Test: Structure of Atom- 2 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Structure of Atom- 2
Radiation of λ = 155 nm was irradiated on Li (work function = 5eV) plate. The stopping potential (in eV) is.
Increasing order of magnetic moment among the following species is __________ .
Na+, Fe+3, Co2+, Cr+2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
If in the hydrogen atom P.E. at ∞ is choosen to be 13.6 eV then the ratio of T.E. to K.E. for 1st orbit of H-atom is __________ .
The light radiations with discrete quantities of energy are called ___________ .
The ratio of the energy of a photon of 2000 Å wavelength radiation to that of 4000 Å radiation is
Which electronic level would allow the hydrogen atom to absorb a photon but not to emit a photon:
The third line in Balmer series corresponds to an electronic transition between which Bohr's orbits in hydrogen :
The orbital angular momentum of an electron in 2s orbital is :
Which quantum number is not related with Schrodinger equation :
The shortest wavelength of He atom in Balmer series is x, then longest wavelength in the Paschene series of Li+2 is :
An electron in a hydrogen atom in its ground state absrobs energy equal to the ionisation energy of Li+2. The wavelength of the emitted electron is
An electron, a proton and an alpha particle have kinetic energies of 16E, 4E and E respectively. What is the qualitative order of their de-Broglie wavelengths?
Given ΔH for the process Li(g) → Li+3(g) + 3e- is 19800 kJ/mole & IE1 for Li is 520 then IE2 & IE3 of Li+ are respectively (approx, value) :
The ratio of difference in wavelengths of 1st and 2nd lines of Lyman series in H-like atom to difference in wavelength for 2nd and 3rd lines of same series is :
If radius of second stationary orbit (in Bohr's atom) is R. Then radius of third orbit will be
The ratio of wave length of photon corresponding to the α-line of lyman series in H-atom and β-line of Baimer series in He+ is
Three energy levels P, Q, R of a certain atom are such that EP < EQ < ER. If λ1, λ2, and λ3, are the wave length of radiation corresponding to transition R → Q : Q → P and R → P respectively. The correct relationship between λ1, λ2 and λ3 is
The Value of (n2 + n1) and for He+ ion in atomic spectrum are 4 and 8 respectively. The wavelength of emitted photon when electron jump from n2 to n1 is
Number of possible spectral lines which may be emitted in bracket series in H atom if electrons present 9th excited level returns to ground level, are
The first use of quantum theory to explain the structure of atom was made by :
The wavelength associated with a golf ball weighing 200g and moving at a speed of 5m/h is of the order:
The longest wavelength of He+ in Paschen series is "m", then shortest wavelength of Be3+ in Paschen series is (in terms of m) :
What is uncertainity in location of a photon of wavelength 5000 Å if wavelength is known to an accuracy of 1 pm?
Consider the following nuclear reactions involving X & Y.
X → Y + 2He4 Y → 8O18 + 1H1
If both neutrons as well as protons in both the sides are conserved in nuclear reaction then moles of neutrons in 4.6 gm of X :
Electromagnetic radiations having λ = 310 Å are subjected to a metal sheet having work function = 12.8 eV. What will be the velocity of photoelectrons with maximum Kinetic energy.
Assuming Heisenberg Uncertainity Principle to be true what could be the miniumum uncertainity in de–Broglie wavelength of a moving electron accelerated by Potential Difference of 6V whose uncertainity in position is 7/22 n.m.
A 1-kW radio transmitter operates at a frequency of 880 Hz. How many photons per second does it emit -
On the basis of Bohr's model, the radius of the 3rd orbit is -


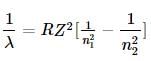
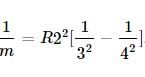 (1)
(1)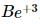 the expression becomes
the expression becomes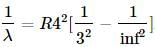 (2)
(2)