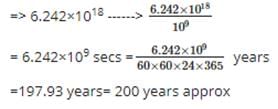Test: Electrostatics - 2 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Electrostatics - 2
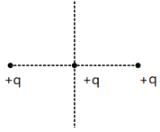
Three positive charges of equal value q are placed at the vertices of an equilateral triangle. The resulting lines of force should be sketched as in
What will be the value of a charge q, such that when it is placed at the centre of two equal and like charges Q, the three charges are in equilibrium.
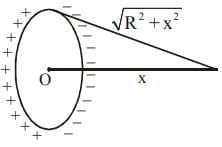
A charged particle having some mass is resting in equilibrium at a height H above the centre of a uniformly charged non-conducting horizontal ring of radius R. The force of gravity acts downwards. The equilibrium of the particle will be stable -
In space of horizontal EF(E = (mg)/q) exist as shown in figure and a mass m attached at the end of a light rod. If mass m is released from the position shown in figure find the angular velocity of the rod when it passes through the bottom most position.
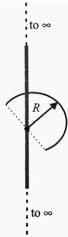
Find the force experienced by the semicircular rod charged with a charge q, placed as shown in figure. Radius of the wire is R and the infinitely long line of charge with linear density l is passing through its centre and perpendicular to the plane of wire.
A wheel having mass m has charges +q and –q on diametrically opposite points. It remains in equilibrium on a rough inclined plane in the presence of uniform vertical electric field E =
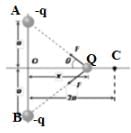
Two equal negative charges –q are fixed at the point (0, a) and (0,– a) on the y-axis. A charge +Q is released from rest at the point (2a, 0) on the x-axis. The charge Q will :
Mid way between the two equal and similar charges, we placed the third equal and similar charge. Which of the following statements is correct, concerned to the equilibrium along the line joining the charges ?
Two fixed charges 4Q (positive) and Q (negative) are located at A and B, the distance AB being 3 m.
Select the correct statement : (Only force on a particle is due to electric field)
Consider a conductor with a spherical cavity in it. A point charge q0 is placed at the centre of cavity and a point charge Q is placed outside conductor.
Statement-1 : Total charge induced on cavity wall is equal and opposite to the charge inside.
Statement-2 : If cavity is surrounded by a Gaussian surface, where all parts of Gaussian surface are
located inside the conductor,

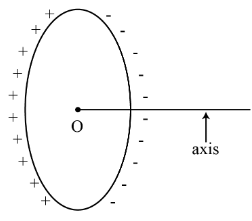
The figure shows a nonconducting ring which has positive and negative charge non uniformly distributed on it such that the total charge is zero. Which of the following statements is true ?
If we use permittivity e, resistance R, gravitational constant G and voltage V as fundamental physical quantities, then -
A particle of mass m and charge q is thrown in a region where uniform gravitational field and electric field are present. The path of particle
Statement - 1 : A positive point charge initially at rest in a uniform electric field starts moving along electric lines of forces. (Neglect all other forces except electric forces)
Statement - 2 : Electric lines of force represents path of charged particle which is released from rest in it.
Two equal negative charges are fixed at the points [0, a] and [0, –a] on the y-axis. A positive charge Q is released from rest at the points [2a, 0] on the x-axis. The charge Q will -
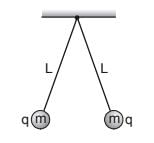
Two small balls, each having equal positive charge Q are suspended by two insulating strings of equal length L from a hook fixed to a stand. If the whole set-up is transferred to a satellite in orbit around the earth,the tension in each string is equal to
An electric dipole is placed at an angle of 30o to a non-uniform electric field. The dipole will experience
Two point charges +8q and –2q are located at x = 0 and x = L respectively. The location of a point onthe x axis at which the net electric field due to these two point charges is zero is:
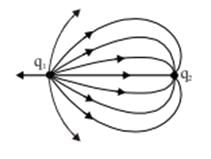
The figure shows the electric field lines in the vicinity of two point charges. Which one of the following statements concerning this situation is true?
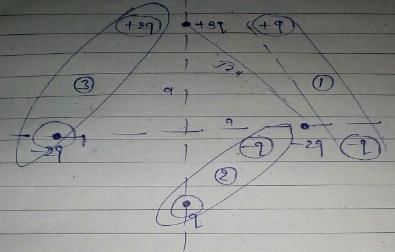
Four charges are placed each at a distance a from origin. The dipole moment of configuration is
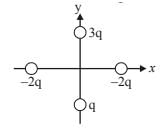
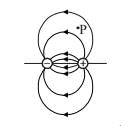
Figure shows the electric field lines around an electric dipole. Which of the arrows best represents the electric field at point P?
A uniform electric field 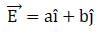 , intersects a surface of area A. What is the flux through this area if thesurface lies in the yz plane?
, intersects a surface of area A. What is the flux through this area if thesurface lies in the yz plane?
If 109 electrons move out of a body to another body every second, how much time is approximately required to get a total charge of 1 C on the other body?
A uniform line charge with linear density λ lies along the y-axis. What flux crosses a spherical surface centered at the origin with r = R
Electric lines of force never intersect each other because
A neutral point lies at the center of the line joining the charges when
The dimensions of 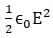 where [∈0 : permittivity of free space ; E: electric field]
where [∈0 : permittivity of free space ; E: electric field]



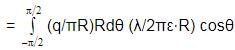
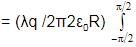 cosθdθ=(λq/2π2ε0R) [sinθ]−π/2π/2
cosθdθ=(λq/2π2ε0R) [sinθ]−π/2π/2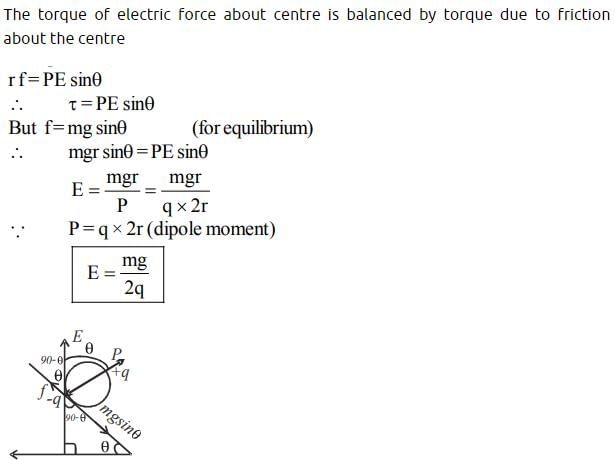
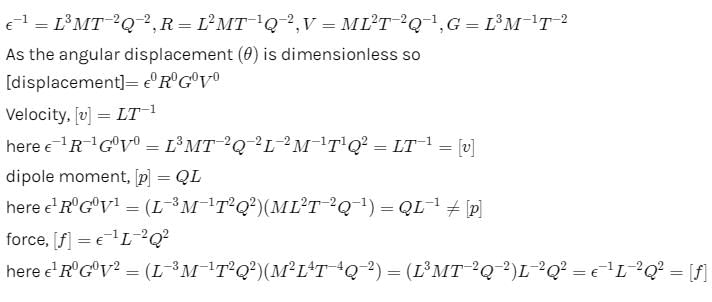

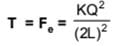
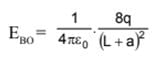

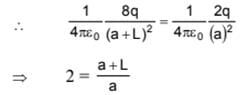
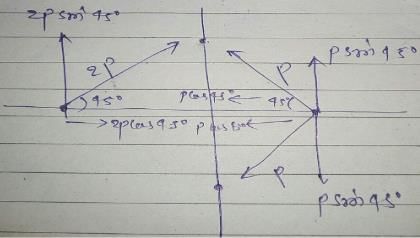
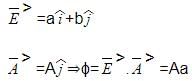
 secs
secs