Laxmikanth Test: Making of the Constitution- 1 - UPSC MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Laxmikanth Test: Making of the Constitution- 1
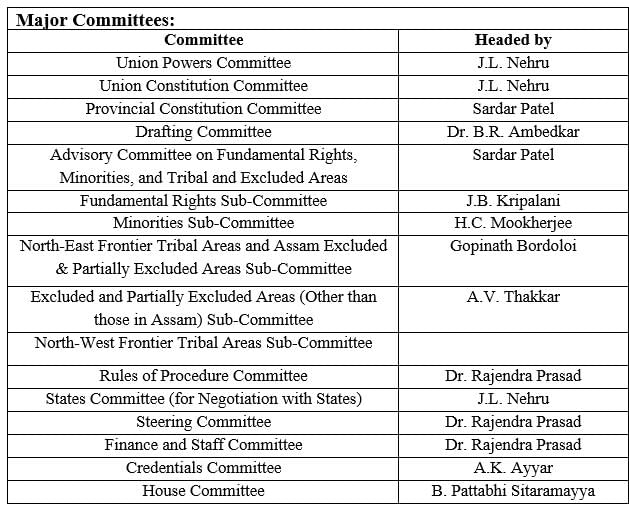
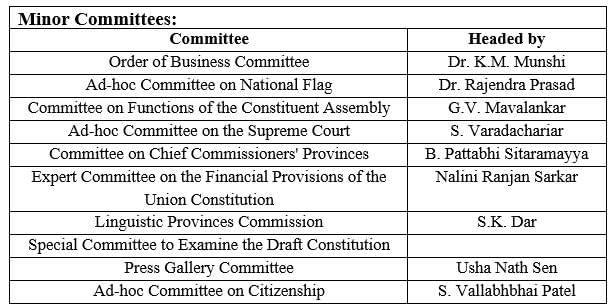
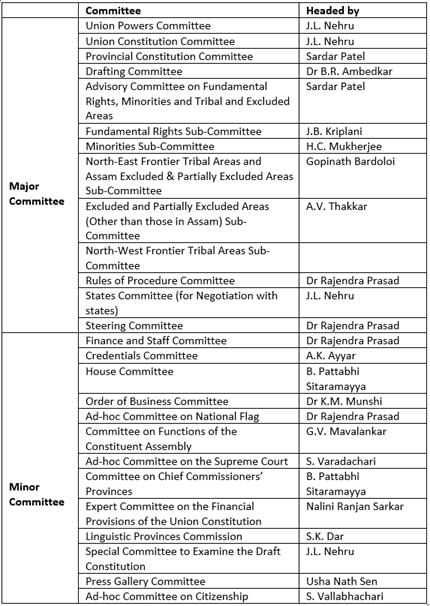
Which of the following committee was not a Major Committee under the Constituent Assembly?
1. Committee on the Functions of the Constituent Assembly
2. Ad-hoc Committee on Citizenship
3. Provincial Constiution Committee
4. Committee for North-East Frontier Tribal Areas
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
1. Committee on the Functions of the Constituent Assembly
2. Ad-hoc Committee on Citizenship
3. Provincial Constiution Committee
4. Committee for North-East Frontier Tribal Areas
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
What was the total number of members in the Constituent Assembly, including representatives of the Indian States?
Consider the following provisions of the Constitution of India:
1. Citizenship
2. Electoral Process in India
3. Fundamental Duties
4. Fundamental Rights
5. Formation of States and Union Territories
Which of the above provisions came into existence on November 26, 1949?
1. Citizenship
2. Electoral Process in India
3. Fundamental Duties
4. Fundamental Rights
5. Formation of States and Union Territories
Which of the above provisions came into existence on November 26, 1949?
Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Indian Constitution?
1. The original constitution of India was handwritten by Prem Behari Narain Raizada.
2. It was written in a flowing italic style.
3. The calligraphy of the Hindi version of the original constitution was done by Vasant Krishan Vaidya.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Consider the following statements regarding the Constituent Assembly of India:
1. The Constituent Assembly first convened on December 9, 1946, under the chairmanship of Dr. Sachidanand Sinha.
2. Dr. Rajendra Prasad was elected as the permanent Chairman of the Constituent Assembly on December 11, 1946.
3. The Muslim League actively participated in the proceedings of the Constituent Assembly from the beginning.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding the Constitution of India adopted on November 26, 1949:
1. The preamble was not the part of the original draft of the Indian Constitution and was inserted by the 1st Constitutional Amendment Act.
2. It had 395 articles, and 8 schedules.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following provisions of the 'Objective Resolution' passed by the Constituent Assembly on 22nd January 1947
- Adequate safeguards shall be provided for minorities, backward and tribal areas, and depressed and other backward classes.
- All power and authority of Sovereign Independent India, its constituent parts and organs of government, are derived from the head of state.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements:
1. January 26 was specifically chosen as the ‘date of commencement’ of the Constitution because on this day in 1930 that Poorna Swaraj day was celebrated.
2. With the commencement of the Constitution, the Indian Independence Act of 1947 and the Abolition of Privy Council Jurisdiction Act (1949) were repealed.
Which of the following statements above is/are not correct?
Consider the following pairs of Committees under the Constituent Assembly and their Chairman:
1. States Committee (Committee for Negotiating with States) - Jawaharlal Nehru
2. Provincial Constitution Committee - Sardar Patel
3. Drafting Committee - Dr B.R. Ambedkar
4. Special Committee to Examine the Draft Constitution- Dr Rajendra Prasad
Which of the above pairs are matched correctly?
The constituent assembly was constituted under the scheme formulated by the Cabinet Mission Plan. Regarding the plan consider the following statements:
1. Allocation of seats for each province and princely state to be in proportion to their respective population
2. Representatives to be elected through proportional representation using a single transferable vote.
3. The representatives of the princely state were to be nominated by the heads of princely states.
4. Out of 300 seats allotted to British India, 292 members were to be drawn from the governor’s provinces and 8 from the chief commissioners’ provinces.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Arrange the following events in their correct chronological order:
1. Ratification of India’s membership of the Commonwealth
2. Adoption of National Flag
3. Adoption of National Anthem
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
As a member of the constituent Assembly, Sardar Patel did not lead which of the following committees?
1. Committee on Tribal and Excluded Areas
2. Committee on Minority Affairs
3. Committee on Fundamental Rights
4. Committee on Devolution of Power to the Union
Consider the following statements regarding the drafting and commencement of the Indian Constitution:
1. The Drafting Committee of the Constituent Assembly was set up on August 29, 1947.
2. The Constitution of India came into full effect on 26 November 1949.
3. The original Constitution of India contained 395 Articles and eight Schedules.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements:
1. Constituent Assembly adopted the national flag on July 22, 1947.
2. Constituent Assembly adopted the national anthem on January 24, 1950.
3. Constituent Assembly elected Dr Rajendra Prasad as the first President of India on January 24, 1950.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements about the objectives laid down by the Constituent Assembly:
1. India was to be an independent sovereign republic including both British India and the princely states.
2. All authority and powers of the States were to be derived from the people, guaranteeing them freedom of economic and political justice, equality of status, and equality before the law.
3. Only the princely states were to be granted full autonomy and residuary powers.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Which of the following provision is not borrowed by the Indian Constitution from the American Constitution?
Consider the following pairs:
1. Written Constitution - British Constitution
2. Federal System - American Constitution
3. Residuary Powers with Centre - Irish Constitution
4. Supreme Court - American Constitution
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
Consider the following statements:
1. Prem Behari Narain Raizada was the calligrapher of the Indian Constitution.
2. The calligraphy of the Hindi version of the original constitution was done by Beohar Rammanohar Sinha.
3. Nand Lal Bose illuminated, beautified and ornamented the original Constituion.
Which of the statement given above is/are not correct?
The Constituent Assembly was constituted in November 1946 under the scheme formulated by the Cabinet Mission Plan. What was/were the salient features of the assembly?
1. The assembly had representation from both British India and princely states.
2. The system of proportional representation was adopted.
3. There was no communal representation in the assembly.
4. The Assembly included important ministers of the British Cabinet as ex -officio members.
Select the correct answer using the codes below:
The first draft of the Constitution of India was prepared in _____by the Advisory Branch of the Constituent Assembly.
How were the seats in each province distributed among the main communities for representation in the Constituent Assembly?
Consider the following pairs:
1. Fundamental Duties - American Constitution
2. Privileges of Members of Parliament - British Constitution
3. Federal Structure- Canadian Constitution
4. Directive Principles of State Policy - Soviet Constitution
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: India is known as a "Union of States," inspired by the Constitution of Canada.
Statement-II: The Directive Principles of State Policy in India are borrowed from the Constitution of USA.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
Arrange the following countries based on the time taken by the framers of the Constitution of those countries.
1. America
2. Australia
3. India
4. South Africa
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: The Constitution of India is a document adapted to Indian conditions and environment.
Statement-II: Jawaharlal Nehru emphasized the importance of establishing a government system acceptable to the people.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?