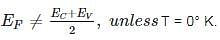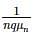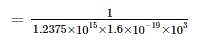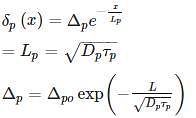Test: Electronic Devices - 1 - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Electronic Devices - 1
Read the following statements regarding semiconductor and mark the incorrect answer.
- In P type semiconductor, holes as minority charge carrier
- In N type semiconductor, electron as majority charge carrier.
- It has conductivity in between the insulator and conductor.
- At zero absolute temperature, intrinsic semiconductor behaves as a conductor.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Semiconductors have ______ conduction band and ______ valence band.
Hole mobility in Ge at room temperature is 1900 cm2/V-sec. The diffusion coefficient is ________cm2/sec.
(Write answer to one decimal point.)
(Take kT = 25 mV)
The Difference between the donor energy level and fermi level in a n-type semiconductor in where 25% of the atoms are ionised at 300 k is:
A semiconductor with intrinsic carrier concentration 1 × 1010 cm-3 at 300°K has both valence and conduction band effective densities of states NC and NV equal to 1019 cm-3. The band gap Eg is _____ eV. (Write answer to one decimal point.)
In a very long p-type Si bar with doping concentration Na = 1017 cm-3, excess holes are injected such that excessive concentration of holes at x = 0 is 5 × 1016 cm-3. The hole concentration at x = 1 μm is _____ × 1017 cm-3. Take μp = 500 cm2/v-s and recombination time constant τp = 10-8 s, kT = 0.0259 eV (Write answer to two decimal point.)
In an intrinsic semiconductor, the Fermi energy level EF doesn’t lie in the middle of the band gap cause:
A silicon bar is doped with donor impurities ND = 2.25 × 1015 cm-3. If the electron mobility μn = 1000 cm2/v-s then the approximate value of resistivity of silicon bar assuming partial ionization of 55% is __________ (Ω - cm)
Holes are injected into n-type Ge so that the at the surface of the semiconductor hole concentration is 1014/cm3. If diffusion constant of a hole in Ge is 49cm2/sec and minority carrier lifetime is τp = 10-3 sec. Then the hole concentration Δp at a distance of 4mm from the surface is ______1014/cm3.


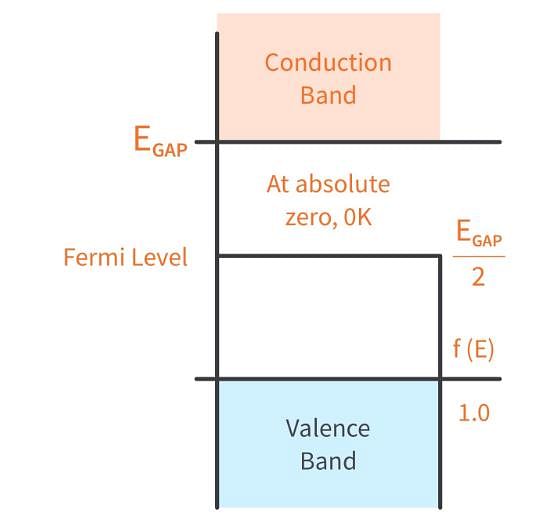
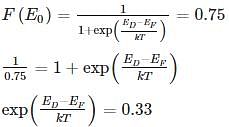

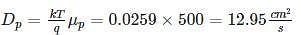
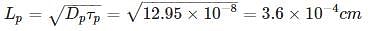
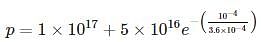
 Where NC and NV are density of state in valence and conduction bond respectively.
Where NC and NV are density of state in valence and conduction bond respectively.