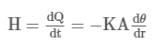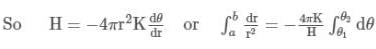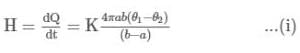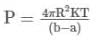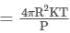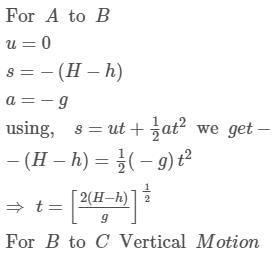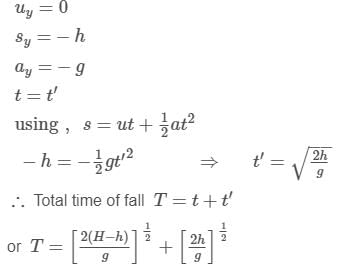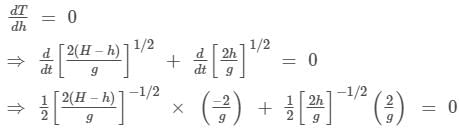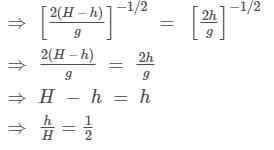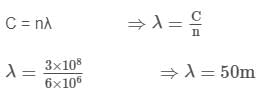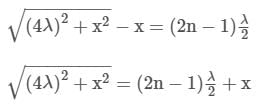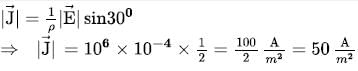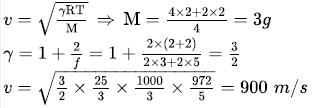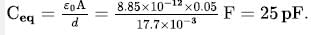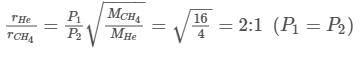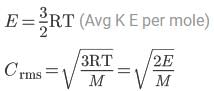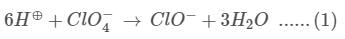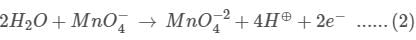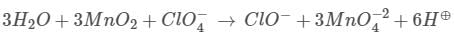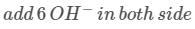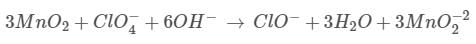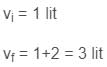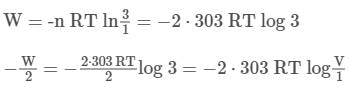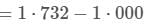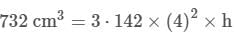JEE Main Practice Test- 9 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Main Practice Test- 9
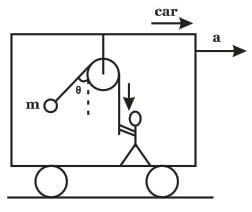
A bob is hanging over a pulley inside a car through a string. The second end of the string is in the hand of a person standing in the car. The car is moving with constant acceleration 'a' directed horizontally as shown in figure. Other end of the string is pulled with constant acceleration 'a' vertically.The tension in the string is equal to :

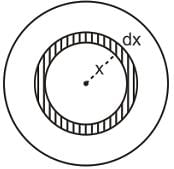
A uniform sphere has a mass M and radius R. Find the pressure p inside the sphere, caused by gravitational compression, as a function of the distance r from its centre. (γ is universal gravitational constant)
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A 220 volt input is supplied to a transformer. The output circuit draws a current of 2.0 ampere at 440 volts. If the efficiency of the transformer is 80%, the current drawn by the primary windings of the transformer is
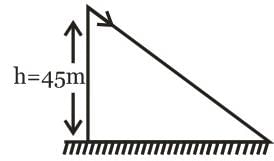
A stone is dropped from a height of 45 m on a horizontal level ground. There is horizontal wind blowing due to which horizontal acceleration of the stone becomes 10 m/s2.(Take g = 10 m/s2).
The time taken (t) by stone to reach the ground and the net horizontal displacement (x) of the stone from the time it is dropped and till it reaches the ground are respectively
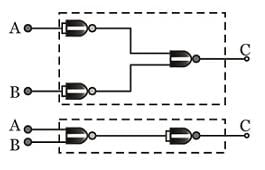
The combination of 'NAND' gates shown here (in figure), are equivalent to
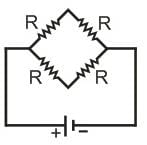
In a Wheatstone's bridge all the four arms have equal resistance R. If the resistance of the galvanometer arm is also R, the equivalent resistance of the combination as seen by the battery is
A neutron moving with speed v makes a head-on collision with a hydrogen atom in ground state kept at rest. Find the minimum kinetic energy of the neutron for which inelastic (completely or partially) collision may take place. The mass of neutron ≈ mass of hydrogen = 1.67 x 10-27 kg
A transistor-oscillator using a resonant circuit with an inductor L (of negligible resistance) and a capacitor C in series produce oscillations of frequency f. If L is doubled and C is changed to 4C, the frequency will be
Compute the bulk modulus of water if its volume changes from 100 litres to 99.5 litre under a pressure of 100 atmosphere.
When a train is at a distance of 2km, its engine sounds a whistle. A man near the railway track hears the whistle directly and by placing his ear against the track of the train. If the two sounds are heard at an interval of 5.2 s, find the speed of the sound in iron (material of the rail track). given that velocity of sound in air is 330 ms-1.
Dispersive powers of materials used in lenses of an achromatic doublet are in the ratio 5:3. If the focal length of concave lens is 15 cm, then the focal length of the other lens will be
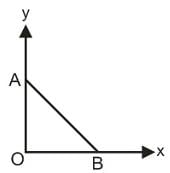
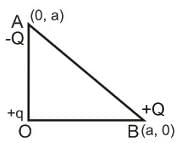
As per the diagram a point charge +q is placed at the origin O. Work done in taking another point charge -Q from the point A [coordinates (0, a)] to another point B [coordinates (a, 0)] along the straight path AB is
A man crosses the river perpendicular to river flow in time t seconds and travels an equal distance down the stream in T-seconds. The ratio of man's speed in still water to the speed of river water will be :
The mean lives of a radioactive substance are 1620 years and 405 years for α - emission and β - emission respectively. Find the time during which three-fourth of a sample will decay if it is decaying both by α – emission and β – emission simultaneously.
An uncalibrated spring balance is found to have a period of oscillation of 0.314 s, when a 1 kg weight is suspended from it, How much does the spring elongate, when a 1 kg weight is suspended from it ? Take π = 3.14
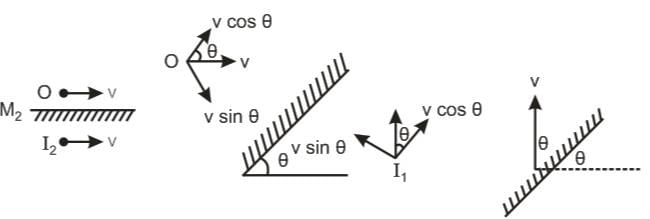
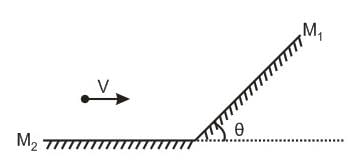
A point object is moving with a speed v in front of an arrangement of two mirrors as shown in figure. If the velocity of image in mirror M1 with respect to image in mirror M2 is n V sinθ, n =
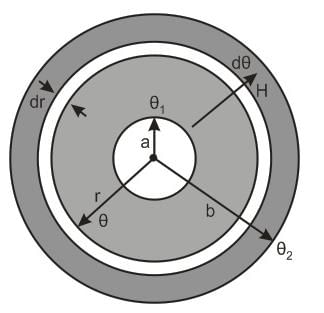
A point source of heat of power P is placed at the centre of a spherical shell of mean radius R. The material of the shell has thermal conductivity k. Calculate the thickness of the shell if temperature difference between the outer and inner surfaces of the shell in steady state is T.
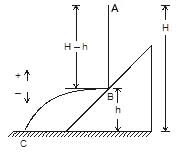
A body falling freely from a given height ‘H’ hits an inclined plane in its path at a height ‘h’. As a result of this impact the direction of the velocity of the body becomes horizontal. For what value of (h/H) the body will take maximum time to reach the ground?
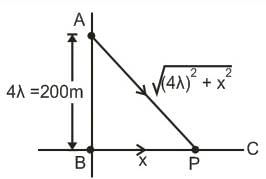
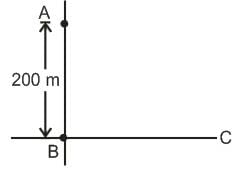
Two radio antennas radiating waves in phase are located at point A and B, 200 m part (Figure). The radio waves have a frequency of 6 MHz. A radio receiver is moved out from point B along a line perpendicular to the line connecting A and B (line BC shown in figure). At what distances from B will there be destructive interference?
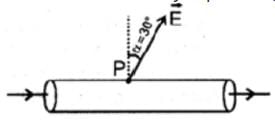
There is a long solid conductor of resistivity ρ=1x10−6Ωm, surrounded by air. There is a steady electric current along the length of the conductor. At point ‘P’ just outside the cylinder the electric field strength E=10−4V/m is directed at an angle of α to the normal to the surface. Find the current density in the conductor in the vicinity of point ‘P’ (see figure)
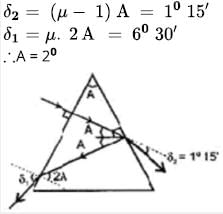
A parallel beam of light falls normally on the first face of a prism of small angle A. At the second face it is partly transmitted and partly reflected. Then the reflected beam strike the first face again and emerges from first surface in a direction making an angle 6030′ with the normal at the first surface. The refracted beam is found to have undergone a deviation of 1
Calculate the angle of prism in degree.
The speed of sound in a mixture of n1=2 moles of He, n2=2 moles of H2 at temperature 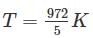 is
is 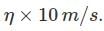 Find
Find 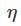 (Take
(Take 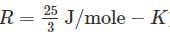 )
)
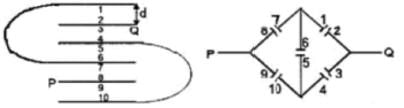
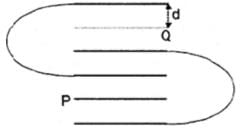
Six identical parallel metallic large plates are located in air at equal distances d to neighbouring plates. The area of each plate is A. Some of the plates are connected by conducting wires to each other. The capacitance of the system of plates between two points P and Q in pF is:
(Take A = 0.05 m2, d = 17.7 mm, ε0=8.85x10−12F/mε0=8.85x10−12F/m).
A long wire PQR is made by joining two wires PQ and QR of equal radii. PQ has a length 4.8 m and mass 0.06 kg. QR has length 2.56 m and mass 0.2 kg. The wire PQR is under a tension of 80 N. A sinusoidal wave pulse of amplitude 3.5 cm is sent along the wire PQ from the end P. No power is dissipated during the propagation of wave pulse. Find amplitude (in mm) of reflected pulse from junction Q.
If helium and methane are allowed to diffuse out of the container under the similar conditions of temperature and pressure, then the ratio of rate of diffusion of helium to methane is .
For a monatomic gas kinetic energy = E, the relation with rms velocity is
A piston is cleverly designed so that it extracts the maximum amount of work out of a chemical reaction, by matching Pexternal to the Pinternal at all times. This 8cm diameter piston initially holds back 1 mol of gas occupying 1 L, and comes to rest after being pushed out a further 2 L at 25oC .After exactly half of the work has been done, the piston has travelled out a total of


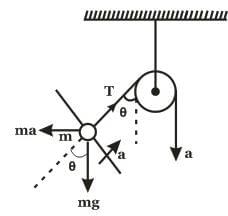
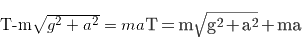
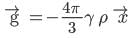
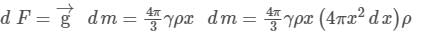
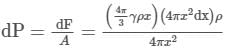
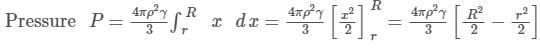
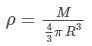
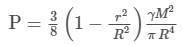
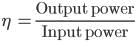
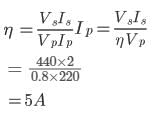
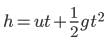
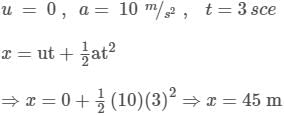
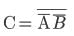 (if a NAND is given only 1 input it s behaves as NOT gate, as it is
(if a NAND is given only 1 input it s behaves as NOT gate, as it is 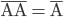 (one input is divided in two and then passed through NAND)
(one input is divided in two and then passed through NAND)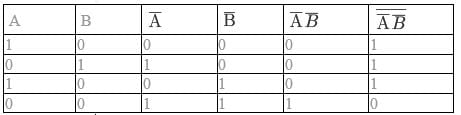
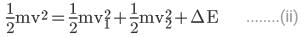
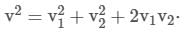
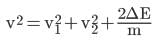
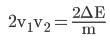
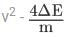
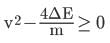
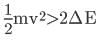
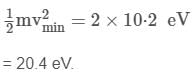
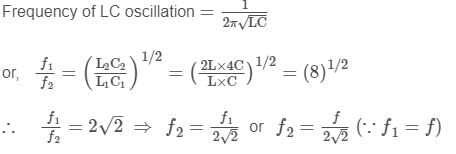

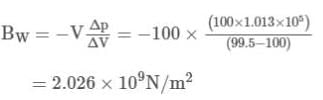
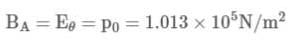
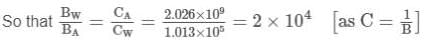
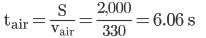
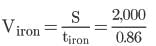
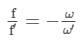
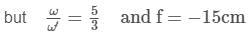
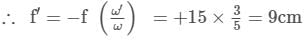
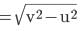

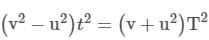 ⇒
⇒ 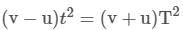
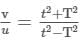
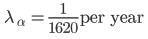
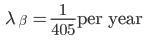
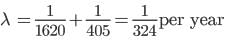
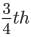 part of the sample has disintegrated, N = N0/4
part of the sample has disintegrated, N = N0/4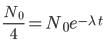
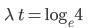
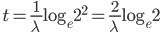

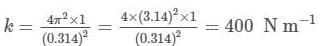
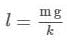
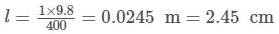
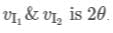 Their magnitudes is v.
Their magnitudes is v.