Olympiad Test: Sorting And Separation Of Materials -1 - Class 6 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Olympiad Test: Sorting And Separation Of Materials -1
The rate of sedimentation is increased by adding ____ to the water.
The process followed to separate grains form the stalks is called
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Look at the picture below and find out the method by which components in the mixture are separated.


When a bottle of soda water is opened, carbon dioxide escapes, producing a fizz. This is due to:
Butter is separated from curd by the process of:
Which of the following is not characteristic of solids?
When we blow air into the balloon, it inflates because:
Select a good conductor of heat among the following options.
The process in which particles of a solid settle down in a liquid is known as:
Which of the following is essential to perform winnowing activity?
Handpicking method is effective in:
Which of the following is an example of irreversible change?
The picture below shows a mixture of beads and flour in a bowl.
Q. Rehan wants to separate the beads from the flour in the bowl. What separation method can he use?

Saimaa is making herself a cup of coffee. She adds in sugar to her coffee. What will happen if she continues adding more coffee powder to her drink?
Which of the following is incorrect?
The picture below shows a teabag in a glass of water.What is the function of the teabag?

Four students are provided with four different substances as listed below:
Student A - Chalk powder
Student B - Salt
Student C - Sand
Student D - Sugar
When these substances are added to water, which of the students will obtain a solution?
Samarth mixed the following things in a bowl, then carried out the following steps.
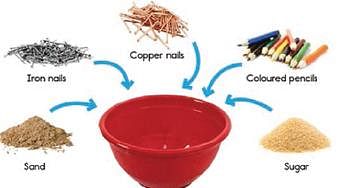
Q. Which two steps are not in a correct sequence?
Step 1: Remove the pencils by sorting them by hand.
Step 2: Use a magnet to separate the iron nails.
Step 3: Pour water into the mixture of sand and sugar.
Step 4: Remove the copper nails by sorting by hand, or by using a sieve.
Step 5: Use filtration to separate the sand.
Step 6: Use evaporation to obtain the sugar.
Which of the following properties of materials is not considered during classification?
Which of the following mixtures is a true solution?

















