Molecular Biology MCQ 1 - IIT JAM MCQ
21 Questions MCQ Test - Molecular Biology MCQ 1
Retrotransposons are different from DNA transposons in that they
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
In E.coli, which component of translation machinery carries out the function for the given statements.
(i) Recognition of termination codons UAG and UAA
(ii) Recruitment of f-met - tRNA on small ribosomal subunit
(i) Recognition of termination codons UAG and UAA
(ii) Recruitment of f-met - tRNA on small ribosomal subunit
Deletion mutations would cause frameshift mutations. In which of the following would their effect be the most?
Match the transcription factors (Column A) with their functions (Column B)

Which of the following indicates that primitive life forms lacked both DNA and enzymes?
If an intron fails to get removed from an mRNA, and it is 25 nucleotides long, then how many more amino acids would the final polypeptide contain?
Match the translation inhibitor antibiotics(column A) with their mode of action (column B)

Which of the following is incorrect for tryptophan operon?
What would be mRNA from the following DNA sequence?
5' G A T C A C C G A T C A T 3'
Which of the following functions does DNA packaging serve?
Which of the following events occur when E. coli is straved for tryptophan ?
Binding of RNA polymerase to its specific promoter in E.coli:-
Consider the following statements
P) The length of the DNA is directly proportional to the gene density
Q) DNA proofreading by RNA polymerase is done by backtracking
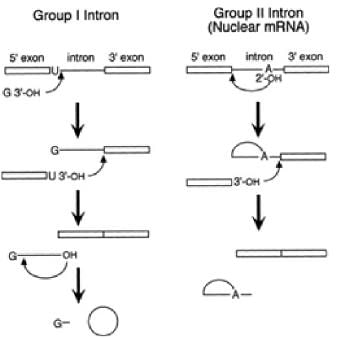
R) Splicing of nuclear mRNA occurs in the nucleus
Which of the following statements are true regarding lac operon ?
The number of base pairs in a double helical B-DNA molecule is 5430. The number of turns in the molecule will be ____________ [Answer in integer]
If the base composition of A in a dsDNA molecule is 20%, the amount of G (in %) present in this DNA would be ______________ [Answer in integer]
E.coli cells were grown in a medium containing heavy nitrogen and were later transferred to a medium containing light nitrogen. The percent of DNA expected to have been made up of light nitrogen after three generations ___________ [Answer upto one decimal place]
If the number of amino acids in a protein is 226 , then the number of nucleotides coding for the protein will be ____________ [Answer in integer]