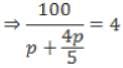SNAP Mock Test - 5 (New Pattern) Included RC's - CAT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - SNAP Mock Test - 5 (New Pattern) Included RC's
A passage is followed by questions pertaining to the passage. Read the passage and answer the questions. Choose the most appropriate answer.
Meteorological seasons are reckoned by temperature, with summer being the hottest quarter of the year and winter the coldest quarter of the year. Using this reckoning, the Roman calendar began the year and the spring season on the first of March, with each season occupying three months. In 1780 the Societas Meteorologica Palatina, an early international organization for meteorology, defined seasons as groupings of three whole months. Ever since, professional meteorologists all over the world have used this definition. So, in meteorology for the Northern hemisphere: spring begins on 1 March, summer on 1 June, autumn on 1 September, and winter on 1 December.
Ecologically speaking, a season is a period of the year in which only certain types of floral and animal events happen (e.g.: flowers bloom—spring; hedgehogs hibernate—winter). So, if we can observe a change in daily floral/animal events, the season is changing.
Traditional seasons are reckoned by insolation, with summer being the quarter of the year with the greatest insolation and winter the quarter with the least. In traditional reckoning, the seasons begin at the cross-quarter days. The solstices and equinoxes are the midpoints of these seasons.
In Australia, the traditional aboriginal people defined the seasons by what was happening to the plants, animals and weather around them. This led to each separate tribal group having different seasons, some with up to eight seasons each year. However, most modern Aboriginal Australians follow either four or six meteorological seasons, as do non-Aboriginal Australians.
In India, and in the Hindu calendar, there are six seasons or Ritu: Hemant (pre-winter), Shishira (Winter), Vasanta (Spring), Greeshma (Summer), Varsha (Rainy) and Sharad (Autumn).
Q. In the context of this passage, which of the following options best describes the meaning of ‘insolation’?
Meteorological seasons are reckoned by temperature, with summer being the hottest quarter of the year and winter the coldest quarter of the year. Using this reckoning, the Roman calendar began the year and the spring season on the first of March, with each season occupying three months. In 1780 the Societas Meteorologica Palatina, an early international organization for meteorology, defined seasons as groupings of three whole months. Ever since, professional meteorologists all over the world have used this definition. So, in meteorology for the Northern hemisphere: spring begins on 1 March, summer on 1 June, autumn on 1 September, and winter on 1 December.
Ecologically speaking, a season is a period of the year in which only certain types of floral and animal events happen (e.g.: flowers bloom—spring; hedgehogs hibernate—winter). So, if we can observe a change in daily floral/animal events, the season is changing.
Traditional seasons are reckoned by insolation, with summer being the quarter of the year with the greatest insolation and winter the quarter with the least. In traditional reckoning, the seasons begin at the cross-quarter days. The solstices and equinoxes are the midpoints of these seasons.
In Australia, the traditional aboriginal people defined the seasons by what was happening to the plants, animals and weather around them. This led to each separate tribal group having different seasons, some with up to eight seasons each year. However, most modern Aboriginal Australians follow either four or six meteorological seasons, as do non-Aboriginal Australians.
In India, and in the Hindu calendar, there are six seasons or Ritu: Hemant (pre-winter), Shishira (Winter), Vasanta (Spring), Greeshma (Summer), Varsha (Rainy) and Sharad (Autumn).
A passage is followed by questions pertaining to the passage. Read the passage and answer the questions. Choose the most appropriate answer.
Meteorological seasons are reckoned by temperature, with summer being the hottest quarter of the year and winter the coldest quarter of the year. Using this reckoning, the Roman calendar began the year and the spring season on the first of March, with each season occupying three months. In 1780 the Societas Meteorologica Palatina, an early international organization for meteorology, defined seasons as groupings of three whole months. Ever since, professional meteorologists all over the world have used this definition. So, in meteorology for the Northern hemisphere: spring begins on 1 March, summer on 1 June, autumn on 1 September, and winter on 1 December.
Ecologically speaking, a season is a period of the year in which only certain types of floral and animal events happen (e.g.: flowers bloom—spring; hedgehogs hibernate—winter). So, if we can observe a change in daily floral/animal events, the season is changing.
Traditional seasons are reckoned by insolation, with summer being the quarter of the year with the greatest insolation and winter the quarter with the least. In traditional reckoning, the seasons begin at the cross-quarter days. The solstices and equinoxes are the midpoints of these seasons.
In Australia, the traditional aboriginal people defined the seasons by what was happening to the plants, animals and weather around them. This led to each separate tribal group having different seasons, some with up to eight seasons each year. However, most modern Aboriginal Australians follow either four or six meteorological seasons, as do non-Aboriginal Australians.
In India, and in the Hindu calendar, there are six seasons or Ritu: Hemant (pre-winter), Shishira (Winter), Vasanta (Spring), Greeshma (Summer), Varsha (Rainy) and Sharad (Autumn).
Q. In the context of this passage, which of the following options best describes the meaning of ‘reckon’?
Ecologically speaking, a season is a period of the year in which only certain types of floral and animal events happen (e.g.: flowers bloom—spring; hedgehogs hibernate—winter). So, if we can observe a change in daily floral/animal events, the season is changing.
Traditional seasons are reckoned by insolation, with summer being the quarter of the year with the greatest insolation and winter the quarter with the least. In traditional reckoning, the seasons begin at the cross-quarter days. The solstices and equinoxes are the midpoints of these seasons.
In Australia, the traditional aboriginal people defined the seasons by what was happening to the plants, animals and weather around them. This led to each separate tribal group having different seasons, some with up to eight seasons each year. However, most modern Aboriginal Australians follow either four or six meteorological seasons, as do non-Aboriginal Australians.
In India, and in the Hindu calendar, there are six seasons or Ritu: Hemant (pre-winter), Shishira (Winter), Vasanta (Spring), Greeshma (Summer), Varsha (Rainy) and Sharad (Autumn).
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A passage is followed by questions pertaining to the passage. Read the passage and answer the questions. Choose the most appropriate answer.
Meteorological seasons are reckoned by temperature, with summer being the hottest quarter of the year and winter the coldest quarter of the year. Using this reckoning, the Roman calendar began the year and the spring season on the first of March, with each season occupying three months. In 1780 the Societas Meteorologica Palatina, an early international organization for meteorology, defined seasons as groupings of three whole months. Ever since, professional meteorologists all over the world have used this definition. So, in meteorology for the Northern hemisphere: spring begins on 1 March, summer on 1 June, autumn on 1 September, and winter on 1 December.
Ecologically speaking, a season is a period of the year in which only certain types of floral and animal events happen (e.g.: flowers bloom—spring; hedgehogs hibernate—winter). So, if we can observe a change in daily floral/animal events, the season is changing.
Traditional seasons are reckoned by insolation, with summer being the quarter of the year with the greatest insolation and winter the quarter with the least. In traditional reckoning, the seasons begin at the cross-quarter days. The solstices and equinoxes are the midpoints of these seasons.
In Australia, the traditional aboriginal people defined the seasons by what was happening to the plants, animals and weather around them. This led to each separate tribal group having different seasons, some with up to eight seasons each year. However, most modern Aboriginal Australians follow either four or six meteorological seasons, as do non-Aboriginal Australians.
In India, and in the Hindu calendar, there are six seasons or Ritu: Hemant (pre-winter), Shishira (Winter), Vasanta (Spring), Greeshma (Summer), Varsha (Rainy) and Sharad (Autumn).
Q. Based on the passage, we can infer all the statements, except:
Meteorological seasons are reckoned by temperature, with summer being the hottest quarter of the year and winter the coldest quarter of the year. Using this reckoning, the Roman calendar began the year and the spring season on the first of March, with each season occupying three months. In 1780 the Societas Meteorologica Palatina, an early international organization for meteorology, defined seasons as groupings of three whole months. Ever since, professional meteorologists all over the world have used this definition. So, in meteorology for the Northern hemisphere: spring begins on 1 March, summer on 1 June, autumn on 1 September, and winter on 1 December.
Ecologically speaking, a season is a period of the year in which only certain types of floral and animal events happen (e.g.: flowers bloom—spring; hedgehogs hibernate—winter). So, if we can observe a change in daily floral/animal events, the season is changing.
Traditional seasons are reckoned by insolation, with summer being the quarter of the year with the greatest insolation and winter the quarter with the least. In traditional reckoning, the seasons begin at the cross-quarter days. The solstices and equinoxes are the midpoints of these seasons.
In Australia, the traditional aboriginal people defined the seasons by what was happening to the plants, animals and weather around them. This led to each separate tribal group having different seasons, some with up to eight seasons each year. However, most modern Aboriginal Australians follow either four or six meteorological seasons, as do non-Aboriginal Australians.
In India, and in the Hindu calendar, there are six seasons or Ritu: Hemant (pre-winter), Shishira (Winter), Vasanta (Spring), Greeshma (Summer), Varsha (Rainy) and Sharad (Autumn).
A passage is followed by questions pertaining to the passage. Read the passage and answer the questions. Choose the most appropriate answer.
Meteorological seasons are reckoned by temperature, with summer being the hottest quarter of the year and winter the coldest quarter of the year. Using this reckoning, the Roman calendar began the year and the spring season on the first of March, with each season occupying three months. In 1780 the Societas Meteorologica Palatina, an early international organization for meteorology, defined seasons as groupings of three whole months. Ever since, professional meteorologists all over the world have used this definition. So, in meteorology for the Northern hemisphere: spring begins on 1 March, summer on 1 June, autumn on 1 September, and winter on 1 December.
Ecologically speaking, a season is a period of the year in which only certain types of floral and animal events happen (e.g.: flowers bloom—spring; hedgehogs hibernate—winter). So, if we can observe a change in daily floral/animal events, the season is changing.
Traditional seasons are reckoned by insolation, with summer being the quarter of the year with the greatest insolation and winter the quarter with the least. In traditional reckoning, the seasons begin at the cross-quarter days. The solstices and equinoxes are the midpoints of these seasons.
In Australia, the traditional aboriginal people defined the seasons by what was happening to the plants, animals and weather around them. This led to each separate tribal group having different seasons, some with up to eight seasons each year. However, most modern Aboriginal Australians follow either four or six meteorological seasons, as do non-Aboriginal Australians.
In India, and in the Hindu calendar, there are six seasons or Ritu: Hemant (pre-winter), Shishira (Winter), Vasanta (Spring), Greeshma (Summer), Varsha (Rainy) and Sharad (Autumn).
Q. According to the passage:
In the following sentences one word or phrase has been used incorrectly. Choose the word that must be changed or modified or deleted to make the sentence correct. There are sentences without any errors too.
There are fairly stringent conditions attached from the provision of affordable housing in the village.
Select the most OPPOSITE of the given word from the given choices.
LACUNA
Fill in the blanks with the most appropriate pair of words from the given options.
Around the table reigned that noisy ________ which usually prevails at such a time among people sufficiently free from the demands of social position not to feel the ________ of etiquette.
Choose the correct option.
ICONOCLAST : TRADITION
Choose the correct spelling from the options given below.
To convert to another religion or belief system.
Choose the appropriate option from among the ones given below
Which of the following sentences does not use a pleonasm?
The following question consists of a set of labelled sentences. These sentences, when properly sequenced, form a coherent paragraph. Choose the most logical order of sentences from the options.
A. Apart from their post-war singles, all their motorcycles had used this distinctive layout until the early 1980s.
B. Bayerische Motoren Werke started building motorcycle engines and then motorcycles after World War I.
C. Many Bayerische Motoren Werke Motorcycles are still produced to this pattern, which is designated the “R series”.
D. These had a “boxer twin” engine, in which an air-cooled cylinder protrudes into the air-flow from each side of the machine.
E. Their first notable motorcycle, after the failed Helios and Flink, was the “R32” in 1923.
Match the part of speech to their usage
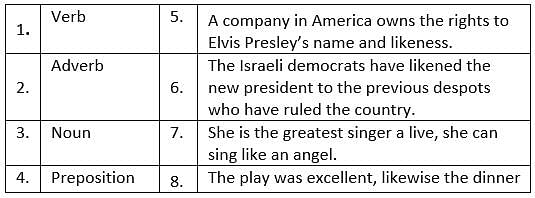
Identify the CORRECT sentence or sentences.
A. If we redistribute wealth from the better to worse, we can help feed the hungry people.
B. Every morning I ate the burnt breakfast, drank the foul coffee and spoke to nobody.
C. Critics claim that the Indian government unfairly favors the IITs when educational dollars are doled out.
Choose the grammatically correct option from the following
Choose the correct option.
When someone refers to someone or something as “the bee’s knees” they mean that it is:
The amount of milk delivered by a milkman to a house is 98 litres over a period of 1 month. During this period, the average milk consumption in that house on weekdays (total 22 days) is 3 litres per day. Find the average daily consumption in that house on weekends, if the month is April.
If 157k-3 > 1; which of the following is true about k ?.
What is the value of log6 169 x log13 6 x log7 64 x log4 49?
The difference between the simple interest and compound interest earned on a sum placed for two years at 8% is Rs.30.72, when the interest is compounded annually. If the interest were to be compounded on a half-yearly basis, what would the difference in the two interest amount approximately be?
What is the total number of ways in which 101 prizes can be distributed among 5 boys if each boy receives an odd number of prizes?
What is the next term in the following series? 12, 14, 116, 1136, ?
In a certain language, if SMILE is coded as XRNQJ, how is MOUSE coded in that language?
Answer the following question based on the information given below.
The figures below provide some data about the subjects taken by all students of a particular school. The square, circle, triangle and rectangle represent Biology, Physics, Maths and Chemistry respectively. The number inside each figure represents the number of students studying each subject. Study the diagram carefully and answer the questions.
Q. How many students study Physics and Maths but not Biology or Chemistry?
Answer the following question based on the information given below.
The figures below provide some data about the subjects taken by all students of a particular school. The square, circle, triangle and rectangle represent Biology, Physics, Maths and Chemistry respectively. The number inside each figure represents the number of students studying each subject. Study the diagram carefully and answer the questions.
Q. How many students study atleast two subjects?
An item is marked at Rs.200 and a discount of 25% is given on MP. The item costs Rs. 80 and another item worth Rs. x is sold with it (at cost). The overall profit made was 50%. Find x (in Rs.).
Three unbiased dice are thrown simultaneously. What is the probability that the sum of the three numbers on them is divisible by 4?
Distance between A and B is 100 m. If P and Q start simultaneously from A and B respectively, then they meet in 4 seconds. If P and Q start simultaneously from A to reach B, then P beats Q by 20 m. How much time will P take to cover 200 m at the same speed?
Answer the questions based on the following graph.
Six friends played seven online games each, in the same week, and their respective scores are given below. The pie chart gives the game wise breakup for Vikas.
Q. If the 2nd game’s score hadn’t been added to Vikas’ total score due to some technical error, then his rank would____. The total score of all the other players remains the same.
Answer the questions based on the following graph.
Six friends played seven online games each, in the same week, and their respective scores are given below. The pie chart gives the game wise breakup for Vikas.
Q. What is the combined score of Vikas in the 4th, 5th and 7th games put together?
Answer the questions based on the following graph.
Six friends played seven online games each, in the same week, and their respective scores are given below. The pie chart gives the game wise breakup for Vikas.
Q. If Deepu and Mayank respectively scored 10% and 15% of their total score in the 3rd game, then by what percentage was the score of Mayank in the 3rd game more than the score of Deepu in the 3rd game?