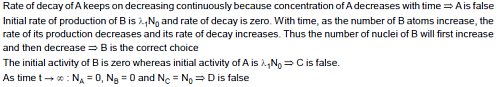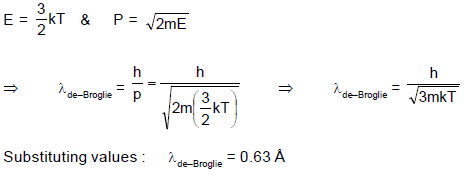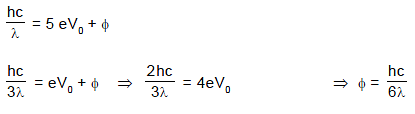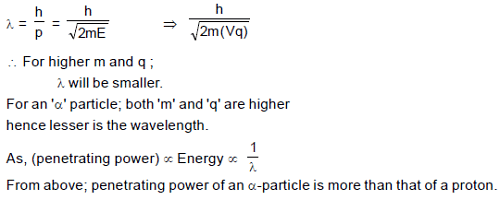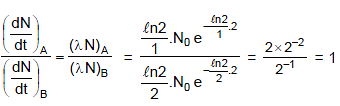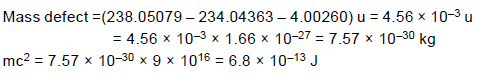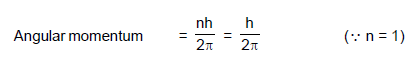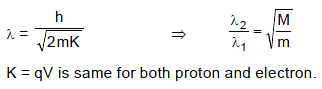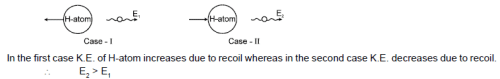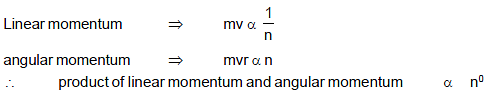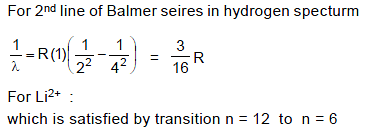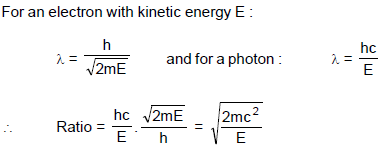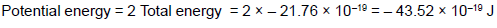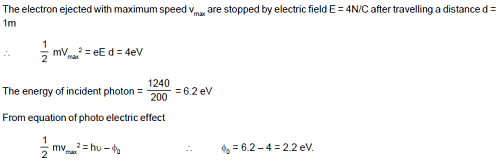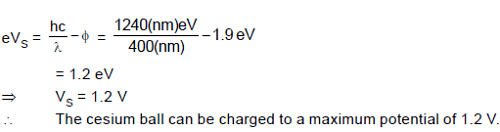Part Test- 6 (JEE Main 2018) - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Part Test- 6 (JEE Main 2018)
A radioactive nuclide A decays to nuclide B which further decays to C. Their disintegration constant are λ1 and λ2 respectively. At t = 0 only nuclei A are present. Number of nuclei A at t = 0 is N0.
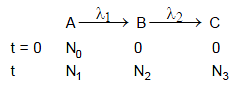
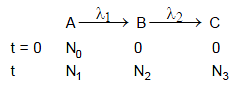
An enclosure filled with helium is heated to a temperature of 400 K. Helium atom emerges out of the enclosure. The mean debroglie wavelength of the helium atoms is :
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
When a metallic surface is illuminated with monochromatic light of wavelength λ, the stopping potential is 5 V0. When the same surface is illuminated with light of wavelength 3λ, the stopping potential is V0. Then the work function of the metallic surface is :
No. of identical photons incident on a perfectly black body of mass m kept at rest on smooth horizontal surface. Then the acceleration of the body if n number of photons incident per second is (Assume wavelength of photon to be λ) :
If we assume that penetrating power of any radiation/particle is inversely proportional to wavelength of the particle then :
Two radioactive sources A and B initially contain equal number of radioactive atoms. Source A has a half-life of 1 hour and source B has a half-life of 2 hours. At the end of 2 hours, the ratio of activity of source A to that of B is :
The radionuclide 238U decays by emitting an alpha particle.
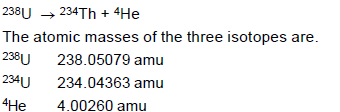
What is the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted alpha particle? Express your answer in Joule.
(1amu =1.67 x 10-27 kg)
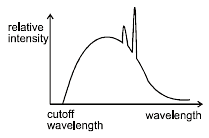
A beam of electrons striking a copper target produces X-rays.Its spectrum is as shown. Keeping the voltage same if the copper target is replaced with a different metal, the cut-off wavelength and characteristic lines of the new spectrum will change in comparision with old as :
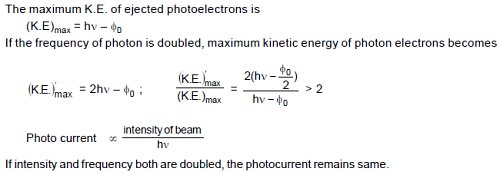
Both the frequency and the intensity of a beam of light falling on the surface of photoelectric material are increased by a factor of two. This will :
The photon radiated from hydrogen corresponding to 2nd line of Lyman series is absorbed by a hydrogen like atom ‘X’ in 2nd excited state. As a result the hydrogen like atom ‘X’ makes a transition to nth orbit. Then,
The angular momentum of an electron in first orbit of Li++ ion is :
An electron is accelerated through a potential difference of V volt. It has a wavelength λassociated with it. Through what potential difference must an electron be accelerated so that its de-Broglie wavelength is the same as that of a proton? Take mass of a proton to be 1837 times larger than the mass of electron.
Two hydrogen atoms are in excited state with electrons residing in n = 2. First one is moving towards left and emits a photon of energy E1 towards right. Second one is moving towards left with same speed and emits a photon of energy E2 towards left. Taking recoil of nucleus into account during emission process
In a hydrogen atom following the Bohr’s postulates the product of linear momentum and angular momentum is proportional to (n)x where ‘n’ is the orbit number. Then ‘x’ is :
One of the lines in the emission spectrum of Li2+ has the same wavelength as that of the 2nd line of Balmer series in hydrogen spectrum. The electronic transition corresponding to this line is :
The ratio of wave length of a photon of energy E and deBroglie wavelength of an electron of mass 'm' having the kinetic energy also E is : (Speed of light = c)
An orbital electron in the ground state of hydrogen has an angular momentum L1 and an orbital electron in the first orbit in the ground state of lithium (double ionised positively charged) has an angular momentum L2 .Then :
If in the first orbit of a hydrogen atom the total energy of the electron is -21.76 x 10-19J, then its electric potential energy will be :
In an x - ray tube, if the accelerating potential difference is changed, then:
All electrons ejected from a surface by incident light of wavelength 200 nm can be stopped before travelling 1 m in the direction of uniform electric field of 4 N/C. The work function of the surface is:
The energy ratio of two Kα photons obtained in x-ray from two metal targets of atomic numbers Z1 and Z2 is:
A cobalt (atomic no. = 27) target is bombarded with electrons, and the wavelengths of its characteristic x-ray spectrum are measured. A second weak characteristic spectrum is also found, due to an impurity in the target. The wavelengths of the Kα lines are 225.0 pm (cobalt) and 100.0 pm (impurity). Atomic number of the impurity is (take b = 1)
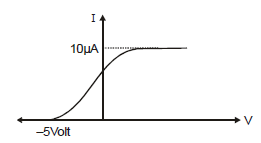
In the photoelectric experiment, if we use a monochromatic light, the I - V curve is as shown. If work function of the metal is 2eV, estimate the power of light used. (Assume efficiency of photo emission = 10–3%, i.e. number of photoelectrons emitted are 10–3% of number of photons incident on metal.)
If first excitation potential of a hydrogen like atom is V volt, then the ionization energy of this atom will be :
The element which has a ka x-rays line of wavelength 1.8 Å is (R =1.1 x 107 m-1 , b=1 and = 0.39)
The radii of nuclei of two atoms are in ratio 3/2 . Assuming them to be Hydrogen like atom, the ratio of their orbital radius for K shell will be (assume no. of proton = No. of neutron for each atom)
A radioactive nucleus can decay by either emitting an α particle or by emitting a β particle. Probability of α decay is 75% while that of β decay is 25%. The decayconstant of α decay is λ1 and that of b decay is λ2 . is
A radioactive nucleus ' X ' decays to a stable nucleus ' Y '. Then the graph of rate of formation of ' Y' against time ' t ' will be :