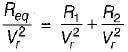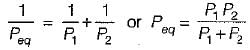Test: Basic & Electric Circuits- 2 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Basic & Electric Circuits- 2
A current of 3 A flows through a resistor of 20 ohms. The energy dissipated in the resistor per minute is
A long uniform coil of a inductance L henries and associated resistance R ohms is physically cut into two exact halves which are then rewound in parallel. The resistance and inductance of the combination are
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
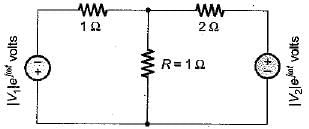
In the circuit shown, the power dissipated in the resistor R is 1 W when only source ‘1’ is present and ‘2’ is replaced by short circuit. The power dissipated in the same resistor R is 4 W when only source '2’ is present and '1' is replaced by a short circuit When both the sources ‘1’ and ‘2’ are present, the power dissipated in R will be

If v, w, q stand for voltage, energy and charge, then v can be expressed as:
In the figure shown below, φ = power-factor angle, W = watts, VA = volt ampere and VAr = volt-ampere .reactive for an ac circuit. The correct figure is
A circuit possesses resistance R and inductive reactance XL in series, its susceptance is given by
If V = a + jb and I = c + jd, then the power is given by
A 230 V, 100 W bulb has resistance RA and a 230 V, 200 W bulb has resistance RB. Here,
1. RA > RB
2. RB > RA
3. RA = 2 RB
4. RB = 2 RA
5. RA = 4 RB
From these, the correct answer is
The voltage phapor of a circuit is 10∠15° V and the current phasor is 2∠- 45° A. The active and the reactive powers in the circuit are
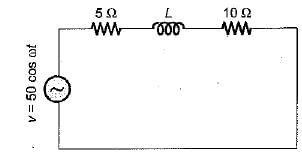
In the circuit shown below, if the power consumed by the 5 Ω resistor is 10 W, then power factor or the circuit will be
The minimum requirements for causing flow of current are.
For a fixed supply voltage, the current flowing through a conductor will increase when its
Two registors R1, and R2 give combined resistance of 4.5 Ω when in series and 1 Ω when in parallel. The resistances are
Which of the following is not equivalent to watts?
Two heaters, rated at 1000 W, 250 V each are connected in series across a 250 V, 50 Hz ac mains. The total power drawn from the supply would be
A 100 watt light bulb burns on an average of 10 hours a day for one week. The weekly consumption of energy will be
Assertion (A): The direction of flow of conventional current is taken opposite to that of electrons.
Reason (R): Electrons have negative charge.
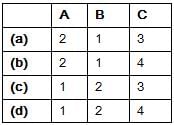
Match List-I (Materials) with List-lI (Range of resistivity) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I
A. Conducting materials
B. Semiconductor materials
C. insulating material
List-II
1. 100 to 102 Ω-m
2. 10-8 to 10-6 Ω-m
3. 1012to 1018 Ω-m
4. 1020 to 1030 Ω-m
Codes:
A constant current source supplies a current of 200 mA to a load of 2 kΩ When the load is changed to 100 Ω, the load current is


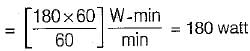
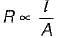
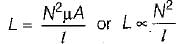
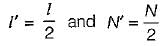
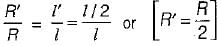

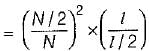
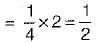
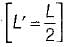
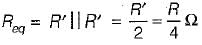
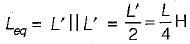
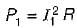
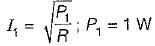
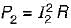
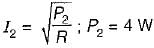
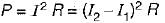
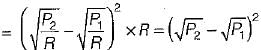
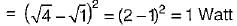
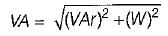
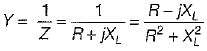
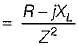
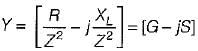
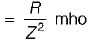
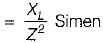
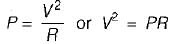

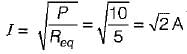
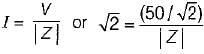
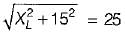
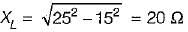
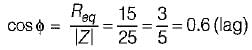
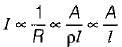
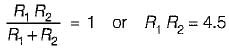
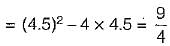
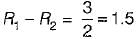 ...(ii)
...(ii)