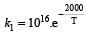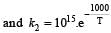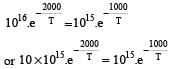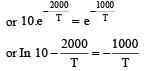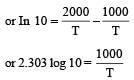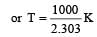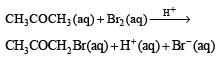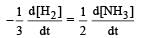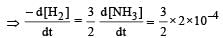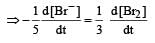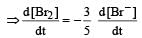31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Chemical Kinetics - 2 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - 31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Chemical Kinetics - 2
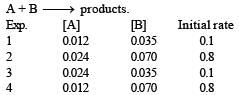
Select the rate law that corresponds to data shown for the following reaction [1994]

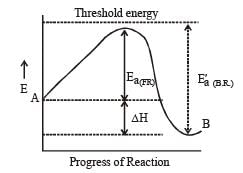
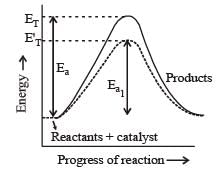
For an exothermic reaction, the energy of activation of the reactants is [1994]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A chemical reaction is catalyzed by a catalyst X.Hence X [1995]
A substance 'A' decomposes by a first or der reaction starting initially with [A] = 2.00 m and after 200 min, [A] becomes 0.15 m. For this reaction t1/2 is [1995]
The rate of reaction depends upon the [1995]
In a reversible reaction the energy of activation of the forward reaction is 50 kcal. The energy of activation for the reverse reaction will be [1996]
In a reaction, A + B → Product, rate is doubled when the concentration of B is doubled, and rate increases by a factor of 8 when the concentrations of both the reactants (A and B) are doubled, rate law for the reaction can be written as
Activation energy of a chemical reaction can be determined by [1998]
Half life of a first order reaction is 4 s and the initial concentration of the reactants is 0.12 M.The concentration of the reactant left after 16 s is [1999]
In the following reaction , how is the rate of appearance of the underlined product related to the rate of disappearance of the underlined reactant ? [2000]
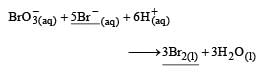
When a biochemical reaction is carried out in laboratory in the absence of enzyme then rate of reaction obtained is 10–6 times, then activation energy of reaction in the presence of enzyme is
For the reaction 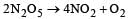 rate and rate constant are 1.02 × 10–4 mol lit–1 sec–1 and 3.4 × 10–5 sec–1 respectively then concentration of N2O5 at that time will be [2001]
rate and rate constant are 1.02 × 10–4 mol lit–1 sec–1 and 3.4 × 10–5 sec–1 respectively then concentration of N2O5 at that time will be [2001]
 , rate of reaction
, rate of reaction 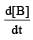 is equal to
is equal to
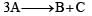 , it would be a zero order reaction when[2002]
, it would be a zero order reaction when[2002]
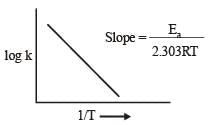
The temperature dependence of rate constant (k) of a chemical reaction is written in terms of Arrhenius equation, 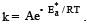 . Activation energy
. Activation energy 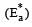 of the reaction can be calculated by plotting [2003]
of the reaction can be calculated by plotting [2003]
If the rate of the reaction is equal to the rate constant, the order of the reaction is [2003]
The activation energy for a simple chemical reaction A → B is Ea in forward direction. The activation energy for reverse reaction [2003]
The reaction A → B follows first order kinetics.The time taken for 0.8 mole of A to produce 0.6 mole of B is 1 hour. What is the time taken for conversion of 0.9 mole of A to produce 0.675 mole of B?[2003]
The rate of a first order reaction is 1.5 × 10–2 mol L–1 min–1 at 0.5 M concentration of the reactant.The half life of the reaction is [2004]
For a first order reaction A → B th e reaction rate at reactant concentration of 0.01 M is found to be 2.0 x 10-5 mol L-1 S-1. The half life period of the reaction is [2 00 5]
The rate of reaction between two reactants A and B decreases by a factor of 4 if the concentration of reactant B is doubled. The order of this reaction with respect to reactant B is:[2005]
For the reaction 2A + B → 3C + D which of the following does not express the reaction rate ? [2006]
Consider the reaction [2006] 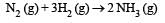 The equality relationship between
The equality relationship between 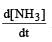 and
and 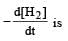
The reaction of hydrogenandiodine monochloride is given as: [2007]
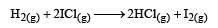
The reaction is of first order with respect to H2(g) and ICI(g), following mechanisms were proposed.
Mechanism A:
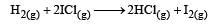
Mechanism B:
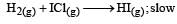
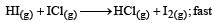
Which of the above mechanism(s) can be consistent with the given information about the reaction?
In a first-order reaction A → B, if k is rate constant and inital concentration of the reactant A is 0.5 M, then the half-life is [2007]
If 60% of a first order reaction was completed in 60 minutes, 50% of the same reaction would be completed in aproximately [2007]
The rate constants k1 and k2 for two different reactions are 1016 . e–2000/T and 1015 . e–1000/T, respectively. The temperature at which k1 = k2 is :
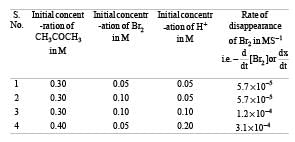
The bromination of acetone that occurs in acid solution is represented by this equation. [2008]
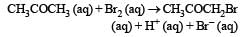
These kinetic data were obtained for given reaction concentrations.
Initial Concentrations, M
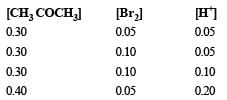
Initial rate, disappearance of Br2, Ms–1
5.7×10–5
5.7 × 10–5
1.2 × 10–4
3.1 × 10–4
Base on these data, the rate equations is:
For the reaction, 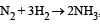 , [2009]
, [2009]
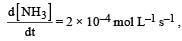 the value of
the value of
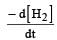 would be dt:
would be dt:
In the reaction [2009]
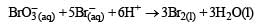
The rate of appearance of bromine (Br2) is related to rate of disappearance of bromide ions as following:


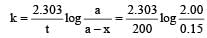
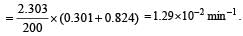
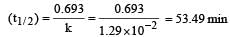
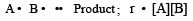
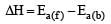

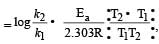 where k1 is the rate constant at temperature T1 and k2 is the rate constant at temperature T2 and Ea is the activation energy. Therefore activation energy of chemical reaction is determined by evaluating rate constant at two different temperatures.
where k1 is the rate constant at temperature T1 and k2 is the rate constant at temperature T2 and Ea is the activation energy. Therefore activation energy of chemical reaction is determined by evaluating rate constant at two different temperatures.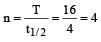
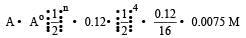
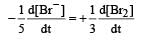
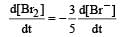
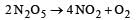
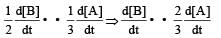
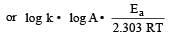
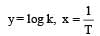
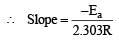
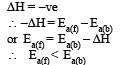
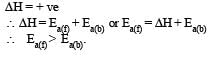
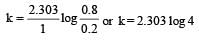
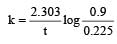
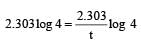
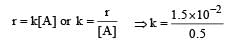
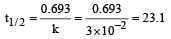
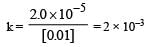
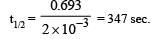
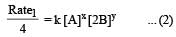

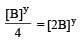
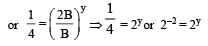
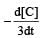 will not represent the reaction rate. It should not have –ve sign as it is product. since
will not represent the reaction rate. It should not have –ve sign as it is product. since 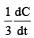 show the rate of formation ofproduct C which will be positive.
show the rate of formation ofproduct C which will be positive.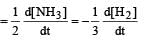
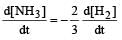
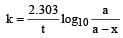
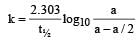
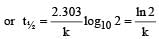
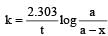
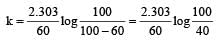
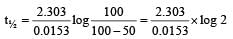
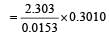 = 45.31 min.
= 45.31 min.