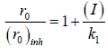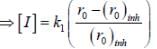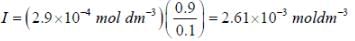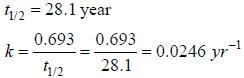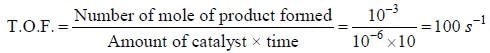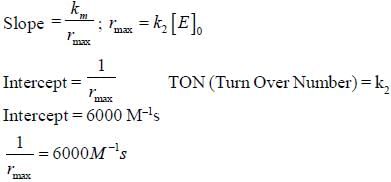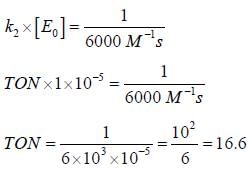Chemical Kinetics - Chemistry MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Chemical Kinetics
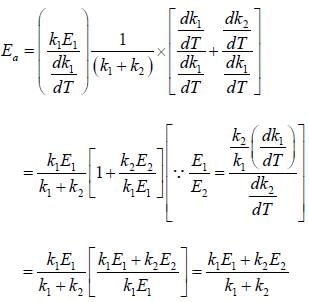
If A reacts to form either B or C according to reactions,  if E1 is the activation energy for the first reaction and E2 is the activation energy for the second reaction then Ea, the observed activation energy for the disappearance of A is
if E1 is the activation energy for the first reaction and E2 is the activation energy for the second reaction then Ea, the observed activation energy for the disappearance of A is
 if E1 is the activation energy for the first reaction and E2 is the activation energy for the second reaction then Ea, the observed activation energy for the disappearance of A is
if E1 is the activation energy for the first reaction and E2 is the activation energy for the second reaction then Ea, the observed activation energy for the disappearance of A is The following reaction was carried out in water

the initial concentration of was 0.25 molL–1 and the concentration after 10 min was 0.23 molL–1. The rate of disappears of I– (in untis of M min–1) and rate of appearance of I2.

the initial concentration of was 0.25 molL–1 and the concentration after 10 min was 0.23 molL–1. The rate of disappears of I– (in untis of M min–1) and rate of appearance of I2.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
For the reaction, A + B → C +D, Δh = 20 kJ/mole. The activation energy of the forward reaction is 85 kJ/mole. The activation energy of the reverse reaction
Consider the following variation
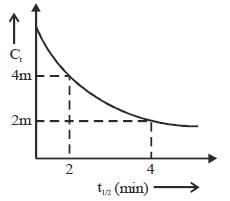
The order of reaction is _______________
For the following sequential reaction,
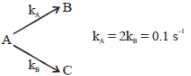
time at which [B] maximum is _____(in sec).
The percent transmittance of a solution having absorbance (optical density) 1.0 is ____________
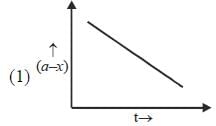
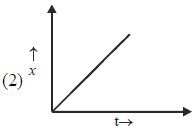
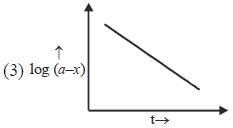
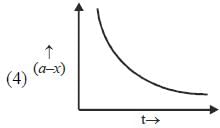
Which of the following curves represent(s) a zero order reaction
A catalyst increases the rate of a chemical reaction by
(1) increasing the activation energy
(2) decreasing the activation energy
(3) increasing the average K.E. of the molecule
(4) increasing the number of active molecules.
The rate of the elementary reaction at 25oC

Is given by rate = 1.7 x 10-18[H2][I2] - 2.4 x 10-21 [HI]2
The rate of decomposition of gaeseous HI to H2 and I2 at 25ºC is given by the equilibrium constant for the formation of HI from H2 and I2 at 25ºC is
Time constant τ is the required for the conc. of a reactant to fall to 1/e of its initial value then?
For the first order reaction,
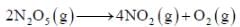
A is 4.3 x 1013 s-1 and Ea is 103.35 KJ/mole. The value of k at 300K is
The frequency factors for a unimolecular gas reaction occuring at 473K is 2.5×1013 s–1 . The value of entropy of activation is
Cyclohexane inter converts between a chair and a boat structure. The activation parameters for the reaction from the chair to boat form of the molecule are  The value of standard Gibbs energy of activation and the rate constant and the rate constant for this reaction at 325K
The value of standard Gibbs energy of activation and the rate constant and the rate constant for this reaction at 325K
The rate law for the reaction between Co(g) to form phosgene (Cl2CO)
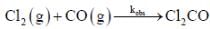
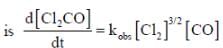
Show that the following mechanism is consistent with this rate law
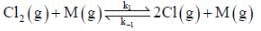 (Fast equilibrium)
(Fast equilibrium)
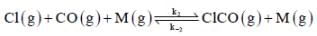 (Fast equilibrium)
(Fast equilibrium)
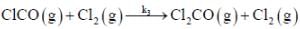 (Slow)
(Slow)
Where M is any gas molecule present in the reaction container. The value of kobs in terms of the rate constants for the individual. Steps of the reaction mechanism
A substance, when dissolved in water at 10-3 M, absorbs 10% of incident radiation in a path of 1 cm length. What should be the concentration of the solution if it were to absorb 90% of the same radiation?
For a reaction with rate equation - dc/dt = kc2, Co and C are the concentration of the reactant at time zero and t respectively. If 10 minutes were required for C0 to becomes C0/2 the time required for Co to becomes C0/4 is ____ min. (Answer should be an integer).
The concentration of non-competitive inhibitor(k1 = 2.9 x 10-4 moldm-3) needed to yield to 90% inhibiten of an enzyme catalysed reaction is ______mol dm-3. (Round off to two decimal places).
During Nuclear-explosion, one of the product is 90Sr with half-life is 28.1 year. If 1μg od 90Sr was absorbed in the bones of a newly born baby instead of calcium. How much of it will remain after 10 year if it is not lost metabolically? (in unit of μg) (Round off to two decimal places).
In a homogeneous catalytic reaction, 1.0 M of a substrate band, 1.0 μM of a catalyst yield 1.0 mM of a product in 10S. The turnover frequency (TOF) of the reaction(s-1) is ______(answer should be an integer)
In the Linewear Burk plot of (initial rate)–1 vs (initial substrate concentration)–1. For an enzyme catalyzed reacts following Michael Menten mechanism. The y-intercept is 6000 M–1s. If the initial enzyme concentration is 1×10–5 M. The turn over number is


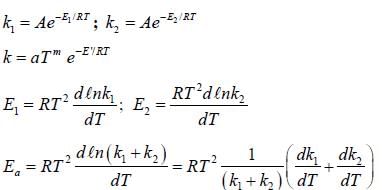
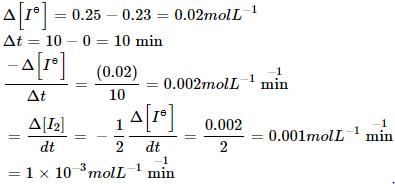
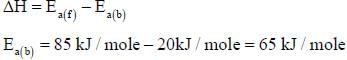
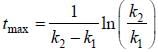
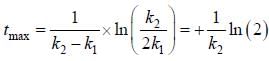
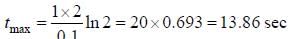
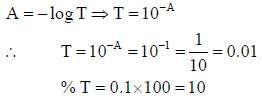
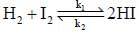
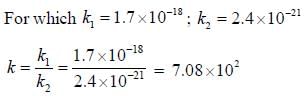
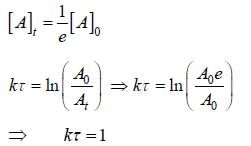
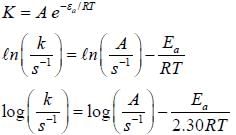
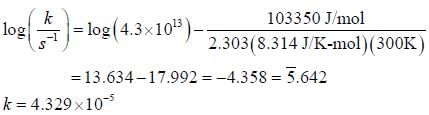

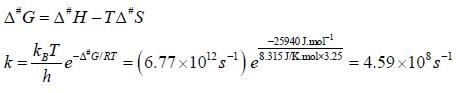
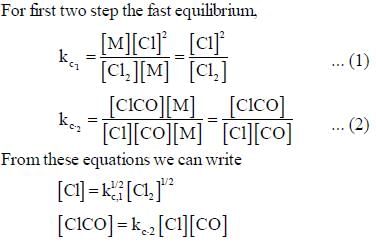
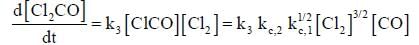
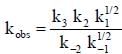
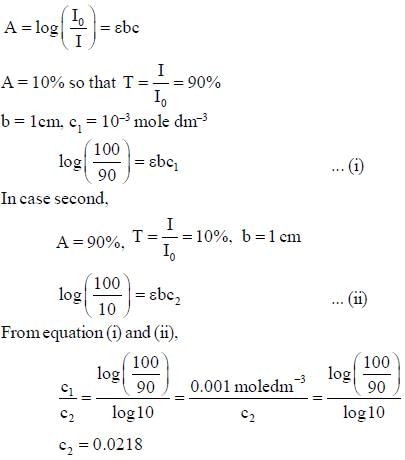
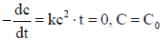
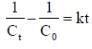 ...(i)
...(i)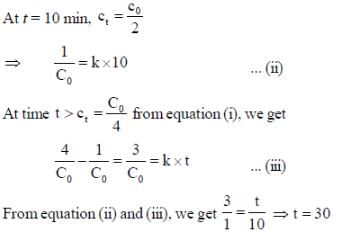
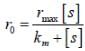 ...(i)
...(i)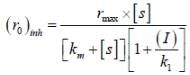 ...(ii)
...(ii)