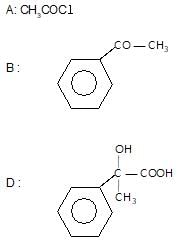
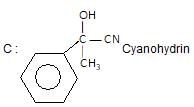
Which one of the following acids will not form acid chloride with SOCI2?
" },"encodingFormat": "text/html","text": "Which one of the following acids will not form acid chloride with SOCI2?
","suggestedAnswer": [{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 0, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "C6H5COOH
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Which one of the following acids will not form acid chloride with SOCI2?
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 1, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "C6H5 — CH2 — COOH
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Which one of the following acids will not form acid chloride with SOCI2?
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 2, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "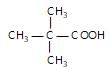
Which one of the following acids will not form acid chloride with SOCI2?
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 3, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "HCOOC2H5
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Which one of the following acids will not form acid chloride with SOCI2?
" }}],"acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "position": 3, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "d", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Which one of the following acids will not form acid chloride with SOCI2?
" }, "answerExplanation": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "SOCl2 is a lewis acid, it reacts with alcohols & carbxylic acids due to hydroxy group.
." }}},{"@type": "Question","typicalAgeRange": "4-35","educationalLevel": "intermediate","eduQuestionType": "Multiple choice","learningResourceType": "Practice problem","name": "Recollect the concept of Aldehydes & Ketones, Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives to solve the ques", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "In the reaction,
(X) will be:
In the reaction,
(X) will be:
C6H5CH2COCI
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "In the reaction,
(X) will be:
(C6H5 —CH2CO)2O
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "In the reaction,
(X) will be:
Both (a) and (b)
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "In the reaction,
(X) will be:
C6H5 —CHCI2
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "In the reaction,
(X) will be:
In the reaction,
(X) will be:
It is an example F.C acylation
." }}},{"@type": "Question","typicalAgeRange": "4-35","educationalLevel": "intermediate","eduQuestionType": "Multiple choice","learningResourceType": "Practice problem","name": "Recollect the concept of Aldehydes & Ketones, Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives to solve the ques", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "In the given reaction (P) is: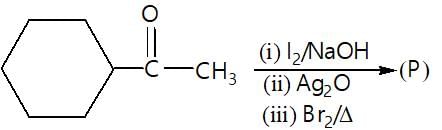
In the given reaction (P) is: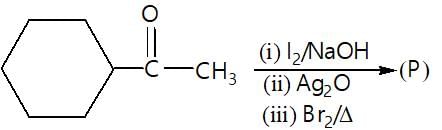
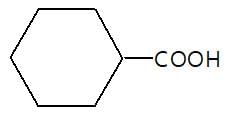
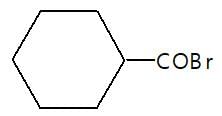
In the given reaction (P) is: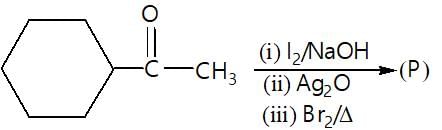
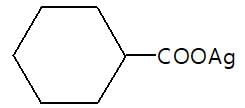
In the given reaction (P) is: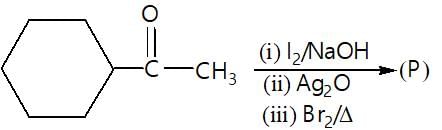
In the given reaction (P) is: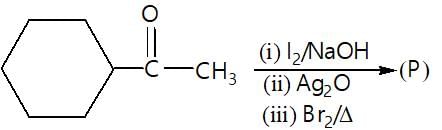
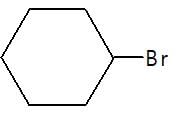
In the given reaction (P) is: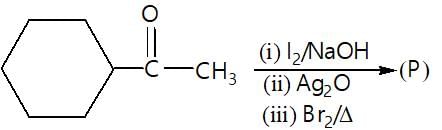
In the given reaction (P) is: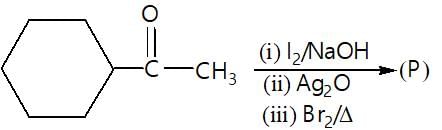
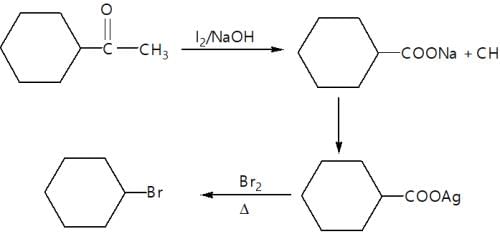
In the given reaction,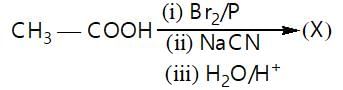
(X) will be:
In the given reaction,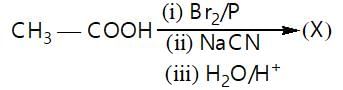
(X) will be:
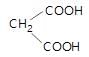
In the given reaction,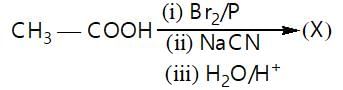
(X) will be:
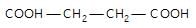
In the given reaction,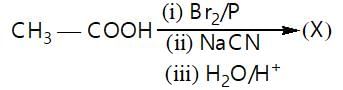
(X) will be:
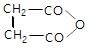
In the given reaction,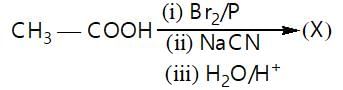
(X) will be:
In the given reaction,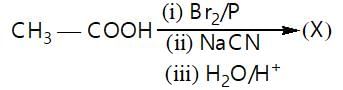
(X) will be:
In the given reaction,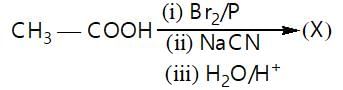
(X) will be:
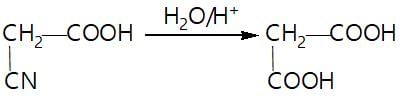
In the given reaction,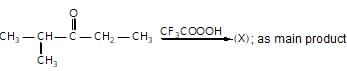
(X) will be :
In the given reaction,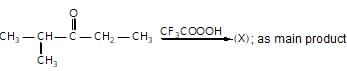
(X) will be :

In the given reaction,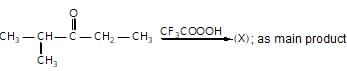
(X) will be :
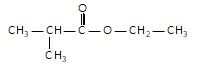
In the given reaction,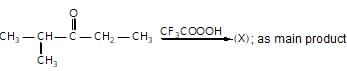
(X) will be :
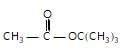
In the given reaction,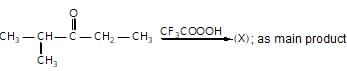
(X) will be :
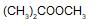
In the given reaction,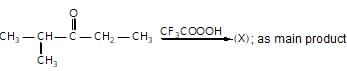
(X) will be :
In the given reaction,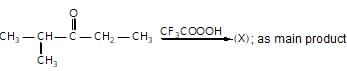
(X) will be :
Baeyer-villiger oxidation, O-atom is added to the alkyl group with higher +I effect
." }}},{"@type": "Question","typicalAgeRange": "4-35","educationalLevel": "intermediate","eduQuestionType": "Multiple choice","learningResourceType": "Practice problem","name": "Recollect the concept of Aldehydes & Ketones, Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives to solve the ques", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "(A) of the reaction is :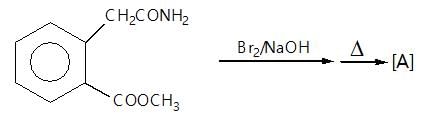
(A) of the reaction is :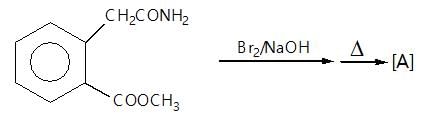
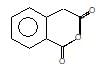
(A) of the reaction is :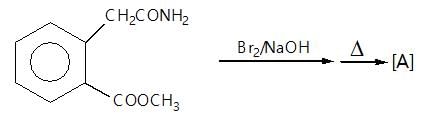
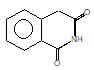
(A) of the reaction is :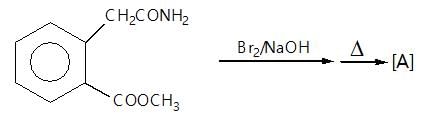
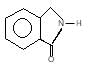
(A) of the reaction is :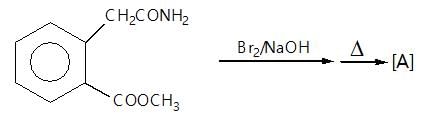
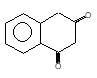
(A) of the reaction is :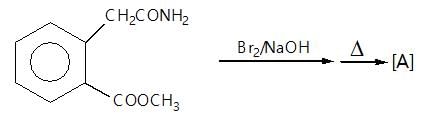
(A) of the reaction is :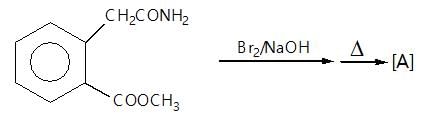
Hoffmann’s bromamide followed by intramolecular substitution
." }}},{"@type": "Question","typicalAgeRange": "4-35","educationalLevel": "intermediate","eduQuestionType": "Multiple choice","learningResourceType": "Practice problem","name": "Recollect the concept of Aldehydes & Ketones, Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives to solve the ques", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Which of the following compounds has highest pKa value?
" },"encodingFormat": "text/html","text": "Which of the following compounds has highest pKa value?
","suggestedAnswer": [{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 0, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "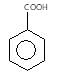
Which of the following compounds has highest pKa value?
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 1, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "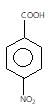
Which of the following compounds has highest pKa value?
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 2, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "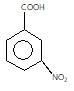
Which of the following compounds has highest pKa value?
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 3, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "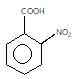
Which of the following compounds has highest pKa value?
" }}],"acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "position": 0, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "a", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Which of the following compounds has highest pKa value?
" }, "answerExplanation": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Weaker acids have higher pKa
." }}},{"@type": "Question","typicalAgeRange": "4-35","educationalLevel": "intermediate","eduQuestionType": "Multiple choice","learningResourceType": "Practice problem","name": "Recollect the concept of Aldehydes & Ketones, Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives to solve the ques", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "In the reaction,
the oxidizing agent can be :
In the reaction,
the oxidizing agent can be :
alkaline KMnO4
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "In the reaction,
the oxidizing agent can be :
acidified K2C2O7
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "In the reaction,
the oxidizing agent can be :
Benedict’s solution
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "In the reaction,
the oxidizing agent can be :
all of these
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "In the reaction,
the oxidizing agent can be :
In the reaction,
the oxidizing agent can be :
Only aldehyde is oxidised without affecting π-bond, so, Fehling’s solution/Benedict’s solution are more appoprate
." }}},{"@type": "Question","typicalAgeRange": "4-35","educationalLevel": "intermediate","eduQuestionType": "Multiple choice","learningResourceType": "Practice problem","name": "Recollect the concept of Aldehydes & Ketones, Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives to solve the ques", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "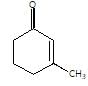 is the final product obtained when one of the following is reacted with base :
is the final product obtained when one of the following is reacted with base :
 is the final product obtained when one of the following is reacted with base :
is the final product obtained when one of the following is reacted with base :
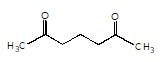
 is the final product obtained when one of the following is reacted with base :
is the final product obtained when one of the following is reacted with base :
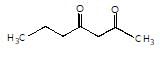
 is the final product obtained when one of the following is reacted with base :
is the final product obtained when one of the following is reacted with base :
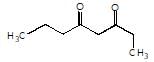
 is the final product obtained when one of the following is reacted with base :
is the final product obtained when one of the following is reacted with base :
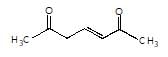
 is the final product obtained when one of the following is reacted with base :
is the final product obtained when one of the following is reacted with base :
 is the final product obtained when one of the following is reacted with base :
is the final product obtained when one of the following is reacted with base :
Given compound is formed by intramolecular aldol
." }}},{"@type": "Question","typicalAgeRange": "4-35","educationalLevel": "intermediate","eduQuestionType": "Multiple choice","learningResourceType": "Practice problem","name": "Recollect the concept of Aldehydes & Ketones, Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives to solve the ques", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Which of the following does not undergo aldol condensation?
" },"encodingFormat": "text/html","text": "Which of the following does not undergo aldol condensation?
","suggestedAnswer": [{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 0, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "CICH2CHO
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Which of the following does not undergo aldol condensation?
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 1, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "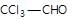
Which of the following does not undergo aldol condensation?
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 2, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "C6H5CH2CHO
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Which of the following does not undergo aldol condensation?
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 3, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "CH3CHO
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Which of the following does not undergo aldol condensation?
" }}],"acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "position": 1, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "b", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Which of the following does not undergo aldol condensation?
" }, "answerExplanation": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "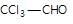 is chloral, it gives chloroform with alkali.
is chloral, it gives chloroform with alkali.

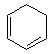

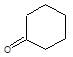

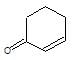

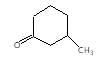


It is an example of oppaneur oxidation where only 20 alcohols are oxidised to ketone.
." }}},{"@type": "Question","typicalAgeRange": "4-35","educationalLevel": "intermediate","eduQuestionType": "Multiple choice","learningResourceType": "Practice problem","name": "Recollect the concept of Aldehydes & Ketones, Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives to solve the ques", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Which of the following is present in Fehling’s slution?
" },"encodingFormat": "text/html","text": "Which of the following is present in Fehling’s slution?
","suggestedAnswer": [{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 0, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "Potassium tartrate
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Which of the following is present in Fehling’s slution?
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 1, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "Sodium oxalate
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Which of the following is present in Fehling’s slution?
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 2, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "Sodium potassium oxalate
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Which of the following is present in Fehling’s slution?
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 3, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "Sodium potassium tartrate
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Which of the following is present in Fehling’s slution?
" }}],"acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "position": 3, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "d", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Which of the following is present in Fehling’s slution?
" }, "answerExplanation": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "It is a fact
." }}},{"@type": "Question","typicalAgeRange": "4-35","educationalLevel": "intermediate","eduQuestionType": "Multiple choice","learningResourceType": "Practice problem","name": "Recollect the concept of Aldehydes & Ketones, Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives to solve the ques", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Under Wolff-Kishner reduction conditions, the conversion which may be brough about is :
" },"encodingFormat": "text/html","text": "Under Wolff-Kishner reduction conditions, the conversion which may be brough about is :
","suggestedAnswer": [{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 0, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "benzaldehyde into benzyl alcohol
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Under Wolff-Kishner reduction conditions, the conversion which may be brough about is :
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 1, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "cyclohexanol into cyclohexanone
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Under Wolff-Kishner reduction conditions, the conversion which may be brough about is :
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 2, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "cyclohexanone into cyclohexanol
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Under Wolff-Kishner reduction conditions, the conversion which may be brough about is :
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 3, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "benzophenone into diphenylmethane
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Under Wolff-Kishner reduction conditions, the conversion which may be brough about is :
" }}],"acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "position": 3, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "d", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Under Wolff-Kishner reduction conditions, the conversion which may be brough about is :
" }, "answerExplanation": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Wolff-kishner reduction converts carbonyl group to alkane
." }}},{"@type": "Question","typicalAgeRange": "4-35","educationalLevel": "intermediate","eduQuestionType": "Multiple choice","learningResourceType": "Practice problem","name": "Recollect the concept of Aldehydes & Ketones, Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives to solve the ques", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "In the give reaction,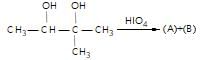
(A) and (B) respectively are :
In the give reaction,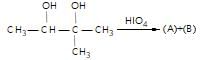
(A) and (B) respectively are :
CH3CHO and CH3CHO
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "In the give reaction,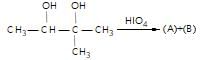
(A) and (B) respectively are :
CH3COCH3 and CH3CHO
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "In the give reaction,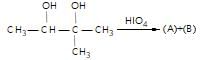
(A) and (B) respectively are :
CH3COCH3 and CH3COCH3
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "In the give reaction,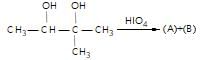
(A) and (B) respectively are :
CH3COOH and CH3COCH3
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "In the give reaction,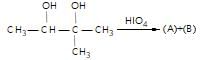
(A) and (B) respectively are :
In the give reaction,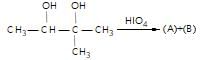
(A) and (B) respectively are :
HIO4 dissociates vicinal diols to carbonyls or carboxylic acids.
." }}},{"@type": "Question","typicalAgeRange": "4-35","educationalLevel": "intermediate","eduQuestionType": "Multiple choice","learningResourceType": "Practice problem","name": "Recollect the concept of Aldehydes & Ketones, Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives to solve the ques", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Acetophenone can be obtained by the distillation of :
" },"encodingFormat": "text/html","text": "Acetophenone can be obtained by the distillation of :
","suggestedAnswer": [{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 0, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "(C6H5COO)2Ca
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Acetophenone can be obtained by the distillation of :
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 1, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "(CH3COO)2Ca
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Acetophenone can be obtained by the distillation of :
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 2, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "(C6H5COO)2Ca and (CH3COO)2Ca
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Acetophenone can be obtained by the distillation of :
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 3, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "(C6H5COO)2Ca and (HCOO)2Ca
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Acetophenone can be obtained by the distillation of :
" }}],"acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "position": 2, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "c", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Acetophenone can be obtained by the distillation of :
" }, "answerExplanation": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Acetophenone is unsymmetrical ketone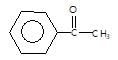
Which of the following pairs can be separated by the use of sodium bisulphite?
" },"encodingFormat": "text/html","text": "Which of the following pairs can be separated by the use of sodium bisulphite?
","suggestedAnswer": [{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 0, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "
Which of the following pairs can be separated by the use of sodium bisulphite?
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 1, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "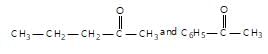
Which of the following pairs can be separated by the use of sodium bisulphite?
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 2, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "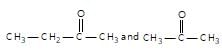
Which of the following pairs can be separated by the use of sodium bisulphite?
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 3, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "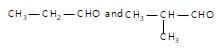
Which of the following pairs can be separated by the use of sodium bisulphite?
" }}],"acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "position": 1, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "b", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Which of the following pairs can be separated by the use of sodium bisulphite?
" }, "answerExplanation": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "It can be used to distinguish methyl aliphatic ketones from aromatic ketones, as aromatic ketones do not give white ppt.
." }}},{"@type": "Question","typicalAgeRange": "4-35","educationalLevel": "intermediate","eduQuestionType": "Multiple choice","learningResourceType": "Practice problem","name": "Recollect the concept of Aldehydes & Ketones, Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives to solve the ques", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Consider the following,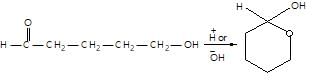
The above reaction is an example of:
Consider the following,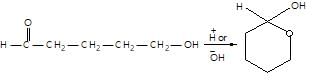
The above reaction is an example of:
intermolecular hemiacetal formation
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Consider the following,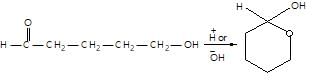
The above reaction is an example of:
intramolecular hemiacetal formation
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Consider the following,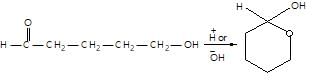
The above reaction is an example of:
intramolecular acetal formation
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Consider the following,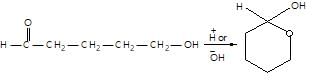
The above reaction is an example of:
intermolecular acetal formation
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Consider the following,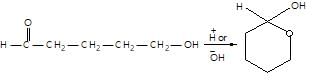
The above reaction is an example of:
Consider the following,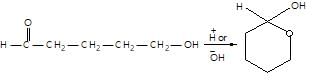
The above reaction is an example of:
Conceptual
." }}},{"@type": "Question","typicalAgeRange": "4-35","educationalLevel": "intermediate","eduQuestionType": "Multiple choice","learningResourceType": "Practice problem","name": "Recollect the concept of Aldehydes & Ketones, Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives to solve the ques", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Schiff’s reagent is used for the differentiation between:
" },"encodingFormat": "text/html","text": "Schiff’s reagent is used for the differentiation between:
","suggestedAnswer": [{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 0, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "HCHO and CH3CHO
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Schiff’s reagent is used for the differentiation between:
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 1, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "CH3COCH3 and CH3CHO
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Schiff’s reagent is used for the differentiation between:
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 2, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "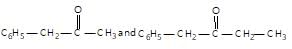
Schiff’s reagent is used for the differentiation between:
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 3, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "HCHO and C6H5CHO
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Schiff’s reagent is used for the differentiation between:
" }}],"acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "position": 1, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "b", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Schiff’s reagent is used for the differentiation between:
" }, "answerExplanation": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Aldehydes can restore colour while ketones do not.
." }}},{"@type": "Question","typicalAgeRange": "4-35","educationalLevel": "intermediate","eduQuestionType": "Multiple choice","learningResourceType": "Practice problem","name": "Recollect the concept of Aldehydes & Ketones, Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives to solve the ques", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "In the given reaction,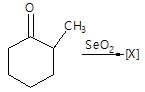
[X] will be
In the given reaction,
[X] will be
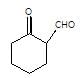
In the given reaction,
[X] will be
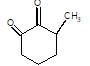
In the given reaction,
[X] will be
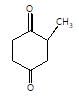
In the given reaction,
[X] will be
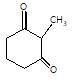
In the given reaction,
[X] will be
In the given reaction,
[X] will be
SeO2 is regioselective oxidising agent.
." }}},{"@type": "Question","typicalAgeRange": "4-35","educationalLevel": "intermediate","eduQuestionType": "Multiple choice","learningResourceType": "Practice problem","name": "Recollect the concept of Aldehydes & Ketones, Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives to solve the ques", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Product (A) of the reaction is: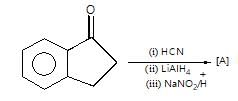
Product (A) of the reaction is:
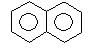
Product (A) of the reaction is:
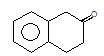
Product (A) of the reaction is:
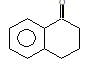
Product (A) of the reaction is:
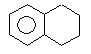
Product (A) of the reaction is:
Product (A) of the reaction is:
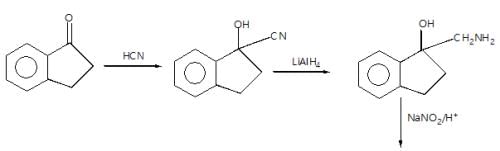
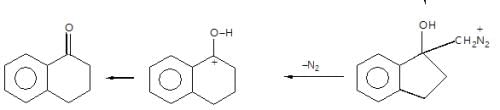
In the given reaction sequence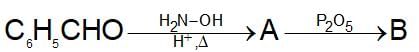
A and B respectively are :
In the given reaction sequence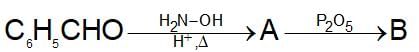
A and B respectively are :
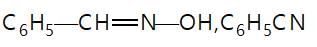
In the given reaction sequence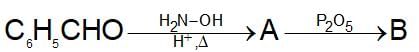
A and B respectively are :
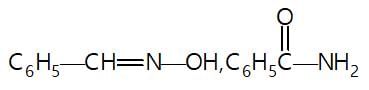
In the given reaction sequence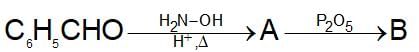
A and B respectively are :
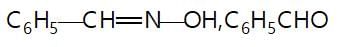
In the given reaction sequence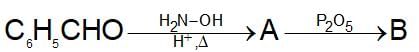
A and B respectively are :
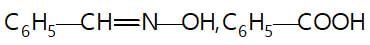
In the given reaction sequence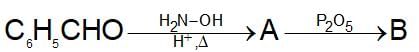
A and B respectively are :
In the given reaction sequence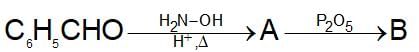
A and B respectively are :
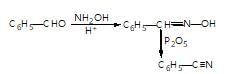
Which carbonyl group of the given compound is most reactive for nucleophilic addition reaction?
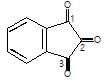
Which carbonyl group of the given compound is most reactive for nucleophilic addition reaction?

1
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Which carbonyl group of the given compound is most reactive for nucleophilic addition reaction?

2
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Which carbonyl group of the given compound is most reactive for nucleophilic addition reaction?

3
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Which carbonyl group of the given compound is most reactive for nucleophilic addition reaction?

All have equal reactivity
", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Which carbonyl group of the given compound is most reactive for nucleophilic addition reaction?

Which carbonyl group of the given compound is most reactive for nucleophilic addition reaction?

Conceptual
." }}},{"@type": "Question","typicalAgeRange": "4-35","educationalLevel": "intermediate","eduQuestionType": "Multiple choice","learningResourceType": "Practice problem","name": "Recollect the concept of Aldehydes & Ketones, Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives to solve the ques", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Which of the following carbonyl compounds when treated with dilute acid forms a stable cation?
" },"encodingFormat": "text/html","text": "Which of the following carbonyl compounds when treated with dilute acid forms a stable cation?
","suggestedAnswer": [{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 0, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "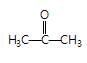
Which of the following carbonyl compounds when treated with dilute acid forms a stable cation?
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 1, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "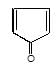
Which of the following carbonyl compounds when treated with dilute acid forms a stable cation?
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 2, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "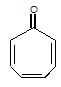
Which of the following carbonyl compounds when treated with dilute acid forms a stable cation?
" }},{ "@type": "Answer", "position": 3, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "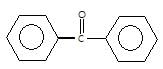
Which of the following carbonyl compounds when treated with dilute acid forms a stable cation?
" }}],"acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "position": 2, "encodingFormat": "text/html", "text": "c", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Which of the following carbonyl compounds when treated with dilute acid forms a stable cation?
" }, "answerExplanation": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "Cation formed is aromatic in compound (c)
." }}},{"@type": "Question","typicalAgeRange": "4-35","educationalLevel": "intermediate","eduQuestionType": "Multiple choice","learningResourceType": "Practice problem","name": "Recollect the concept of Aldehydes & Ketones, Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives to solve the ques", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "In the given reaction.
X will be:
In the given reaction.
X will be:
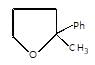
In the given reaction.
X will be:
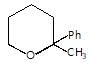
In the given reaction.
X will be:

In the given reaction.
X will be:
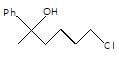
In the given reaction.
X will be:
In the given reaction.
X will be:
Intramolecular SN reaction
." }}},{"@type": "Question","typicalAgeRange": "4-35","educationalLevel": "intermediate","eduQuestionType": "Multiple choice","learningResourceType": "Practice problem","name": "Recollect the concept of Aldehydes & Ketones, Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives to solve the ques", "comment": { "@type": "Comment", "text": "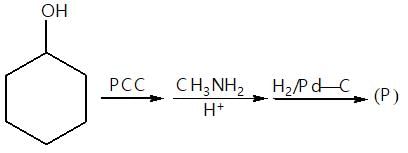
(P) will be:

(P) will be:
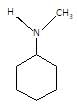

(P) will be:
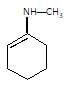

(P) will be:
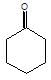

(P) will be:
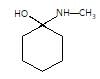

(P) will be:

(P) will be:
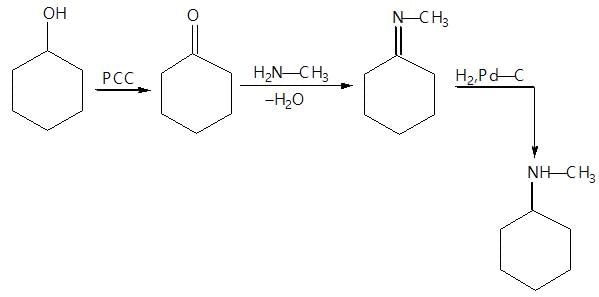
Aldehydes & Ketones, Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives - Class 12 MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Aldehydes & Ketones, Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives
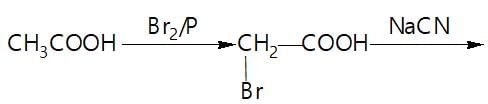
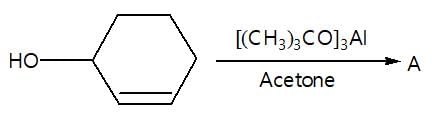
In a set of reaction acetic acid yielded product D,

The structure of D would be:

The structure of D would be:
The reactivity of carboxylic acid derivatives from highest reactivity to lowest reactiviy is:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
What is the product of the following reaction?


Which of the following is most acidic?
Which one of the following acids will not form acid chloride with SOCI2?
In the given reaction,
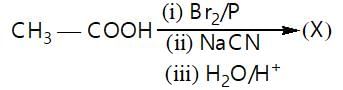
(X) will be:
In the given reaction,
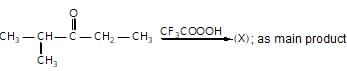
(X) will be :
Which of the following compounds has highest pKa value?
In the reaction,

the oxidizing agent can be :
 is the final product obtained when one of the following is reacted with base :
is the final product obtained when one of the following is reacted with base :
Which of the following does not undergo aldol condensation?
Which of the following is present in Fehling’s slution?
Under Wolff-Kishner reduction conditions, the conversion which may be brough about is :
In the give reaction,
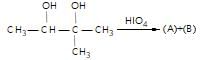
(A) and (B) respectively are :
Acetophenone can be obtained by the distillation of :
Which of the following pairs can be separated by the use of sodium bisulphite?
Consider the following,
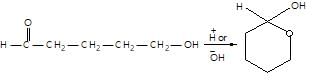
The above reaction is an example of:
Schiff’s reagent is used for the differentiation between:
In the given reaction,

[X] will be
Product (A) of the reaction is:

In the given reaction sequence
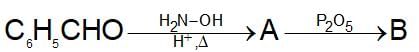
A and B respectively are :
Which carbonyl group of the given compound is most reactive for nucleophilic addition reaction?

Which of the following carbonyl compounds when treated with dilute acid forms a stable cation?
In the given reaction.

X will be: