Test: Introduction to 8085 & Its Functional Organisation - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Introduction to 8085 & Its Functional Organisation
A programme written in machine language is called the
The number of input pins of 8085 microprocessor are
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
In 8085 microprocessor the number of interrupts maskable and non-maskable are
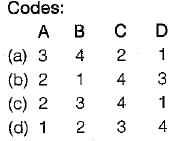
Match List-I with List-ll and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-1
A. Operating system
B. Locator
C. Editor
D. Debugger
List-ll
1. Allows user to examine the contents of registers and memory locations after each step of execution.
2. A program of collection of programs which are usually stored on discs.
3. A program which assigns specific memory addresses for the machine codes of the program to be loaded into the memory.
4. A program which allows user to write source program or text into RAM.
The interrupt pin TRAP of a 8085 microprocessor is
Consider the following statements:
1. A cross assembler runs on the microcomputer on which it produces machine codes.
2. A resident assembler runs on a computer other than that for which it produces object codes.
3. The program written in hexadecimal system List-i is converted into binary system by a program called Monitor program.
4. Macros are the assembler directive which are commands to the assembler itself.
Which of the above statements are correct?
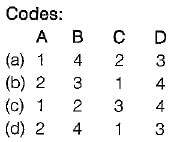
Match List-I with List-li and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
List-l
A. Compiler
B. Assembler
C. Interpreter
D. System Software
List-II
1. High-level language program into machine codes, statementwise.
2. High-level language program into machine language program.
3. Controls the overall operation of a computer. ,
4. Assembly language program into a machine language program.
Assertion (A): The writing of a program in assembly language is much easier and faster as compared to the writing of program in machine language.
Reason (R): An assembly language is a low- level language
A micro controller differs from a microprocessor in terms of
A microprocessor program written in assembly language is translated into machine language. The number of instructions in the machine language when compared with the number of instructions in assembly language is

















