Test: Our Body And Health - 1 - Class 5 MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Our Body And Health - 1
The heart is the organ that pumps blood to the whole body. It has different chambers through which blood passes before being pumped throughout the body. How many chambers does the human heart have?
By the time food reaches the large intestine only water and roughage are left. It is here that most water is absorbed and stool is created. What is the approximate length of the large intestine?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following is the longest bone in our body?
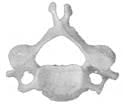
The backbone consists of 33 special bones most of which have cartilage tissue between them. What are the bones of the backbone called?
A large part of the human body by weight is water. What percentage of the adult human body is water?
These blood vessels take blood away from the heart to different parts of the body. The aorta is the biggest of these vessels. Which vessels are we talking about?
In addition to eating a balanced diet, it is also very important to exercise regularly for good physical health. Which of the following is the correct benefit of exercise?
When a body is infected with HIV, the immune system gets suppressed. This results in Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome also known as AIDS. AIDS allows life-threatening infections and cancers to thrive most often causing death. What does HIV stand for?
Human beings are warm-blooded creatures. This means that for the body systems to function, the body temperature must remain constant. What is the average body temperature of a human being in Celsius?
The respiratory system (involving inhalation and exhalation processes) is responsible for taking in oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air. Which of the following is the sequence in which events occur in the inhalation process?
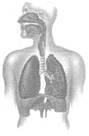
P: Air pressure inside your lungs drops. Q: The diaphragm contracts. R: Air from outside rushes into your lungs.

















