Test: Reaction Mechanism Level - 5 - Chemistry MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Reaction Mechanism Level - 5
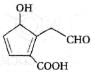
The major product formed in the following reaction is:
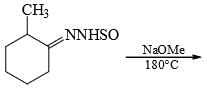

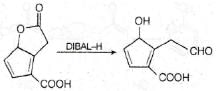
The major product formed in the following reaction is:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
In the cyclisation reaction given below, the most probable product formed is:
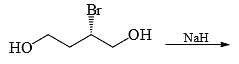

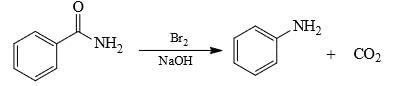
The major product formed in the reaction given below is
: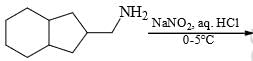
The major product formed in the following reaction is:
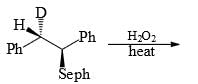
Compare the stability of the following carbocation:
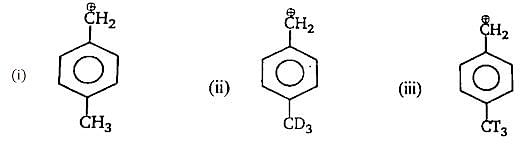
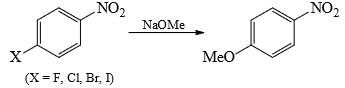
The correct order of reactivity of p-halonitrobenzens in the following reaction is
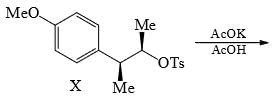
Solvolysis of the optically active compound X gives, mainly:
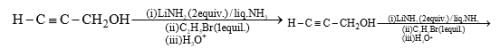
The major product obtained in the following reaction, is
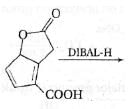
The major product formed in the following reaction is:
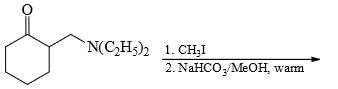
Increasing order of stability of following carbocations (give least stable first)?
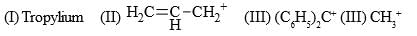
What is the nucleophilicity order for SN2 reaction:
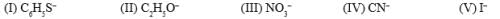
Select order of effectiveness of Lewis acid catalyst in Friedel-Crafts reaction:
For the reaction between alkyl halide and OH- increase in solvent polarity generally
Reactive intermediate formed in the following reaction is:
An SN2 reaction at an asymmetric carbon atom of a dextro alkyl halide always gives a:
Reaction of ethyne with HCN in presence of Ba (CN)2 is an example of:
Consider the following carbocations is most stable:
When 2-chloro-2-methylbutane is refluxed with alcoholic KOH, the main product obtained is:
Using given codes, arrange the following compounds in decreasing order of the rate of solvolysis by SN1 mechanism:
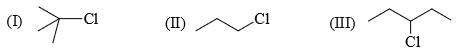
1, 3-Dichloropropane one reaction with Zn and NaI gives:
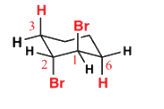
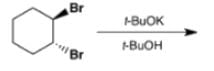
Which is the final main product of the following reaction of trans-1,2-dibromocyclohexane?
The intermediate in the reaction of m-bromoanisole with sodamide in liquid amnonia has:
Which of the alkyl halides undergoes most readily for nucleophilic substitution reaction:
The reaction of ethanolic KOH on 1, 1-dichloropropane gives:
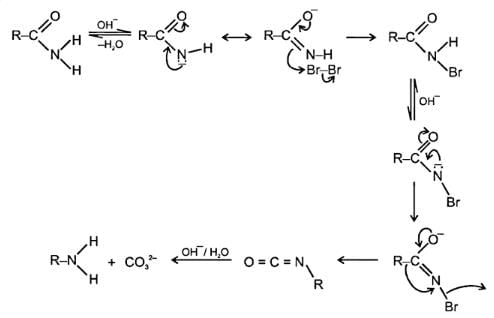
Which reactive intermediate is believed to be part of the reaction shown:

In this transformation,
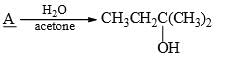
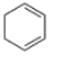
What is the best structure for A?