Test: Circulatory System - 1 - Class 10 MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Circulatory System - 1
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The circulation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood to the lungs is classified as
Erythrocytes of adult rabbit and other mammals are formed in :-
What divides the left side of the heart from the right side?
The microcirculation and macro circulation are classified as two part of
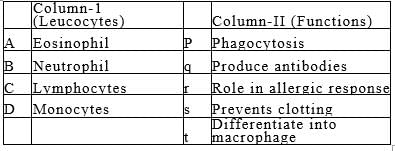
Match the different leucocytes given under Column I with their functions given under Column II. Choose the answer that gives the correct combination of alphabets of two columns :-
In the diagram of the vertical section of human heart given below certain parts have been indicated by alphabets. Choose the answer in which these alphabets have been correctly matched with the parts they indicate :-
A sudden increase in the number of white blood cells in the blood is a sign of :-
Clotting of blood is achieved with the help of the following :-

















