Test: First Law of Thermodynamics - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: First Law of Thermodynamics - 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Key concept in analyzing the filling of an evacuated tank is
During a thermodynamic process, 84 kJ of heat flows into the system and the work done by the system is 32 kJ. The increase in internal energy of the system is
The specific heat at constant pressure for an ideal gas is given by
cp = 0.9 + (2.7 x 10-4) T (kJ/kgK)
Where T is in kelvin. The change in enthalpy for this ideal gas undergoing a process in which the temperature changes from 27°C to 127°C is most nearly.
A closed system undergoes a process 1-2 for which the values of Q1-2 and W1-2 are +20 kJ and +50 kJ respectively. If the system is returned to state 1 and Q2-1 is - 10 kJ what is the value of work W2-1
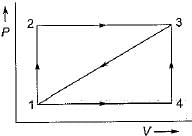
Given that along the path 1-2-3 a system absorbs 100 kJ as heat and does 60 kJ work while along the path 1 -4-3 it does 20 kJ work (see figure given). The heat absorbed during the cycle 1-4-3 is
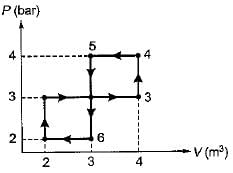
The network output for the cycle 1-2-3-4 -5-6-1 shown in figure is
In a reversible isothermal expansion process fluid expands from 10 bar and 2 m3 to 2 bar and 10 m3. During the process the heat supplied is at the rate of 100 kW. What is the rate of work done during the process
The state of an ideal gas is changed from (T1, P1) to (T2, P2) in a constant volume process. To calculate the change in enthalpy (Δh) ail of the following properties/variables are required.
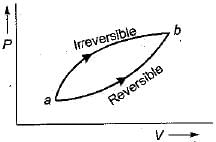
For the two paths as shown in the figure, one reversible and one irreversible, to change the state of the system from a to b.
The net work done for the closed system shown in the given pressure-volume diagram is
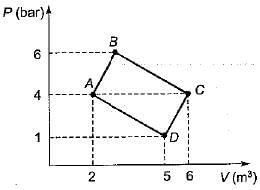
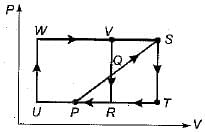
Two ideal heat engine cycles are represented in the given figure. Assume VQ = QR, PQ = QS and UP = PR= RT. If the work interaction for the rectangular cycle (WVRU) is 48 Nm, then the work interaction for the other cycle PST is
A mixture of gases expands from 0.03 m3 to 0.06 m3 at a constant pressure of 1 MPa and absorbs 84 kJ of heat during the process. The change in internal energy of the mixture is



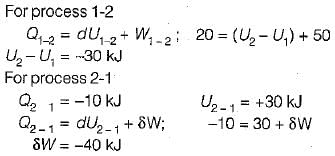
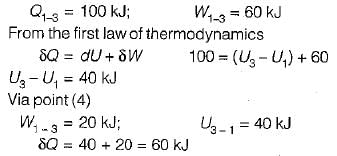
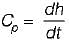 Calculation of Change in Enthalpy (Δh) in Constant Volume Process
Calculation of Change in Enthalpy (Δh) in Constant Volume Process















