Thermodynamics MCQ - 2 (Advanced) - JEE MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Thermodynamics MCQ - 2 (Advanced)
An ideal gas is taken from state A (Pressure P, Volume V) to the state B (Pressure P/2, Volume 2V) along a straight line path in PV diagram as shown in the adjacent figure.
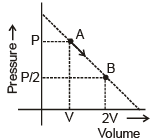
Select the correct statement (s) among the following
The normal boiling point of a liquid `A' is 350 K. ΔHvap at normal boiling point is 35 kJ/mole. Pick out the correct statement (s). (Assume ΔHvap to be independent of pressure).
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following statement(s) is/are false :
Two moles of an ideal gas (Cv,m = 3/2 R) is subjected to following change of state.
The correct statement is/are :
A piston cyclinder device initially contains 0.2 m3 neon (assume ideal) at 200 kPa inside at T1°C. A valve is now opened and neon is allowed to escape until the volume reduces to half the initial volume. At the same time heat transfer with outside at T2° C ensures a constant temperature inside.
Select correct statement(s) for given process
If one mole monoatomic ideal gas was taken through process AB as shown in figure, the select correct option (s).
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct
A cylindrical container of volume 44.8 litres is containing equal no. of moles (in integer no.) of an ideal monoatomic gas in two sections A and B separated by an adiabatic frictionless piston as shown in figure. The initial temperature and pressure of gas in both section is 27.3 K and 1 atm. Now gas is section `A' is slowly heated till the volume of section B becomes (1/8)th of initial volume.
Q.
What will be the final pressure in container B.
A cylindrical container of volume 44.8 litres is containing equal no. of moles (in integer no.) of an ideal monoatomic gas in two sections A and B separated by an adiabatic frictionless piston as shown in figure. The initial temperature and pressure of gas in both section is 27.3 K and 1 atm. Now gas is section `A' is slowly heated till the volume of section B becomes (1/8)th of initial volume.
Q.
Final temperature in container A will be
A cylindrical container of volume 44.8 litres is containing equal no. of moles (in integer no.) of an ideal monoatomic gas in two sections A and B separated by an adiabatic frictionless piston as shown in figure. The initial temperature and pressure of gas in both section is 27.3 K and 1 atm. Now gas is section `A' is slowly heated till the volume of section B becomes (1/8)th of initial volume.
Q.
Change in enthalpy for section A in Kcal.
The vapour pressure of H2O(l) at 353 K is 532 mm Hg. The external pressure on H2O (l) taken in a cylinder fitted with frictionless movable piston initially containing 0.9 L (= 0.9 kg) of H2O (l) at 353 K is increased to 1 atm. Temperature remained constant. Now, heat is supplied keeping pressure constant till 0.45 L of H2O (l) = (0.45 kg) is evaporated to form H2O (g) at 373 K. Carefully observe the diagrams provided and from given data, answer the following questions.
Q.
ΔH when system is taken from state 1 to state 2 (Joule) ?
The vapour pressure of H2O(l) at 353 K is 532 mm Hg. The external pressure on H2O (l) taken in a cylinder fitted with frictionless movable piston initially containing 0.9 L (= 0.9 kg) of H2O (l) at 353 K is increased to 1 atm. Temperature remained constant. Now, heat is supplied keeping pressure constant till 0.45 L of H2O (l) = (0.45 kg) is evaporated to form H2O (g) at 373 K. Carefully observe the diagrams provided and from given data, answer the following questions.
Q.
Total change in DU going from state 1 to 3 (kJ) ?
The vapour pressure of H2O(l) at 353 K is 532 mm Hg. The external pressure on H2O (l) taken in a cylinder fitted with frictionless movable piston initially containing 0.9 L (= 0.9 kg) of H2O (l) at 353 K is increased to 1 atm. Temperature remained constant. Now, heat is supplied keeping pressure constant till 0.45 L of H2O (l) = (0.45 kg) is evaporated to form H2O (g) at 373 K. Carefully observe the diagrams provided and from given data, answer the following questions.
Q.
Total change in enthalpy going from state 1 to state 3 (kJ) ?
The vapour pressure of H2O(l) at 353 K is 532 mm Hg. The external pressure on H2O (l) taken in a cylinder fitted with frictionless movable piston initially containing 0.9 L (= 0.9 kg) of H2O (l) at 353 K is increased to 1 atm. Temperature remained constant. Now, heat is supplied keeping pressure constant till 0.45 L of H2O (l) = (0.45 kg) is evaporated to form H2O (g) at 373 K. Carefully observe the diagrams provided and from given data, answer the following questions.
Q.
What is the work done in going state 1 to state 3 to in Joules.
comprehension-3
Two moles of helium gas are taken over the cycle ABCDA, as shown in the P-T diagram.
Q.
Assuming the gas to be ideal the work done by the gas in taking it from A to B is -
Two moles of helium gas are taken over the cycle ABCDA, as shown in the P-T diagram.
Q.
The work done involved in taking it from D to A is
Two moles of helium gas are taken over the cycle ABCDA, as shown in the P-T diagram.
Q.
The net work done involved in the cycle ABCDA is
Match Column-I with Column-II
Column - I Column-II
(Ideal Gas) (Related equation)
(A) Reversible isothermal (P) W = 2.303 nRT log (P2/P1) process
(B) Reversible adiabatic (Q) W = nCV,m (T2 _ T1) process
(C) Irreversible adiabatic (R) PV = nRT process
(D) Irreversible isothermal (S) process
Match the column - I with column-II
Note that column - I may have more than one matching options in column-II
Column-I Column-II
(A) Reversible adiabatic compression (P) DSsystem > 0
(B) Reversible vaporisation (Q) DSsystem < 0
(C) Free expansion of ideal gas in vacuum (R) DSsurroudning < 0
(D) Dissociation of CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g) (S) DSsurrounding = 0
Statement-1 : There is no change in enthalpy of an ideal gas during compression at constant temperautre.
Statement-II : Enthalpy of an ideal gas is a function of temperature and pressure.
Statement-1 : Due to adiabatic free expansion, temperature of a real gas always increases
Statement-II : If a real gas is at inversion temperature then no change in temperature is observed in adiabatic free expansion.
Statement-1 : There is no change in enthalpy of an ideal gas during compression at constant pressure.
Statement-II : Enthalpy of an ideal gas is a function of temperature .

















