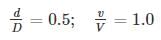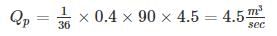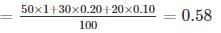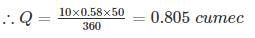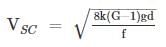Test: Environmental Engineering- 3 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Environmental Engineering- 3
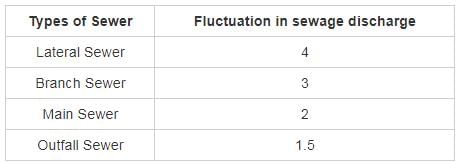
Which sewer is having the maximum fluctuations in sewer discharge?
The Maximum velocity through a circular channel takes place when the depth of flow is equal to:
For the Sewer of size 550 mm, it is designed to run “x” times full. The value of x is
Consider the following statements for Sewers
1. Maximum Daily Discharge is two times average daily discharge
2. Maximum Hourly Discharge is three times average daily discharge
3. Minimum Daily discharge is Half of the average daily discharge
4. Minimum Hourly discharge is 2/3rdof the average daily discharge.
Identify the incorrect Statement?
Two pipe system of providing building drainage consists of
The slope of a 1.0 m diameter concrete sewer laid at a slope of 1 in 1000, develops a velocity of 1 m/s, when flowing full. When it is flowing half – full, the velocity of flow through the sewer will be
A watershed of area 90 hectare has a runoff coefficient of 0.4. A storm of duration larger than the time of concentration of the watershed and of intensity 4.5 cm/h creates a peak discharge of
The drainage discharge of a town of 10 hectares area, consisting of 50% cc paved (k = 1.0), 30% unpaved (k = 0.20) and remaining as wooded (k = 0.10) with a maximum rain intensity of 5 cm/hr, would be computed by Rational formula, as equal to ----
In a city of population 2 Lakhs, the average per capita water demand is 135 L/c/day. To provide with the sewerage facilities in the town sewer is to be designed. Calculate the design discharge (m3/s) through the branch sewer if it is given that sewer is designed to carry 3 times the average discharge. Assume 80% of the water supplied in the city enters in the sewer
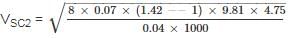
Calculate the minimum velocity (m/sec) required to transport Coarse sand through a sewer of 35 cm diameter with sand particles of 0.97 mm diameter and specific gravity 2.59, and organic matter of 4.75 mm average size with a specific gravity of 1.42. The friction factor for the sewer material may be assumed as 0.04 and roughness coefficient of 0.013. Consider k = 0.05 for inorganic solids and 0.07 for organic solids.