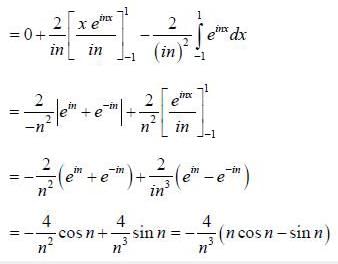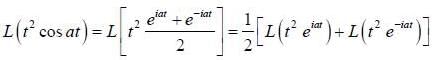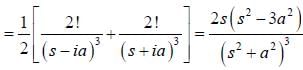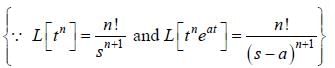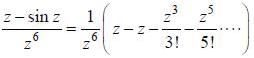Test: Mathematical Physics - 2 - Physics MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Mathematical Physics - 2
For the function 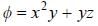 at the point (1, 2, -1), find its rate of change with distance in the direction
at the point (1, 2, -1), find its rate of change with distance in the direction 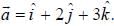
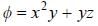 at the point (1, 2, -1), find its rate of change with distance in the direction
at the point (1, 2, -1), find its rate of change with distance in the direction 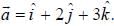
Evaluate the line integral 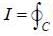 (exy + cos x sin y) dx + (ex + sin x cos y)dy, around the curve 'C'
(exy + cos x sin y) dx + (ex + sin x cos y)dy, around the curve 'C' 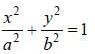
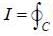 (exy + cos x sin y) dx + (ex + sin x cos y)dy, around the curve 'C'
(exy + cos x sin y) dx + (ex + sin x cos y)dy, around the curve 'C' 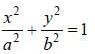
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
If a unitary matrix U is written as A + iB, where A and B are Hermitian matrix with non degenerate eigenval ues. then
If (A)nxn is a square matrix, and elements of matrix A(aij) are such that
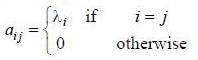
then value of det (eA) is equal to
If solution y(x), of the differential equation 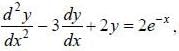 subjected to the boundary conditions y(0) = 2, y'(0) = 1 has the form y(x) = Ae-x + Bex + Ce2x, then the value of A + B - C is
subjected to the boundary conditions y(0) = 2, y'(0) = 1 has the form y(x) = Ae-x + Bex + Ce2x, then the value of A + B - C is
(upto two decimal places)
The range of values ofz, for which the following complex power series converges, 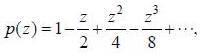 is Izl < A, then A is .................. (answer should be an integer)
is Izl < A, then A is .................. (answer should be an integer)
If the matrix 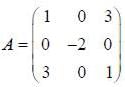 can be diagonalised by a transformation of the form S* AS = A', where S has the normalized eigenvectors of A as its columns, then A' is
can be diagonalised by a transformation of the form S* AS = A', where S has the normalized eigenvectors of A as its columns, then A' is
If 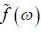 is the fourier transformation of
is the fourier transformation of 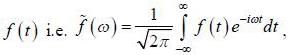 then the fourier trans form of f ' (t) is
then the fourier trans form of f ' (t) is
If a complex function f (z) lias a pole of order m at z = z0. then f'(z) has a pole of order
If the fourier series for Isin θ| in the range -π < θ < π is given by 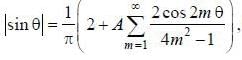 then the value of A is .........
then the value of A is .........
If the fourier expansion of 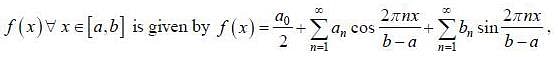 then the value of a2 if
then the value of a2 if 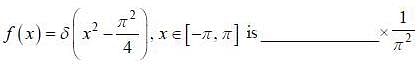
If z = xy, where y = tan-1 t and x = sin t, then the value of dz/dt is equal to
If y (x) is the solution of the differential equation 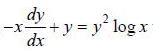 with y(1) = -1, then
with y(1) = -1, then
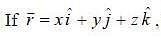 then the value of integral
then the value of integral 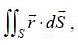 where ‘S’ is the surface given by z = 12, x2 - y2 < 25 (taken anticlockwise), is
where ‘S’ is the surface given by z = 12, x2 - y2 < 25 (taken anticlockwise), is
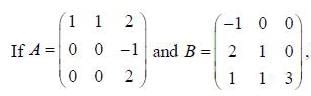 then which of the following statements is true about A and B
then which of the following statements is true about A and B
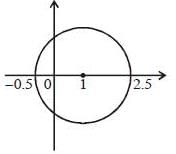
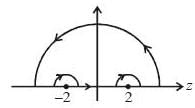
The value of the integral 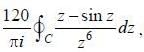 where C is closecl contour defined by the equation 2 |z - 1| - 3 = 0, traversed in the clockwise direction, is _______________________ (answer should be an integers)
where C is closecl contour defined by the equation 2 |z - 1| - 3 = 0, traversed in the clockwise direction, is _______________________ (answer should be an integers)


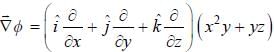
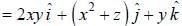
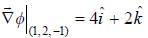
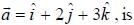
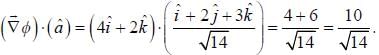
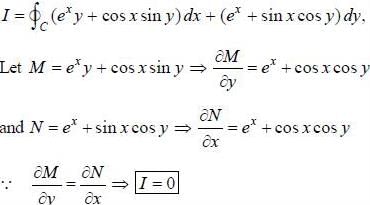
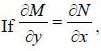 . then vector function is conservative and hence line integral (work clone) along a closed path is zero)
. then vector function is conservative and hence line integral (work clone) along a closed path is zero) 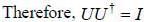
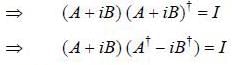
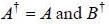 = B)
= B)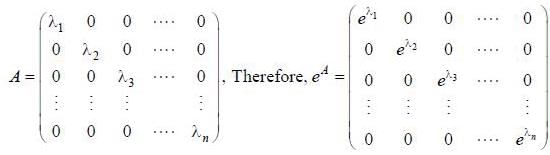
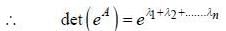
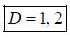
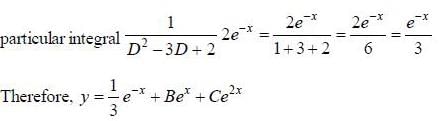
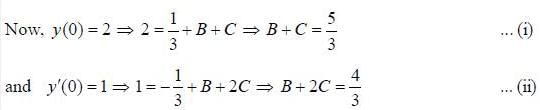
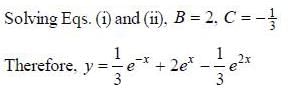
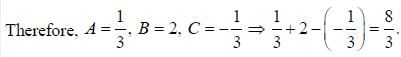
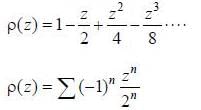
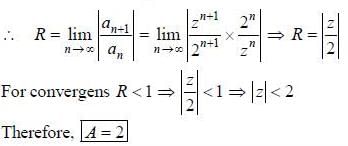

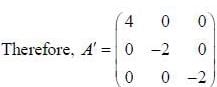
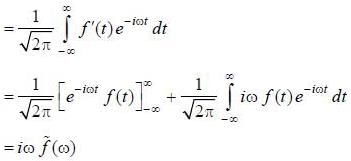
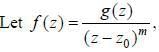 where g is analytic at z0 and g(z0) ≠ 0
where g is analytic at z0 and g(z0) ≠ 0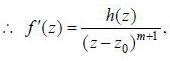 where h(z) = (z - z0) g'(z) - mg(z) is analytic at z = z0 and h(z0) = - mg (z0) ≠ 0
where h(z) = (z - z0) g'(z) - mg(z) is analytic at z = z0 and h(z0) = - mg (z0) ≠ 0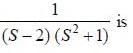
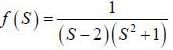
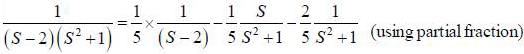
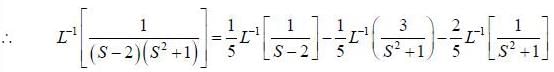
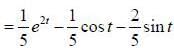
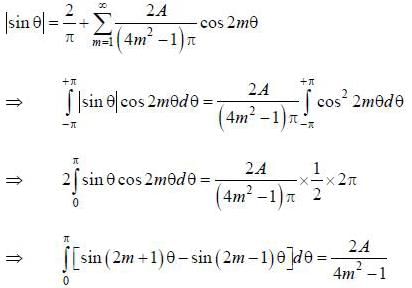
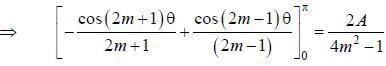
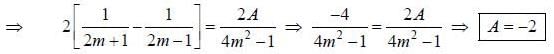
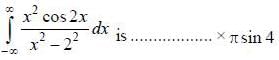
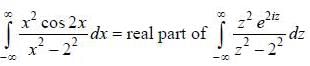

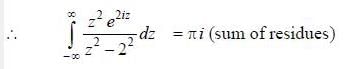
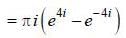
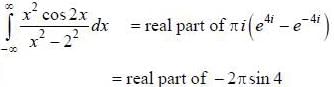
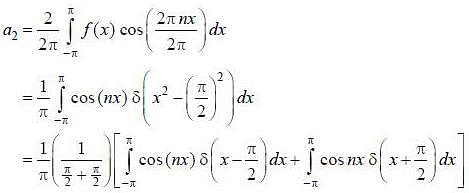
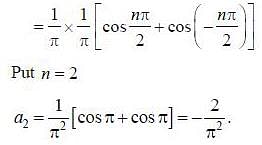
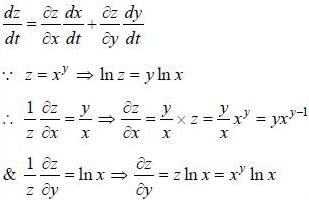
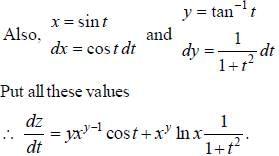
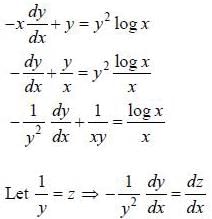


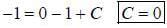
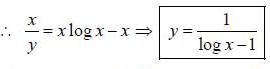
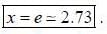
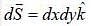
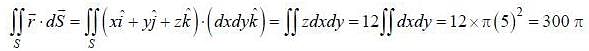
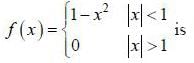
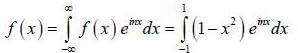
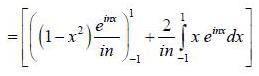 (integrating by parts)
(integrating by parts)