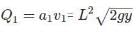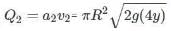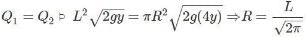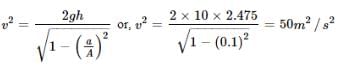JEE Previous Year Questions: Fluid Mechanics - JEE MCQ
17 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Previous Year Questions: Fluid Mechanics
A large open tank has two holes in the wall. One is a square hole of side L at a depth y from the top and the other is a circular hole of radius R at a depth 4y from the top. When the tank is completely filled with water, the quantities of water flowing out per second from both holes are the same. Then, R is equal to :
[JEE 2000 (Scr.)]
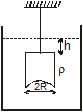
A hemispherical portion of radius R is removed from the bottom of a cylinder of radius R. The volume of the remaining cylinder is V and its mass is M. It is suspended by a string in a liquid of density r where it stays vertical. The upper surface of the cylinder is at a depth h below the liquid surface. The force on the bottom of the cylinder by the liquid is
[JEE 2001 (Scr.)]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
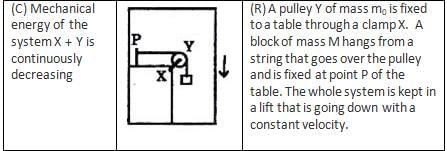
A wooden block, with a coin placed on its top, floats in water as shown in figure. The distances l and h are shown there. After some time the coin falls into the water. Then


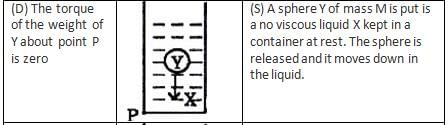
A uniform solid cylinder of density 0.8 gm/cm3 floats in equilibrium in a combination of two non mixing liquids A and b with its axis vertical. The densities of the liquids A and B are 0.7gm/cm3, and 1.2 g/cm3 respectively. The height of liquid A is hA = 1.2 cm. The length of the part of the cylinder immersed in liquid B is hB = 0.8 cm.
(a) Find the total force exerted by liquid A on the cylinder.
(b) Find h, the length of the part of the cylinder in air.
(c) The cylinder is depressed in such a way that its top surface is just below the upper surface of liquid A and is then released. Find the acceleration of the cylinder immediately after it is released.
[JEE 2002]
Consider a horizontally oriented syringe containing water located at a height of 1.25 m above the ground. The diameter of the plunger is 8 mm and the diameter of the nozzle is 2mm. The plunger is pushed with a constant speed of 0.25 m/s. Find the horizontal range of water stream on the ground.
Take g = 10 m/s2.
[JEE 2004]
Water is filled in a container upto height 3m. A small hole of area `a' is punched in the wall of the container at a height 52.5 cm from the bottom. The cross sectional area of the container is A. If then v2 is (where v is the velocity of water coming out of the hole)
[JEE 2005 (Scr.)]
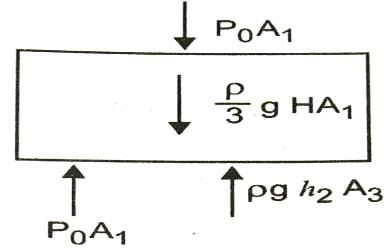
A wooden cylinder of diameter 4r, height h and density r/3 is kept on a hole of diameter 2r of a tank, filled with water of density r as shown in the figure. The height of the base of cylinder from the base of tank is H.
If level of liquid starts decreasing slowly when the level of liquid is at a height h1 above the cylinder, the block just starts moving up. Then, value of h1 is
[JEE 2006]
A wooden cylinder of diameter 4r, height h and density r/3 is kept on a hole of diameter 2r of a tank, filled with water of density r as shown in the figure. The height of the base of cylinder from the base of tank is H.
Let the cylinder is prevented from moving up, by applying a force and water level is further decreased. Then, height of water level (h2 in figure) for which the cylinder remains in original position without application of force is
[JEE 2006]
A wooden cylinder of diameter 4r, height h and density r/3 is kept on a hole of diameter 2r of a tank, filled with water of density r as shown in the figure. The height of the base of cylinder from the base of tank is H.
If height h2 of water level is further decreased, then
[JEE 2006]
Statement - 1 The stream of water flowing at high speed from a garden hose pipe tends to spread like a fountain when held vertically up, but tends to narrow down when held vertically down.
and
STATEMENT - 2 In any steady flow of an incompressible fluid, the volume flow rate of the fluid remains constant.
[JEE 2008]
A glass tube of uniform internal radius (r) has a valve separating the two identical ends. Initially, the valve is in a tightly closed position. End I has a hemispherical soap bubble of radius r. End 2 has sub-hemispherical soap bubble as shown in figure. Just after opening the valve.
[JEE 2008]
A small spherical monoatomic ideal gas double is trapped inside a liquid of density r, (see figure). Assume that the bubble does not exchange any heat with the liquid. The bubble contains n moles of gas. The temperature of the gas when the bubble is at the bottom is T0, the height of the liquid is H and the atmospheric pressure is P0 (Neglect surface tension).
[JEE 2008]
Figure :
As the bubble moves upwards, besides the buoyancy force the following forces are acting on it
A small spherical monoatomic ideal gas double is trapped inside a liquid of density r, (see figure). Assume that the bubble does not exchange any heat with the liquid. The bubble contains n moles of gas. The temperature of the gas when the bubble is at the bottom is T0, the height of the liquid is H and the atmospheric pressure is P0 (Neglect surface tension).
[JEE 2008]
Figure :
A small spherical monoatomic ideal gas double is trapped inside a liquid of density r, (see figure). Assume that the bubble does not exchange any heat with the liquid. The bubble contains n moles of gas. The temperature of the gas when the bubble is at the bottom is T0, the height of the liquid is H and the atmospheric pressure is P0 (Neglect surface tension).
[JEE 2008]
Figure :
The buoyancy force acting on the gas bubble is (Assume R is the universal gas constant)
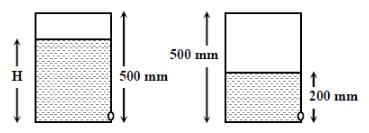
A cylindrical vessel of height 500 mm has an orifice (small hole) at its bottom. The orifice is initially closed and water is filled in it up to height H. Now the top is completely sealed with a cap and the orifice at the bottom is opened. Some water comes out from the orifice and the water level in the vessel becomes steady with height of water column being 200 mm. Find the fall in height (in mm) of water level due to opening of the orifice. [Take atmospheric pressure = 1.0 × 10 5 Nm-2 , density of water = 1000 kg m-3and g = 10 ms-2 . Neglect any effect of surface tension.] (Take temperature to be constant)
[JEE 2009]
Two solid spheres A and B of equal volumes but of different densities dA and dB are connected by a string. They are fully immersed in a fluid of density dF. They get arranged into an equilibrium state as shown in the figure with a tension in the string. The arrangement is possible only if
[JEE 2011]