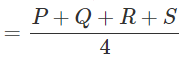Olympiad Test: Motion & Measurement of Distances - Grade 9 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Olympiad Test: Motion & Measurement of Distances
The height of a person is 1.65 m. Express it into cm and mm.
While measuring the length of a wooden box, the reading at one end is 1.5 cm and the other end is 4.7 cm. What is the length of the wooden box?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Rahul and Ravi are playing in a ground. They start running from the same point X simultaneously in the ground and reach point Y at the same time by following paths marked 1 and 2 respectively, as shown in the figure.
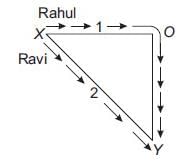
Q. Which of the following is correct statement for the given situation?

A piece of thread folded 6 times is placed along a 15 cm long measuring scale as shown in the figure. The length of the thread is between

Two identical metal balls A and 8 moving in opposite directions with different speeds hit each other at point X as shown in the figure. Changes will most likely appear in their
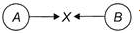
1. Shapes
2. Speeds
3. Directions
4. Volumes
In which year, SI system was recommended by general conference of weights and measures?
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
Write the similarities and differences between the motion of a bicycle and a ceiling fan that has been switched on.
One centimeter on a scale is divided into 20 equal divisions. The least count (minimum value) of this scale is
What do we use to measure curved lengths?
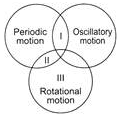
Study the given Venn diagram, Which of the motions described by different bodies are most likely to be I, II and III?
A pendulum swings backwards and forwards passing through Y, middle point of the oscillation. The first time the pendulum passes through Y, a stopwatch is started.
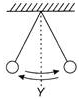
The twenty-first time the pendulum pass through Y, the stopwatch is stopped. The reading is T. What is the time period of the pendulum?
While measuring the length of a knitting needle, the reading of the scale at one end is 3.0 cm and at the other end is 33.1 cm. What is the length of the needle?
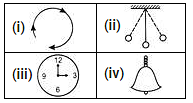
Which of the following motions is/are periodic as well as oscillatory motion?
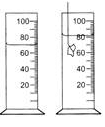
Given figure shows a measuring cylinder (incm3) before and after the immersion of an irregular solid object. The volume of the object is
Four pieces of wooden sticks P, Q, R and S are placed along the length of 15 cm long scale as shown in figure. What is the average length of these sticks?



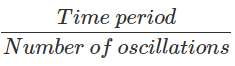 = T/10
= T/10