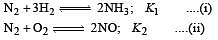
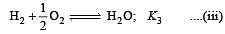
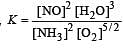
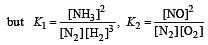
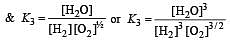
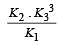
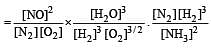
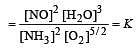
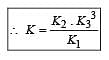
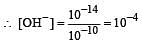
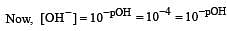
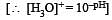
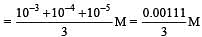
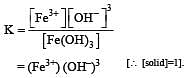
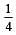 times then forreaction equilibrium constant to remain constant, we have to increase the concentration of [Fe3+] by a factor of 43 i.e 4× 4 × = 64. Thus option (c) is correct answer.
times then forreaction equilibrium constant to remain constant, we have to increase the concentration of [Fe3+] by a factor of 43 i.e 4× 4 × = 64. Thus option (c) is correct answer.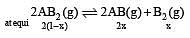
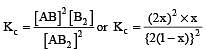
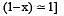
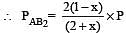 where P is the total pressure.
where P is the total pressure.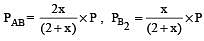
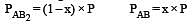
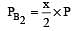
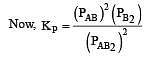
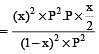
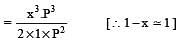
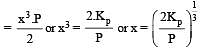

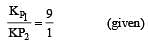
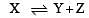
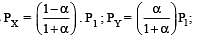
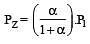
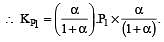
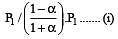
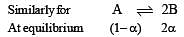
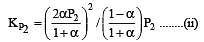
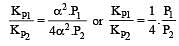
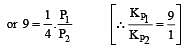
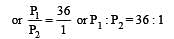
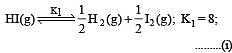
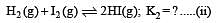
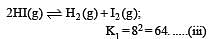
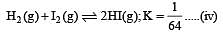
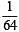 i.e.
i.e.