JEE Advanced Test- 1 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Advanced Test- 1
A simple pendulum is oscillating in a vertical plane. If resultant acceleration of bob of mass m at a point A is in horizontal direction, find the tangential force at this point in terms of tension T and mg.
Hailstones falling vertically with a speed of 10 m/s, hit the wind screen (wind screen makes an angle 30° with the horizontal) of a moving car and rebound elastically. The velocity of the car if the driver finds the hailstones rebound vertically after striking is :
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
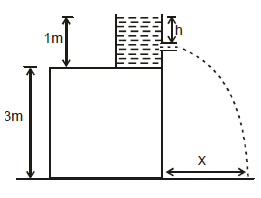
A water tank stands on the roof of a building as shown. Then the value of 'h' for which the distance covered by the water 'x' is greatest is -
 a
a
A U-tube of base length “l” filled with same volume of two liquids of densities ρ and 2ρ is moving with an acceleration “a” on the horizontal plane. If the height difference between the two surfaces (open to atmosphere) becomes zero, then the height h is given by:
A particle A of mass 10/7 kg is moving in the positive direction of x. Its initial position is x = 0 & initial velocity is 1 m/s. The velocity at x = 10 is: (use the graph given)
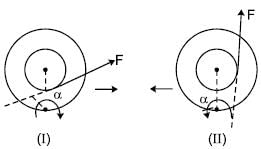
The string of a step rolling wheel is pulled by applying force F with different lines of action in two situations as shown. The wheel starts rolling without slipping due to application of the force :
Two particles start together from a point O and slide down straight smooth wires inclined at 30º & 60º to the vertical & in the same vertical plane as in figure. The relative acceleration of second with respect to first will be (in magnitude & direction) as :
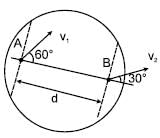
Two points A & B on a disc have velocities v1 & v2 at some moment. Their directions make angles 60° and 30° respectively with the line of separation as shown in figure. The angular velocity of disc is :
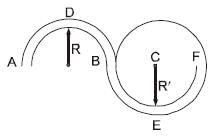
In the figure shown ADB & BEF are two fixed circular paths. A block of mass m enters in the tube ADB through point A with minimum velocity to reach point B. From there it moves on another circular path of radius R'. There it is just able to complete the circle.
The displacement of a body from a reference point is given by, (√x) = 2t-3 where ' x ' is in metres and t in seconds. This shows that the body :
If the resultant force on a system of particles is non-zero, then :
A painter is applying force himself to raise him and the box with an cceleration of 5 m/s2 by a massless rope and pulley arrangement as shown in figure. Mass of painter is 100 kg and that of box is 50 kg. If g = 10 m/s2, then :
Statement-1 : For a disc undergoing fixed axis rotation, the magnitude of angle between velocity and acceleration vector of any moving point on disc at a particular instant of time are same.
Statement-2 : Each moving point on a disc undergoing fixed axis rotation has same angular speed and same angular acceleration at an instant of time. Hence the ratio of magnitude of tangential acceleration and magnitude of centripetal acceleration is same for all moving points at an instant of time.
Statement-1 : The equation of distance travelled by a particle moving in a straight line with constant acceleration in nth second is where letters have usual meaning, is dimensionally incorrect.
Statement-2 : For every equation relating physical quantities to be true, it must have dimensional homogenity.
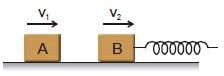
Figure shows block A of mass 0.2 kg sliding to the right over a frictionless elevated surface at a speed of 10 m/s. The block undergoes a collision with stationary block B, which is connected to a nondeformed spring of spring constant 1000 Nm–1. The coefficient of restitution between the blocks is 0.5. After the collision, block B oscillates in SHM with a period of 0.2 s, and block A slides off the left end of the elevated surface, landing a distance 'd' from the base of that surface after falling height 5m. (use π2 = 10; g = 10 m/s2). Assume that the spring does not affect the collision.
Mass of the block B is
Figure shows block A of mass 0.2 kg sliding to the right over a frictionless elevated surface at a speed of 10 m/s. The block undergoes a collision with stationary block B, which is connected to a nondeformed spring of spring constant 1000 Nm–1. The coefficient of restitution between the blocks is 0.5. After the collision, block B oscillates in SHM with a period of 0.2 s, and block A slides off the left end of the elevated surface, landing a distance 'd' from the base of that surface after falling height 5m. (use π2 = 10; g = 10 m/s2) Assume that the spring does not affect the collision.
Amplitude of the SHM as being executed by block B-spring system, is -
Figure shows block A of mass 0.2 kg sliding to the right over a frictionless elevated surface at a speed of 10 m/s. The block undergoes a collision with stationary block B, which is connected to a nondeformed spring of spring constant 1000 Nm–1. The coefficient of restitution between the blocks is 0.5. After the collision, block B oscillates in SHM with a period of 0.2 s, and block A slides off the left end of the elevated surface, landing a distance 'd' from the base of that surface after falling height 5m. (use π2 = 10; g = 10 m/s2) Assume that the spring does not affect the collision.
The distance 'd' will be equal to -
Matrix Match Type
This section contains 1 questions. Each question has four statements (A, B, C and D) given in Column-I and five statements (p,q,r, s and t) in Column-II. Any given statement in Column-I can have correct matching with ONE OR MORE statement(s) in Column-II. The answers to these questions have to be appropriately marked as illustrated in the following example. If the correct matches are A-p, A-r, B-p, B-s, C-r, C-s, D-q and D-t then the answer should be written as : A→ p,r ; B→ p, s ; C → r, s ; D → q, t
Q. A uniform disc of mass M and radius R lies on a fixed rough horizontal surface at time t = 0. Initial angular velocity ωo of each disc (magnitude and sense of rotation) and horizontal velocity v0 of centre of mass is shown for each situation of column-I. Match each situation in column-I with the results given in column-II.


Two particles are projected simultaneously with the same speed vv in the same vertical plane with angles of elevation θ, and 2θ, where θ<45∘. At what time will velocities be parallel?
A man can swim in still water with a speed of 3 m/s. x and y axis are drawn along and normal to the bank of river flowing to right with a speed of 1 m/s. The man starts swimming from origin O at t = 0 second. Assume size of man to be negligible. Locus of all the possible points where man can reach at t = 1 sec. is (x–a)2 + y2 = c2 Find value of ac2.
In the figure shown a small block ‘B’ of mass ‘m’ is released from the top of a smooth movable wedge ‘A’ of the same mass ‘m’. ‘B’ ascends another movable smooth wedge ‘C’ of the same mass. Neglecting friction any where the maximum height attained by ‘B’ on ‘C’ is h/2x Find the value of x .
A cylinder rotating at an angular speed of 50 rev/s is brought in contact with an identical stationary cylinder. Because of the kinetic friction, torques act on the two cylinders, accelerating the stationary one and decelerating the moving one. If the common magnitude of the acceleration and deceleration be one revolution per second square, how long will it take before the two cylinders have equal angular speed ?
The volume occupied by 2.0 mole of N2 at 200K and 8.21 atm pressure, if is
If 10 gram of V2O5 is dissolved in acid and is reduced to V2+ by zinc metal, how many mole of I2 could be reduced by the resulting solution if it is further oxidised to VO2+ ions ?
[Assume no change in state of Zn2+ions] (V = 51, O = 16, I = 127) :
0.5 mole each of two ideal gas A(Cv = 3/2 R) and B(Cv = 5/2 R) are taken in a container and expanded reversibley and adiabatically from V = 1 litre to V = 4 litre starting from initial temperature t = 300K. ΔH for the process (in cal/mol) is
When a weak acid is titrated against a strong base. The pH of solution keeps on changing with amount of base added. In this titration there is a formation of buffer also. If the buffer capacity (here defined as the volume of base of a particular concentration added per unit change in pH), is plotted against volume of base added for titration of 25 ml, 0.1 M HA (weak acid) solution with 0.1 M strong base solution, then the most appropriate curve will be :
One mole of an ideal monoatomic gas expands isothermally against constant external pressure of 1 atm from initial volume of 1L to a state where its final pressure becomes equal to external pressure. If initial temperature of gas is 300 K then total entropy change of system in the above process is :
[R = 0.082 L atm mol–1 K–1 = 8.3 J mol–1K–1].
An electron in a hydrogen like atom makes transition from a state in which its de-Broglie wavelength is λ1 to a state where its de-Broglie wavelength is λ2 then wavelength of photon (λ) generated will be : where m is mass of the electron, c is speed of light in vaccum.
Given
Find out the negative of logarithm of the solubility of solid Zn(OH)2 at 25°C ,at pH=6.Consider Zn(OH)2 makes saturated solution at 25°C.
The curve of pressure volume (PV) against pressure (P) of the gas at a particular temperature is as shown, according to the graph which of the following is / are incorrect (in the low pressure region):


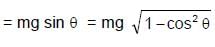
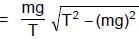
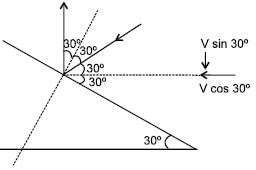
 , since rain fall vertically down.
, since rain fall vertically down.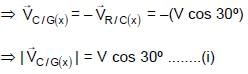
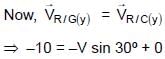
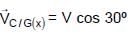
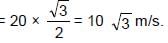
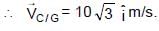
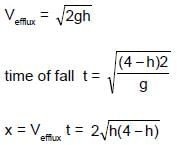
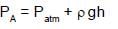
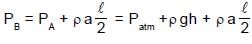
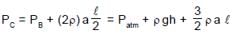 .......(1)
.......(1)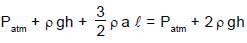
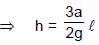
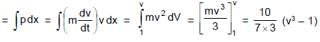
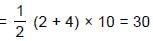
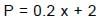
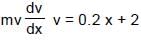
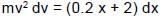
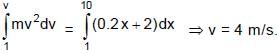
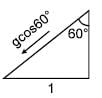
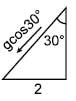
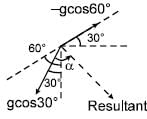
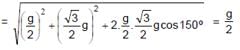
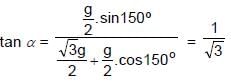 α = 30°
α = 30°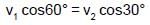
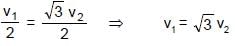
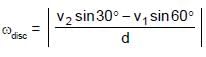
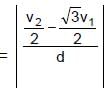
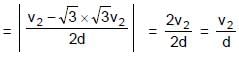
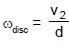
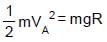
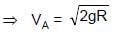
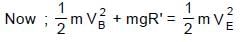
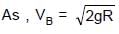
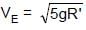
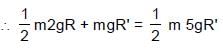
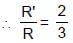
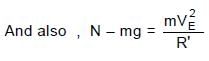
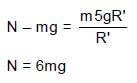
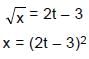
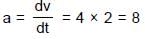
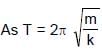
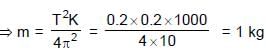
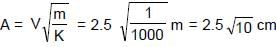
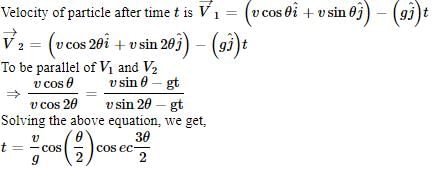
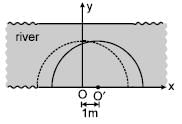
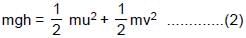
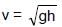 .......(3)
.......(3)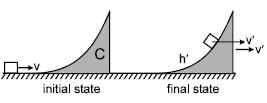
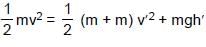 ......... (4)
......... (4)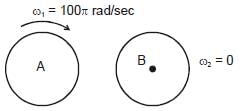
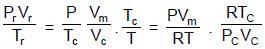
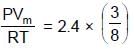
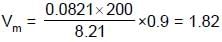
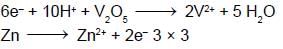
 ....(1)
....(1)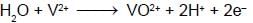
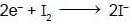
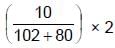 moles of I2 will be reduced by given amount of V2O5 = 0.11 moles of I2
moles of I2 will be reduced by given amount of V2O5 = 0.11 moles of I2 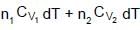
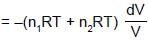
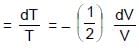
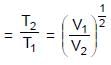
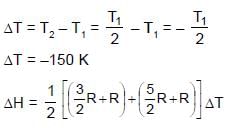
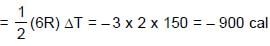
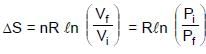

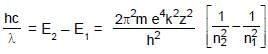
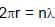
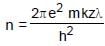
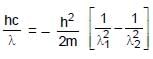
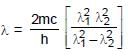
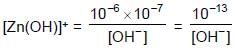
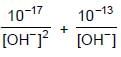 + 10-6 + 10-3 [OH-] + 10-2 [OH-]2
+ 10-6 + 10-3 [OH-] + 10-2 [OH-]2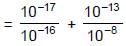 + 10-6 + 10-3 x 10-8 = 10-18 = 10-1 + 10-5 + 10-6 + 10-11 = 10-1
+ 10-6 + 10-3 x 10-8 = 10-18 = 10-1 + 10-5 + 10-6 + 10-11 = 10-1