Test: Reaction Intermediate Level - 2 - Chemistry MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Reaction Intermediate Level - 2
The increasing order of stability of the following free radicals is .
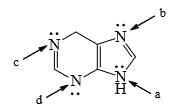
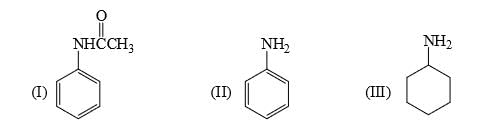
For the following compounds, which nitrogen is the least tendency to be protonated:

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which one among the following carbocations has the longest half-life?
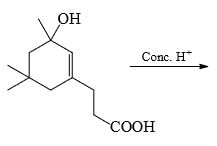
The major product formed in the following reaction is:
The acidity for the following compounds increases in the order:
CH3CH2CH(Br)COOH, CH3CH(Br)CH2COOH, (CH3)2CHCOOH
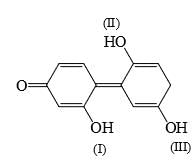
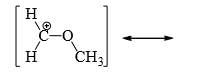
A compound 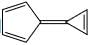 shows a large dipole moment. Which of the following resonance structures
shows a large dipole moment. Which of the following resonance structures
can be used to adequately explain this observation:
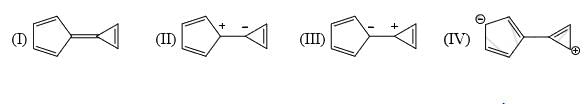
Which of the following is not a valid resonance structure of the others:
Which allylic carbocation is the most stable carbocation:
Which among the following carbocations is most stable:
Which of the following statements about resonance structures is false?
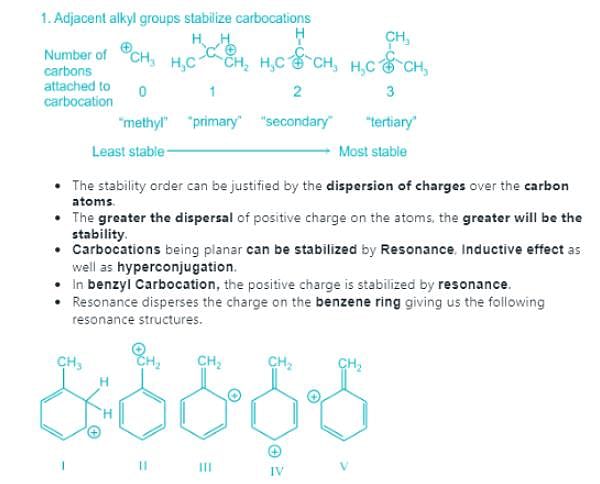
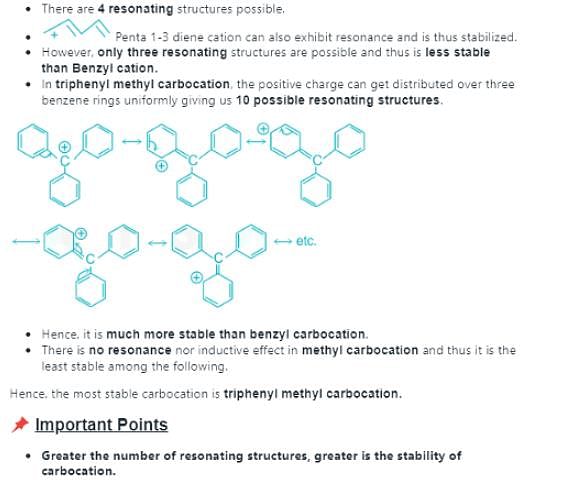
Which of the following carbocations is the most stable?
Which of the following is not a resonance structure of the others:
Rank of the following three compounds in decreasing order of basicity is:
The strength of the following bases decreases in the order:

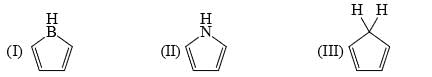
Choose the following species that would be predicted to be aromatic according to Huckel’s rule:
Which of the following phenol would be the most acidic:
Which is an acceptable resonance structure for the following drawing:
The reaction of (+) 2-iodobutane and Nal* in acetone was studied by measuring the rate of incorporation of I* (ki) and the rate of racemisation(kr)
(+) CH3CH(I)CH2CH3 + Nal* → CH3CH(I*)CH2CH3 + Nal
For this reaction, the relationship between kr and ki is
Alkyne hydrogens are more acidic than alkene or alkane hydrogens because:
Which of the following is expected to be the least basic?
The acidity order for the following compound follows the order:
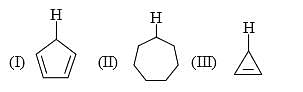
The acidity of the protons H in each of the following is:
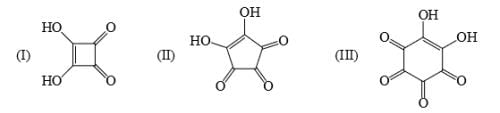
Identify correct acidic strength order in the following compounds:
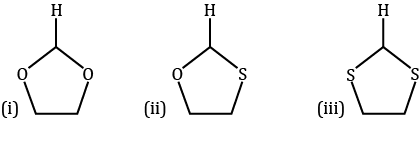
Identify correct acidic strength order in the following compounds:
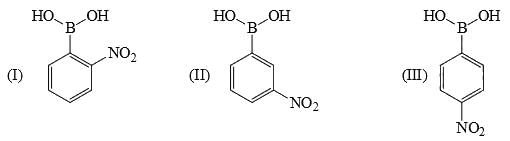
Identify correct acidic strength order in the following compounds:
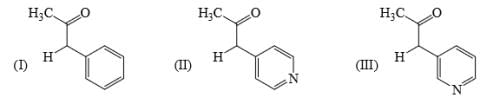
Identify the correct acidic strength order in the following compounds:
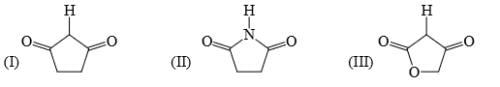
Identify correct acidic strength order in the following compounds:
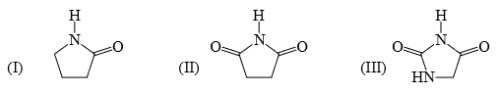
Identify correct acidic strength order in the following compounds: