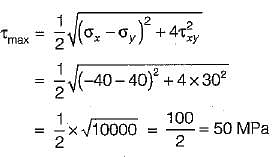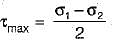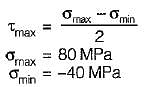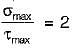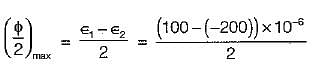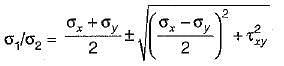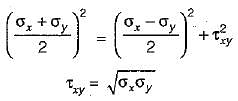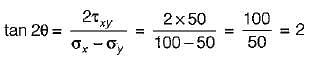Test: Principal Stress & Strain - 1 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Principal Stress & Strain - 1
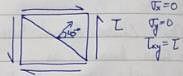
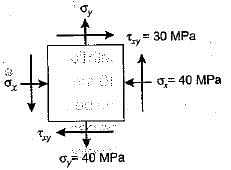
The state of stress at a point in a loaded member is shown in figure. The magnitude of maximum shear stress is

At a point in a strained body carrying two unequal unlike principal stresses p1 and p2 (p1 > p2), the maximum shear stress is given by
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The radius of Mohr’s circle of stress of a strained element is 20 N/mm2 and minor principal tensile stress is 10 N/mm2; The major principal stress is
The principal stresses σ1 , σ2 and σ3 at a point respectively are 80 MPa, 30 MPa and -40 MPa. The maximum shear stress is
Plane stress at a point in a body is defined by principal stress 3σ and σ. The ratio of the normal stress to the maximum shear stress on the plane of maximum shear stress is
A shaft subjected to torsion experiences a pure shear stress τ on the surface. The maximum principal stress on the surface which is at 45° to the axis will have a value
Principal strains at a point are 100 x 10-6 and -200 x 10-6. What is the maximum shear strain at the point?
In a plane stress problem there are normal tensile stresses σx and σy accompanied by shear stress τxy at a point along orthogonal Cartesian coordinates x and y respectively. If it is observed that the minimum principal stress on a certain plane is zero the
A point in a strained body is subjected to a tensile stress of 100 MPa on one plane and a tensile stress of 50 MPa on a plane at right angle to it. If these planes are carrying shear stresses of 50 MPa, then the principal stresses are inclined to the larger normal stress at an angle of
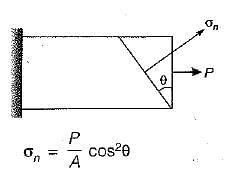
If the normal cross-section A of a member is subjected to a tensile force P, the resulting normal stress on an oblique plane inclined at angle θ to transverse plane will be