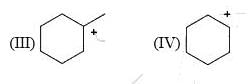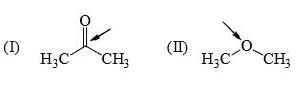Test: Reaction Intermediate Level - 1 - Chemistry MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Reaction Intermediate Level - 1
Which of the following is most reactive as a nucleophile?
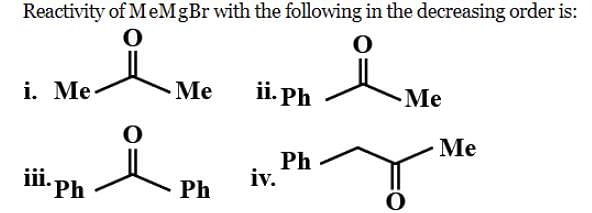
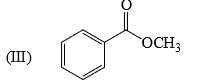
Reactivity of the following towards reaction with LiAlH4 is:
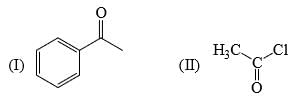
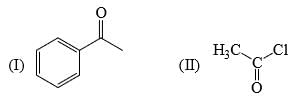

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The relative acidity of the indicated H in each of the following is:
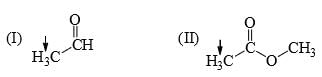
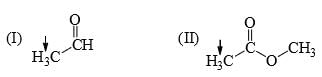

The relative nucleophilicity in polar, protic, solvents of the following is:
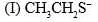
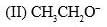
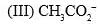
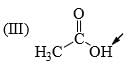
The acidity of the protons H in each of the following is:
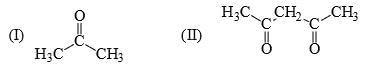
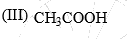
The relative nucleophilicity in polar, protic, solvents of the following is:
(I) CH3OH (II) CH3SH (III) CH3NH2
Reactivity of the following towards reaction with NaBH4 is:
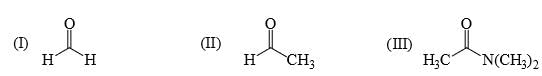
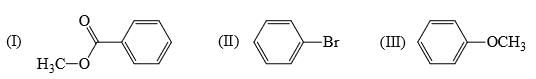
Rate of reaction of CH3COCl/AlCl3 with each of the following is:
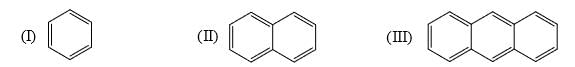
The resonance energy of each of the following is:
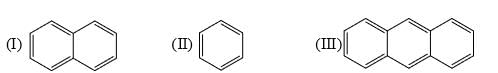
Identify order of per ring resonance energies of each of the following:
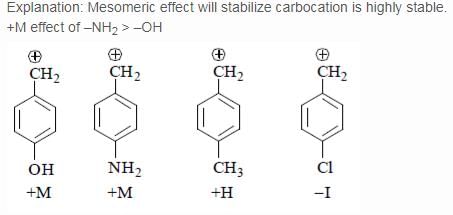
The relative stability of the following carbocations is:
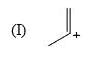
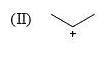
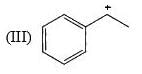
Which of the following systems are resonance contributions of the radical shown below:
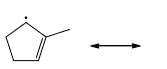
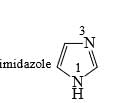
Imidazole has a pKa = 7 with respect to its conjugate acid. Which N is protonated in this conjugate acid and why?
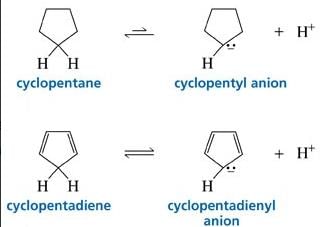
Cyclopentadiene has a pKa = 15, whereas cyclopentane has a pKa > 50. This is because:
Which of the following is most likely to undergo a favourable hydride shift?
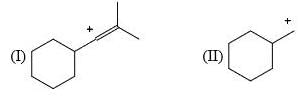
Arrange the following intermediate into decreasing order of stability.
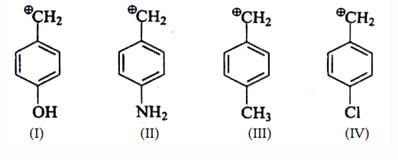
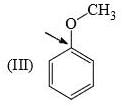
Which of the following forms most stable carbocation upon removal of OH–:
Which of the following carbonium ion is most stable?
Which of the following carbocations would not likely rearrange to a more stable carbocation?
Which one of the following carbocation would you expect a H migration?
Arrange stability of the given carbocations in decreasing order:

Which intermediate is involved in the reaction given below?
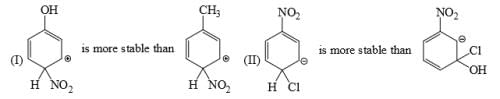
Which is the most stable arenium carbocation:
Which of the following statements is correct:
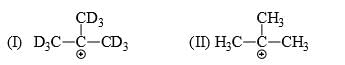
List the following carbocations in order of decreasing stability (starting with the most stable):