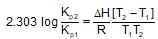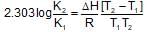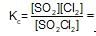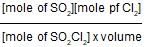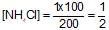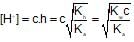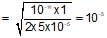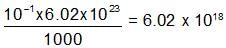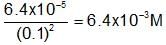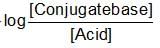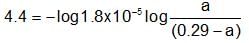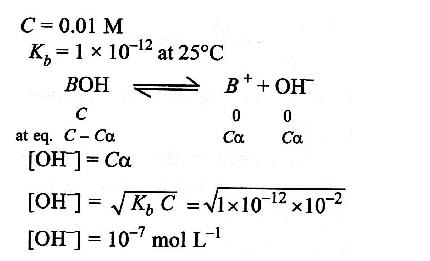Ionic Equilibrium - Class 12 MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Ionic Equilibrium
For which salt the pH of its solution does not change with dilution?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which equilibrium can be decribed as Lewis acid-base reaction but not Bronsted acid-base reaction?
The correct representation for the solubility product constant of Ag2CrO4 is:
The correct statement for the equilibrium is:
HCIO4 + H2O ⇌ H3O+ + CIO-4
The rapid change of pH near the stochiometric point of an acid-base titration is the basic of indicator detection. pH of the solution is related to the ratio of the concentration of conjugate acid (HIn) and base (In- ) form of the indicator by the expression:
One litre of water contains 10-7 mole H+ ions. Degree of ionisation of water is:
If CuSO4 + 5H2O (s) ⇌ CuSO4 . 3H2O(S) + 2H2O(v)Kp = 1.086 * 10-4 atm2 at 250C. The efflorescent nature of CuSO4 5H2O can be noticed when vapour pressure of H2O in atmosphere is:
The equilibrium constant for the reaction, 3C2H2 ⇌ C6H6 ,is 4.0 at T.K. If the equilibrium concentration of C2H2 is 0.5 mol/litre, the concentration of C6H6 is:
40% of a mixture of 0.2 mole of N2 and 0.6 mole of H2 react to give NH3 according to the equation, N2(g) + 3h2(g) ⇌2NH3 (g) at constant temperature and pressure. Then the ratio of the final volume to the initial volume of gases is:
When 20 g of CaCO3 were put into 10 litre flask and heated to 8000C, 35% of CaCO3 remained unreacted at equilibrium. Kp for decomposition of CaCO3 is:
The value of Kp1 and Kp2 for the reactions
X ⇌ Y+Z ..(1)
A ⇌ 2b ....(2)
are in the ration 9 : 1. If degree of dissociation of X and A be equal, them total pressure at equilibrium (1) and (2) are in the ratio:
At constant temperature in one litre vessel, when the reaction, 2SO3(g)→2SO2(g)+O2(g) is at equilibrium, the SO2 concentration is 0.6 M, initial concentration of SO3 is 1 M. The equilibrium constant is:
HCOOH ⇌ HCOO- + H+; Ks = 1.7*10-4
The ionization of formic acid is represented above. Calculate [H+] of a solution initially containing 0.1 M HCOOH and 0.05 M HCOONa:
When NaCI is added gradually to the saturated solution of AgCI then which of the following plot is correct?
The solubility product of different sparingly soluble salts are:
(i) XY = 4x10-20
(ii) X2Y = 3.2x10-11
(iii) XY3 = 2.7 x 10-31
The increasing order of solubility is:
An aqueous solution of hydrogen sulphide shows the equilibrium,
H2S ⇌ H+ +HS-
If dilute hydrochloric acid is added to an aqueous solution of hydrogen sulphide without any change in temperature, then:
The equilibrium constant for decomosition of Hbr at 500 K and 700 K are 10-10 and 10-5 respectively. The reaction is:
The reaction quotient (Q) for the reaction is given by:
N2(g)+3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3;
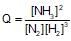
The reaction will proceed from right to left if:
For the gaseous phase reaction, 2NO ⇌ N2 + O2, ΔH° = -43.5 kcal mol-1 which statement is correct for,
N2(g)+O2(g) ⇌ 2NO(g) ?
The volume of the reactions vessel containing an equilibrium mixture in the reaction.
SO2Cl2 (g) ⇌ SO2(g)+Cl2(g)
is increased. When equilibrium is restablished.
100ml of 1N NH4OH (Kb=5x10-5) is neutralized to equivalence point by 1N HCl. The PH of solution at equivalence point is
To 100 mL of 0.1 M AgNO3 solution solid K2SO4 is added. The concentration of K2SO4 that shows the precipitation is,(Ksp for Ag2SO4 = 6.4 x 10-5 M)
The composition of an acidic buffer mixture made up of HA and NaA of total molarity 0.29 having pH = 4.4 and Ka = 1.8 x 10-5 in terms of concentration of salt and acid respectively is:
At 250 C, Kb for a base BOH is 1.0 x 10-12. The [OH- ] in 0.01 M aqueous solution of base is:


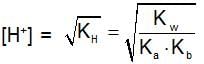
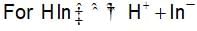
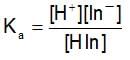
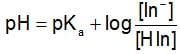
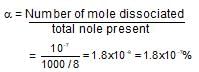
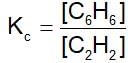
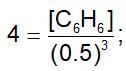
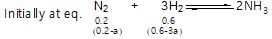
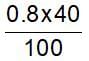 reacts to give
reacts to give 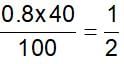 mole of NH3
mole of NH3
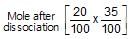
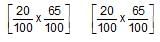
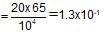
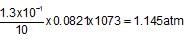
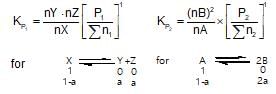
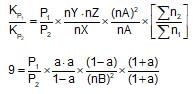
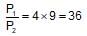
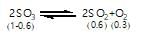
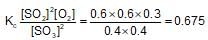
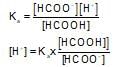
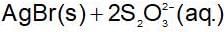
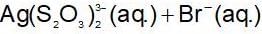
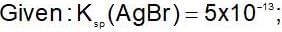
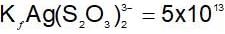
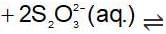
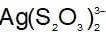
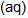
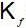
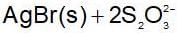
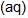
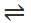
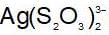
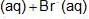
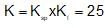
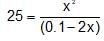
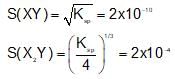
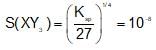
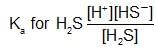 An increase in [H+] will show a decrease in [HS- ] to maintain constant Kavalue.
An increase in [H+] will show a decrease in [HS- ] to maintain constant Kavalue.