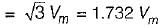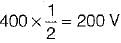Test: Phase Controlled Rectifiers- 2 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Phase Controlled Rectifiers- 2
Consider the following statements associated with single phase full converters:
1. Mid-point converter configuration is used in case the terminals on dc side have to be grounded.
2. The transformer rating in mid-point converter is double the load rating.
3. SCRs are subjected to a peak inverse voltage of 2 Vm in single phase mid-point converter.
4. Bridge converter is preferred over mid-point converter.
Which of these statements are correct?
1. Mid-point converter configuration is used in case the terminals on dc side have to be grounded.
2. The transformer rating in mid-point converter is double the load rating.
3. SCRs are subjected to a peak inverse voltage of 2 Vm in single phase mid-point converter.
4. Bridge converter is preferred over mid-point converter.
Assertion (A): The commutation overlap is more predominant is semiconverters than in full converters.
Reason (R): The commutation period in seconds, when outgoing and incoming SCRs are conducting, is known as the overlap period.
Reason (R): The commutation period in seconds, when outgoing and incoming SCRs are conducting, is known as the overlap period.
For a single-phase full converter having a full load current of I0 match List - I (Overlap angle) with List-ll (Output voltage) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists (Ls = source inductance):
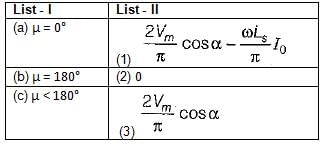
Codes:
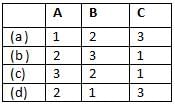

Codes:

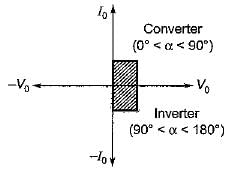
Which of the following converters can feed power in any of the four quadrants?
Consider the following statements:
1. In a full converter, direction of current cannot reverse.
2. Semi-converters are single quadrant converters.
3. A full converter can operate as a two-quadrant converter.
4. A full converter operates as a rectifier in first quadrant and as an inverter in the second quadrant.
5. In a full converter, direction of current cannot reverse but polarity of output voltage can be reversed.
Q. Which of the statements given above are correct?
AC-to-DC circulating current dual converters are operated with which of the following relationship between their triggering angles (α1 and α2)?
A single-phase half-wave controlled converter with resistive load is operated from a 120 V, 50 Hz supply. If the average output voltage is 25% of the maximum possible output voltage, the firing angle of the thyristor would be equal to
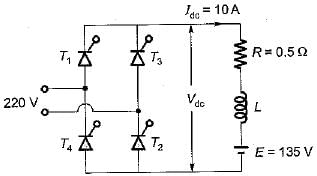
A single phase fully controlled thyristor bridge converter supplies a load consisting of R, L and E has shown in figure below. The inductance L in the circuit is so large that the output current may be considered to be virtually constant. The firing angle α is
Consider the following statements:
1. Fully-controlled and half controlled circuits both are capable of regeneration.
2. The higher the pulse number, the lower is the magnitude of ripple voltage and current in the load-circuit and the a.c. supply.
3. Bridge circuits and half-wave circuits both require same number of thyristors to carry the same current.
4. Half-wave circuits tend to be used for low-voltage, high-current use.Which of the statements given above is/are not correct?
In a 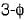 bridge converter the dc load current is 90 A, the commutating inductance per phase is 50 and the
bridge converter the dc load current is 90 A, the commutating inductance per phase is 50 and the 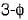 power supply is 2.3 kV, 50 Hz. The reduction in output voltage due to overlap is around
power supply is 2.3 kV, 50 Hz. The reduction in output voltage due to overlap is around
The holding current of SCRs in 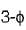 full-converter is 200 mA and the delay time is 2.5 p.sec. Converter is supplied from a star-connected 208 V, 50 Hz supply, has a load of R = 2 Ω L = 8 mH and the firing angle is 60°. The minimum width of gate pulse tp for L = 0 H is
full-converter is 200 mA and the delay time is 2.5 p.sec. Converter is supplied from a star-connected 208 V, 50 Hz supply, has a load of R = 2 Ω L = 8 mH and the firing angle is 60°. The minimum width of gate pulse tp for L = 0 H is
The nature of load current, l.e., whether load is continuous or discontinuous in controlled rectifiers
In a 3-phase full converter, the output voltage during overlap is equal to
The peak inverse voltage in ac to dc converter system is highest in
A transformer is having source voltage of 400 volt and turns ratio of 2:1. The transformer is centre-tapped. If the secondary is connected to single phase full-wave converter, PIV per SCR will be



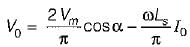

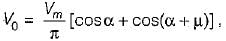
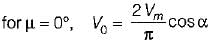
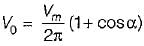
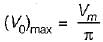
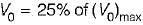
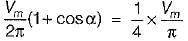
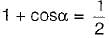
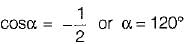
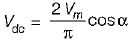
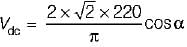
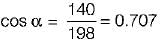
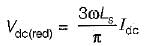
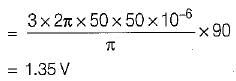
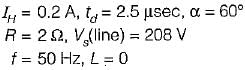
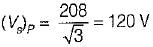
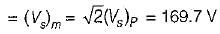
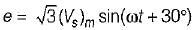
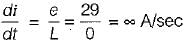
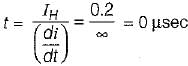
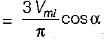
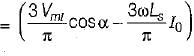
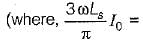 Average value of fall in output voltage due to overlap)
Average value of fall in output voltage due to overlap)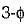 bridge converter =
bridge converter = 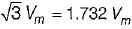
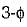 half wave converter
half wave converter