Past Year Questions: Linear Programming - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Past Year Questions: Linear Programming
In an assembly line for assembling toys, five workers are assigned tasks which take times of 10, 8, 6, 9 and 10 minutes respectively. The balance delay for line is
[1996]
If at the optimum in a linear programming problem, a dual variable corresponding to a particular primal constraint is zero, then it means that
[1996]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
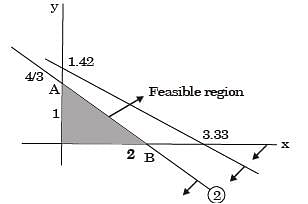
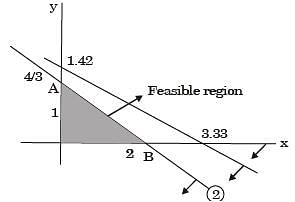
A manufacturer produces two types of products, 1 and 2, at production levels of x1 and x2 respectively. The profit is given is 2x1 + 5x2. The production constraints are:
x1 + 3x2 < 40
3x1 + x2 < 24
x1 + x2 < 10
x1 > 0 x2 > 0
The maximum profit which can meet the constraints is
[2003]
x1 + 3x2 < 40
3x1 + x2 < 24
x1 + x2 < 10
x1 > 0 x2 > 0
The maximum profit which can meet the constraints is
A component can be produced by any of the four processes, I, II, III and IV. Process I has fixed cost of Rs. 20 and variable cost of Rs. 3 per piece.Process II has a fixed cost of Rs. 50 and variable cost of Rs. 1 per piece. Process III has a fixed cost of Rs. 40.00 and variable cost of Rs. 2 per piece. Process IV has fixed cost of Rs. 10 and Variable cost Rs. 4 per piece. If company wishes to produce 100 pieces of the component, from economic point of view it should choose
[2005 : 2 Marks]
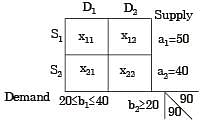
A company has two factories S1, S2 and two warehouses D1, D2. The supplies from S1 and S2 are 50 and 40 units respectively. Warehouse D1 requires a minimum of 20 units and a maximum of 40 units. Warehouse D2 requires a minimum of 20 units and, over and above, it can take as much as can be supplied. A balanced transportation problem is to be formulated for the above situation. The number of supply points, the number of demand points, and the total supply (or total demand) in the balanced transportation problem respectively are
[2005]
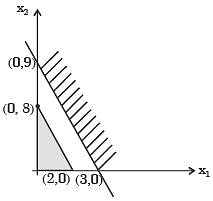
If an additional constraint X1 + X2 < 5 is added, the optimal solution is
[2005]
Let Y1 and Y2 be the decision variables of the dual and v1 and v2 be the slack variables of the dual of the given linear programming problem.The optimum dual variables are
[2005]
A firm is required to procure three items (P, Q, and R). The prices quoted for these items (in Rs.) by suppliers S1, S2 and S3 are given in table. The management policy requires that each item has to be supplied by only one supplier and one supplier supply only one item.The minimum total cost (in Rs.) of procurement to the firm is
[2006]
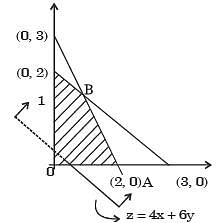
Consider the following Linear Programming Problem (LPP):
Maximize z = 3x1 + 2x2,
Subject to x1 < 4 x2 < = 6
3x1 + 2x2 < 18
x1 > 0, x2 > 0
[2009]
One unit of product P1 requires 3 kg of resource R1 and 1 kg resource R2. One unit of product P2 requires 2 kg of resource R1 and 2 kg of resource R2. The profits per unit by selling product P1 and P2 and Rs. 12000 and Rs 3000 respectively. The manufacturer has 90 kg of resource R1, and 100 kg of resource R2.
The unit worth of resource R2, i.e. dual price of resource R2 in Rs per kg is
[2011]
The manufacturer can make a maximum profit of Rs.
[2011]
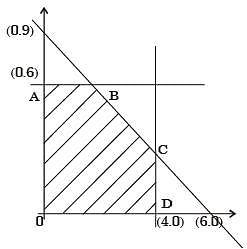
A linear programming problem is shown below:
Maximise 3x + 7y
Subjeot to 3x + 7y < 10
4x + 6y < 8 x, y > 0
[2013]
Maximize z = 15x1 + 20x2
Subject to 12x1 + 4x2 > 36
12x1 + 6x2 > 24 x1,
x2 > 0
The above linear programming problem has
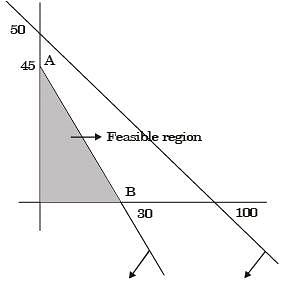
For the linear programming problem:
Maximize z = 3x1 + 2x2
Subject to –2x1 + 3x2 < 9x1 – 5x2 > – 20x1, x2 > 0
The above problem has
[2016]
For the standard transportation linear program with m sources and n destinations and total supply equaling total demand, an optimal solution (lowest cost) with the smallest number of non-zero xij values (amounts from source i to destination j) is desired. The best upper bound for this number is
[2008]
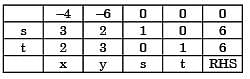
After introducing slack variables s and t, the initial basic feasible solution is represented by the table below (basic variables are s = 6 and t = 6, and the objective function value is 0).
After some simplex iterations, the following table is obtained
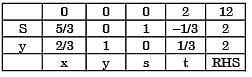
From this, one can conclude that
[2008]
Simplex method of solving linear programming problem uses
[2010]
A company produces two types of toys : P and Q. Production time of Q is twice that of P and the company has a maximum of 2000 time units per day. The supply of raw material is just sufficient to produce 1500 toys (of any type) per day. Toy type Q requires an electric switch which is available @ 600 pieces per day only.The company makes a profit of Rs. 3 and Rs. 5 on type P and Q respectively. For maximizationof profits, the daily production quantities of P and Q toys should respectively be
[2004]
The manufacturer can make a maximum profit of Rs.
[2011]


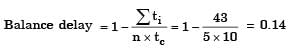 = 14%
= 14%