Solutions MCQ - 1 (Advanced) - JEE MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Solutions MCQ - 1 (Advanced)
At 300 K, the vapour pressure of an ideal solution containing 3 mole of A and 2 mole of B is 600 torr. At the same temperature, if 1.5 mole of A & 0.5 mole of C(non-volatile) are added to this solution the vapour pressure of solution increases by 30 torr. What is the value of 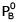 ?
?
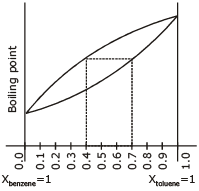
The following graph represents variation of boiling point with composition of liquid and vapours of binary liquid mixture. The graph is plotted at constant pressure.
Which of the following statement is incorrect. Here X & Y stands for mole fraction in liquid and vapour phase respectively
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The freezing point depression of a 0.1 M aq. solution of weak acid (HX) is – 0.20ºc.
What is the value of equilibrium constant for the reaction?
HX(aq)  H+(aq) + X_(aq)
H+(aq) + X_(aq)
[Given : Kf for water 1.8 kg mol-1 K. & Molality = Molarity]
The van't Hoff factor for 0.1 M Ba(NO3)2 solution is 2.74. The degree of dissociation is
The vapour pressure of an aqueous solution is found to be 750 torr at certain temperature `T'. If `T' is the temperature at which pure water boils under atmospheric pressure and same solution show elevation in boiling point ΔTb = 1.04 K, find the atmospheric pressure. (Kb = 0.52 K kg mol-1)
Study the following figure and choose the correct options from the given below (assuming both dissociate completely).
When CuSO4 is dissolved in NH4OH solution then the correct statement is
Acetone and carbon disulphide form binary liquid solution showing positive deviation from Raolut law. The normal polling point (Tb) of pure acetone is less than that of pure CS2. Pick out the incorrect statements among the following.
Passage
Vapour pressure of a solvent is the pressure exerted by vapours when they are in equilibrium with its solvent at that temperature. The vapour pressure of solvent is dependent on nature of solvent, temperature, addition of non-volatile solute as well as nature of solute to dissociate or associate.
The vapur pressuere of a mixture obtained by mixing two volatile liquids is given by PM = . XA +
. XB where
and
are vapour pressures of pure components A and B and XA, XB are their mole fraction in mixture . For solute-solvent system, the realtion become PM =
. XA where B is non-volatile solute.
Q.
The vapour pressure of benzene and its solution with a non-electrolyte are 640 and 600 mm respectively. The molality of the solution is -
Vapour pressure of a solvent is the pressure exerted by vapours when they are in equilibrium with its solvent at that temperature. The vapour pressure of solvent is dependent on nature of solvent, temperature, addition of non-volatile solute as well as nature of solute to dissociate or associate.
The vapur pressuere of a mixture obtained by mixing two volatile liquids is given by PM = . XA +
. XB where
and
are vapour pressures of pure components A and B and XA, XB are their mole fraction in mixture . For solute-solvent system, the realtion become PM =
. XA where B is non-volatile solute.
Q.
A mixture of two volatile liquids A and B for 1 and 3 moles respectivley has a V.P. of 300 mm at 27ºC. If one mole of A is further added to this solution, the vapour pressure becomes 290 mm at 27ºC. The vapour pressure of pure A is -
Vapour pressure of a solvent is the pressure exerted by vapours when they are in equilibrium with its solvent at that temperature. The vapour pressure of solvent is dependent on nature of solvent, temperature, addition of non-volatile solute as well as nature of solute to dissociate or associate.
The vapur pressuere of a mixture obtained by mixing two volatile liquids is given by PM = . XA +
. XB where
and
are vapour pressures of pure components A and B and XA, XB are their mole fraction in mixture . For solute-solvent system, the realtion become PM =
. XA where B is non-volatile solute.
Q.
The amount of solute (mol. wt. 60) required to dissolve in 180 g of water to reduce the vapour pressure to 4/5 of the pure water -
Statement - I. Addition of a non-volatile solute causes a depression in vapour pressure.
Statement - II. Vapour pressure of a solution is directly proportional to mole fraction of solvent.
Statement - I. 0.02 m solutions of urea and sucrose will freeze at same temperature.
Statement - II. Freezing point of a solution is inversely proportional to the concentration of solution.
Statement - I. For isotonic solutions C1 = C2
Statement - II. For isotonic solutions p1 = p2
Statement - I. Benzene-toluene mixture forms ideal solution.
Statement - II. Components with structural similarity forms ideal solution in general.
Statement - I. Dissolution of sulphuric acid in water gives a solution which shows negative deviation.
Statement - II. The solutions which have same vapour pressure at a given temperature are called isotonic solutions.
Statement - I. Greater the molal depression constant of the solvent used less in the freezing point of the solution.
Statement - II. Depression in freezing point depends upon the nature of the solvent
Column I
(A) Ideal solution
(B) Solutions showing positive deviations
(C) Solutions showing negative deviations
Column II
(P) Solute-solvent interactions are weaker than solute-solute
(Q) Solute-solvent interactions are similar to solute-solute
(R) Solute-solvent interactions are stronger than solute-solute interactions
At 25ºC, the vapour pressure of methyl alcohol is 96.0 torr. What is the mole fraction of CH3OH in a solution in which the (partial) vapour pressure of CH3OH is 23.0 torr at 25ºC?
The vapour pressure of pure liquid solvent A is 0.80 atm. When a non-volatile substance B is added to the solvent, its vapour pressure drops to 0.60 atm.what is the mole fraction of the component B in the solution ?
The vapour pressure of pure water at 26ºC is 25.21 torr. What is the vapour pressure of a solution which contains 20.0 glucose, C6H12O6, in 70 g water?
The vapour pressure of pure water at 25ºC is 23.76 torr. The vapour pressure of a solution containing 5.40 g of a nonvolatile substance in 90.0 g water is 23.32 torr. Compute the molecular weight of the solute.
The vapour pressure of ethanol and methanol are 44.5 mm and 88.7 mm Hg respectively. An ideal solution is prepared at the same temperature by mixing 60 g of ethanol with 40 g of methanol. Calculate total vapour pressure of the solution.

















