Test: Boundary Layer Theory - 1 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Boundary Layer Theory - 1
A fluid with kinematic viscosity v flows in laminar stage along a flat plate with free-stream velocity V. At a distance x from the leading edge, the Reynolds number of the flow is given by R = Vx/v. The thickness of the boundary layer at x will be proportional to
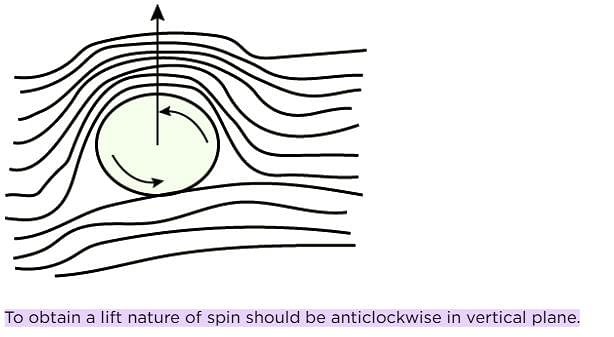
Magnus effect may be used advantageously in games such as cricket, tennis, table tennis and golf. In order to obtain a lift, i.e. a rising curve for the trajectory of the ball, from left to right, the nature of the spin to be given is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
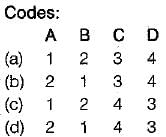
Match List - I with List - ll and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:



A thin smooth plate 1 m wide and 2 m long is towed through water at a velocity of 2 m/s. Assuming that boundary remains laminar, then drag on both sides of the plate is (kinematic viscosity = 10-6 m2/s)
For a turbulent boundary layer (under zero pressure gradient), the velocity profile is described by the one-fifth power law. What is the ratio of displacement thickness to boundary layer thickness?
The velocity distribution for flow over a plate is given by u = 0.5y - y2 where ‘u’ is the velocity in m/s at a distance ‘y’ meter above the plate. If the dynamic viscosity of the fluid is 0.9 N-s/m2, then what is the shear stress at 0.20 m from the boundary?
A very tiny sphere is settling down in a viscous liquid at Reynold’s number = 0.2. Its drag coefficient will be
According to Prandtl-Blassius relation, the thickness of boundary layer in turbulent flow is
where x = distance between leading edge of the body and the section where thickness of boundary layer is required.
Rex = Reynold’s number at a distance x from the leading edge.
In which of the following the friction drag is generally larger than pressure drag?


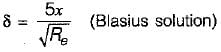
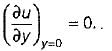

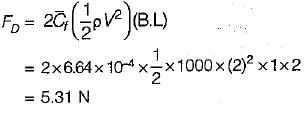
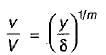
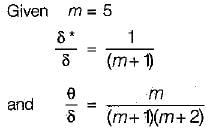
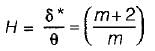
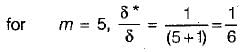
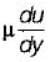 = μ (0.5 - 2y)
= μ (0.5 - 2y)














