Level 3 Test: Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Level 3 Test: Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants
In an embryo sac, the cells that degenerate after fertilization are:
An ovule bent to come at right angles to funicle is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Ubisch bodies are connected with the formation of
Assertion: Groundnut & pea are non endospermic.
Reason: They do not synthesize endosperm.
What is the function of filiform apparatus in an angiosperm embryo sac?
The female gametophyte of a typical dicot at the time of fertilization is
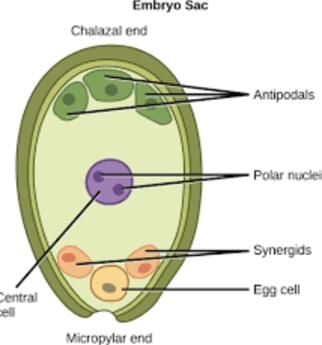
Polygonum type of embryo sac is
Both chasmogamous and cleistogamous flowers are present in
Even in absence of pollinating agents seed-setting is assured in
A dioecious flowering plant prevents
How many microspore mother cells are required to produce 1000 microspores/pollen grains?
Which of the following represents the female gametophyte in angiosperms?
In a breeding experiment, the selected male parent is diploid and the female parent is tetraploid. What will be the ploidy level of the endosperm that will develop after double fertilisation?
The development of fruits without fertilisation of the ovary, is called
When the pollen of a flower is transferred to the stigma of another flower on the same plant, the process is known as
A dicotyledonous plant bears flowers but never produces fruits and seeds. The most probable cause for the above situation is
Male and female flowers are present on different plants (dioecious) to ensure xenogamy, in
Plants with ovaries having only one or a few ovules are generally pollinated by
Which of the following is a water pollinated plant ?

















