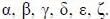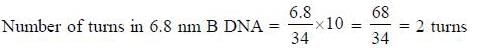Nucleic Acids MCQ - IIT JAM MCQ
21 Questions MCQ Test - Nucleic Acids MCQ
Which of the following technique was used for the determination of structure of DNA by Willkins, Watson and Crick?
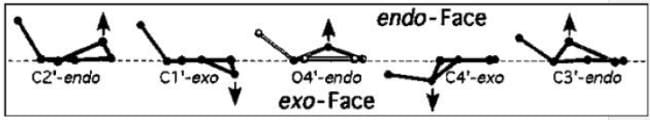
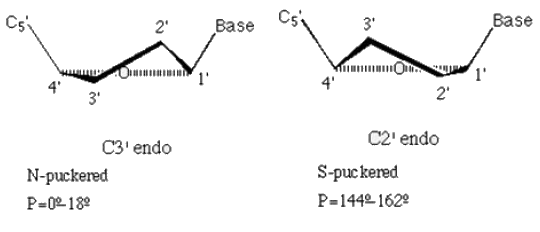
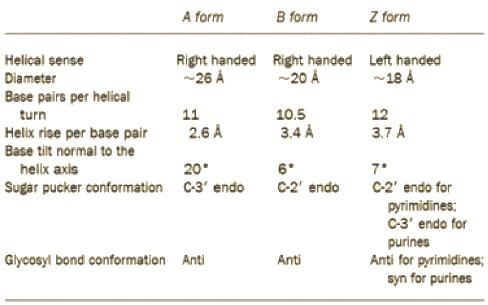
Which of the following is true about the sugar puckering in B DNA
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following nitrogen bases has the highest number of nitrogen atoms
The total number of torsional angles present in per nucleotide in a DNA molecule are
Base pair stacking is a type of stabilizing interaction in the DNA double helix. The exact nature of this interaction is
If a DNA molecule was transferred from biological buffer to a low humidity condition (less than 50% humidity) The most likely transition in the biomolecule would be
Consider the following types of DNA and their properties
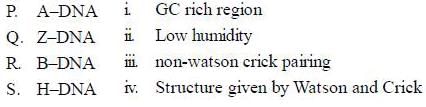
The correct match for the above two columns is
Which of the following is the true orientation for purine and pyrimidine in B-DNA when, Watson crick pairing is known to exist
Among three variants of DNA, A-DNA, B-DNA and Z-DNA, which one will be of shortest length, if the number of base pairs in each DNA molecule is same?
Among the DNA and RNA of the same size/length the ratio of their molecular weights will be
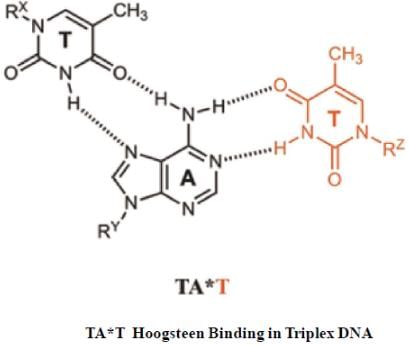
H-DNA is also known as hoogsteen DNA, which is known to contain triple helical structure, due to a special type of pairing called hoogsteen pairing between base pairs. Which of the following statement is true in this context
DNA can be stored in TE buffer containing tris and EDTA, The primary reason for adding EDTA to DNA storing buffer is
Which of the follwing statement is true about the chargaff’s rule
The number of base pairs in the B-DNA molecule of size 6.8 nm is _____________ [Answer in integer]
(Consider 10 bp per turn in B-DNA)
The number of hydrogen bonds in a DNA molecule that has 500 base pairs and whose 20% of the total bases are Guanosine is __________________ [Answer in integer]
It is given that B DNA has 1000 base pairs and each turn is at 10 bp. Also the DNA has twenty negative supercoils in it. The linking number of this B DNA is ______________[Answer in integer]
The size of open reading frame of B-DNA (in nm) encoding a peptide of 200 amino acids will be _______[Answer in integer]