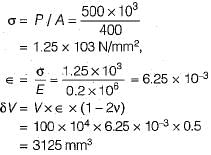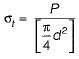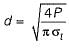Test: Design Against Static Load - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Design Against Static Load - 2
A steel bar 2.5 m long and 20 mm square is elongated by a load of 500 kN. If poisson’s ratio is 0.25, what is the increase in volume? Take E = 0.2 x 106 N/mm2.
The thickness of cotter is generally taken equal to
Where d is the diameter of two rods which are connected by the cotter joint?
Where d is the diameter of two rods which are connected by the cotter joint?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
For a cotter, the ratio of thickness to width is
Calculations for the diameter of the rod in cotter joint are made by considering failure of the rod in
Which of the following statement(s) is/are valid pertaining to a cotter joint?
1. cotter is a flat wedge like piece inserted through the members at right angles to their axes.
2. used for rigid fastening of two rods.
3. rods to be connected are subjected to tensile or compressive stresses along their axes.
4. not suitable for joining members under rotation.
The cotter is uniform in thickness but tapered in width on one side. The normal value of this taper is
A localized compressive stress at the area of contact between two members is known as
Which one of the following graph represents von- mises yield criterion
The piston rod and the cross head in a steam engine are usually connected by means of