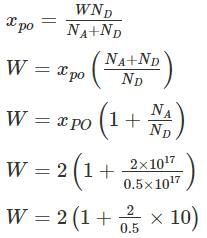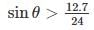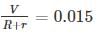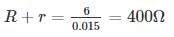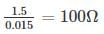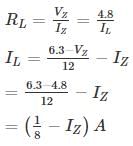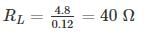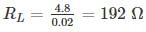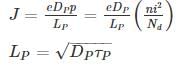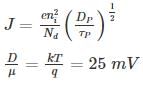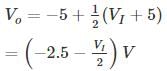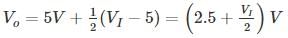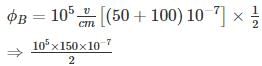Test: Electronic Devices - 3 - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Electronic Devices - 3
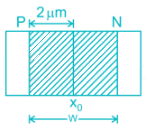
The open-circuit p-n junction diode without any Biasing is shown if NA = 2 × 1017/cm3, ND = 5 × 1016/cm3 then the depletion region width (W) is ______μm

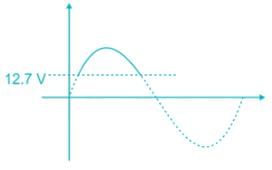
For the diode circuit shown below, If Vs = 24 sin 100πt, and the diode is practical with a cut in voltage of 0.7 V. The conduction angle of the circuit is _______ Degrees.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
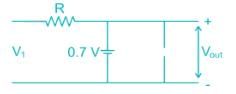
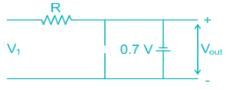
The correct output waveform for the circuit shown if the input is a sinusoidal signal of maximum Amplitude Vmax is

The correct output waveform for the circuit shown if the input is a sinusoidal signal of maximum Amplitude Vmax is
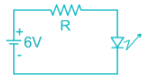
In the circuit shown, the forward biased LED has a voltage drop of 1.5 volts. If the battery voltage is 6V. Then the power displaced in the resistor R in milliwatts is _________mW. Current through LED is 15mA.
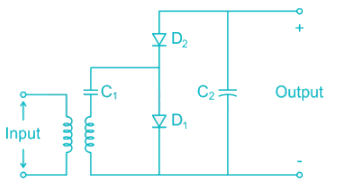
The voltage regulator circuit using a Zener diode is shown. The Zener diode current is limited in the range 5 ≤ iz ≤ 100 mA
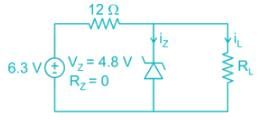
The range of load resistance is
For a P±n Si junction the reverse current at room temperature is 0.9 nA/cm2. If donor density is 1015 cm-3 and intrinsic carrier concentration is 1.05 × 1010. The minority carrier life time is ________ n sec.
[Assume μP = 450 cm2/V-sec, kT = 25mV ]
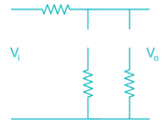
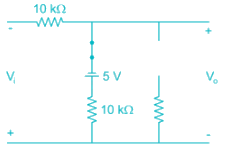
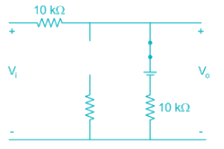
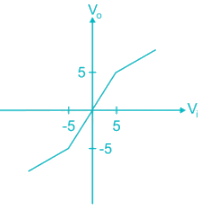
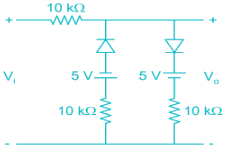
The sketch of output voltage Vo vs. input voltage VI is of from
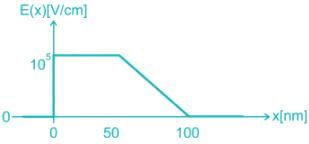
Consider a pn junction at zero bias with an electric distribution as sketched below. Calculate the built-in-potential
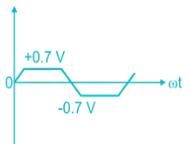
The correct waveform of the output of the given circuit is
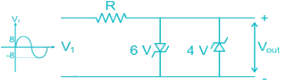
Assume the Zener diodes are ideal with threshold voltage Vk = 0.7
The correct statement regarding depletion and diffusion capacitance is
i) Depletion capacitance is dominant in reverse-bias voltage
ii) Diffusion capacitance is dominant in reverse-bias voltage
iii) The diffusion capacitance is due to a stored charge of minority electrons and minority holes near the depletion region
iv) Depletion capacitance is directly proportional to the width of the depletion region