Chemical - Phase - Ionic Equilibriums - Chemistry MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Chemical - Phase - Ionic Equilibriums
What amount of solid sodium acetate be added into 1 litre of the 0.1 M CH3COOH solution so that the resulting solution has pH almost equal to pKa (CH3COOH) = 4.74
Liquid ammonia ionizes to a slight extent. At –50°C, its ion product is 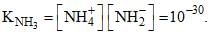 How many amide ions, NH-2are present per mm3 of pure liquid ammonia?
How many amide ions, NH-2are present per mm3 of pure liquid ammonia?
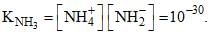 How many amide ions, NH-2are present per mm3 of pure liquid ammonia?
How many amide ions, NH-2are present per mm3 of pure liquid ammonia? For preparing a buffer solution of pH 6 by mixing sodium acetate and acetic acid, the ratio of concentration of salt and acid (Ka = 10–5) should be:
The number of degrees of freedom in the homogenous liquid region of a two component system with a eutectic point, at one atmosphere pressure is:
The maximum number of triple point(s) occuring in one component sulfur system are:
Consider the following equilibrium in a closed vessel  . At a fixed temperature if the volume of the reaction vessel is halved, which of the following statements holds true regarding the equilibrium constant (Kp) and the degree of dissociation (α) of N2O4?
. At a fixed temperature if the volume of the reaction vessel is halved, which of the following statements holds true regarding the equilibrium constant (Kp) and the degree of dissociation (α) of N2O4?
Under conditions of constant temperature and pressure when a system is in equilibrium which of the following quantities is at a minimum:
Based upon the following hypothetical equilibrium at 273 K

Which is the most effective dehydrating agent at 273 K (Aqueous tension at 273 K = 6.0 × 10–3atm)
An equilibrium system for the reaction between hydrogen and iodine to give hydrogen iodine at 765 K in a 5 liter volume contains 0.4 mole of hydrogen, 0.4 mole of iodine and 2.4 moles of hydrogen iodide. The equilibrium constant for the reaction is:

To a 50 ml of 0.1 M HCl solution, 10 ml of 0.1 M NaOH is added and the resulting solution is diluted to 100 ml. What is change in pH of the HCl solution?
To a 100 ml solution of 0.1 M CH3COONa and 0.1 M CH3COOH, 0.4 gm of solid NaOH was added. Assuming volume remains constant, calculate the change in pH value? Given that pKa(CH3COOH) = 4.74.
When equal volumes of the following solution are mixed, precipitation of AgCl (Ksp = 1.8 × 10–10) will occur only with:
How many gram of CaC2O4 will dissolve in one litre of saturated solution? Ksp of CaC2O4 is 2.5 × 10–9mol–2 and its molecular weight is 128:
Let the solubilities of AgCl in H2O, 0.01 M CaCl2; 0.01 M NaCl and 0.05 M AgNO3 be S1, S2, S3, S4 respectively. What is the correct relationship between these quantities?
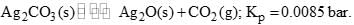 Calculate the minimum mole % of CO2 in air at 1 bar which is sufficient to prevent any loss in weight of Ag2CO3 by decomposition at the same temperature:
Calculate the minimum mole % of CO2 in air at 1 bar which is sufficient to prevent any loss in weight of Ag2CO3 by decomposition at the same temperature:
At temperature T, a compound AB2(g) dissociates according to the reaction 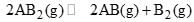 with degree of dissociation α, which is small compared with unity. The expression for Kp, in terms of α and the total pressure, PT is:
with degree of dissociation α, which is small compared with unity. The expression for Kp, in terms of α and the total pressure, PT is:
A reaction mixture containing H2, N2 and NH3 has partial pressures 2 atm, 1 atm and 3 atm respectively at 725 K. If the value of Kp for the reaction.  is4.28 × 10–5atm–2 at 725 K, in which direction the net reaction will go:
is4.28 × 10–5atm–2 at 725 K, in which direction the net reaction will go:
pH of an aqueous solution of Al+3 is likely to be:
The molar solubility (in mol L–1) of a sparingly soluble salt MX4 is ‘s’. The corresponding solubility product is Ksp. s is given in terms of Ksp by the relation:
The phase diagram of a pure substance is sketched below:
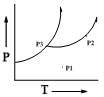
The number of degrees of freedom at points P1, P2 and P3, respectively, are:
Consider a phase diagram of two component simple eutectic system. If XA = 0.8 and XB = 0.2, which of the following composition will never be observed:
The number of phases, components and degrees of freedom, when Ar is added to an equilibrium mixture of NO, O2 and NO2 in gas phase are, respectively:
A pure substance exists in several different phases A, B, C. Its partial phase diagram is shown below:
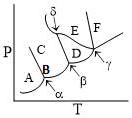
Which of the following statements is correct about the above diagram?
The lowest pressure at which the liquid phase of a pure substance can exist is known as:
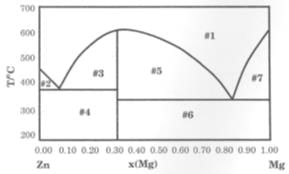
The solid-liquid phase diagram for the Mg-Zn system is shown in the figure below where the vertical line at X(Mg) = 0.33 represents the formation of a congruent melting compound MgZn2.The figure is divided into seven regions depending upon the physical state of the system. The composition of the region #6 represents.
Which of the following does not represent a phase diagram?
For the reaction 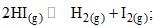 the degree of dissociation (α) of HI(g) is related to equilibrium constant Kp by the expression:
the degree of dissociation (α) of HI(g) is related to equilibrium constant Kp by the expression:



















