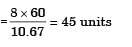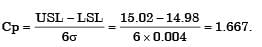Past Year Questions: Production, Planning And Control - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
16 Questions MCQ Test - Past Year Questions: Production, Planning And Control
The manufacturing area of a plant is divided into four quadrants. Four machines have to located one in each quadrant. The total number of possible layouts is
[1995]
Production flow analysis (PFA) is a method of identifying part families that uses data from
[2001]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Two machines of the same production rate are available for use. On machine 1, the fixed cost is Rs. 100 and the variable cost is Rs. 2 per piece produced. The corresponding numbers for the machine are Rs. 200 and Rs. 1 respectively.For certain strategic reasons both the machines are to be used concurrently. The sale price of the first 800 units is Rs. 3.50 per unit & and subsequently it is only Rs. 3.00. The breakeven production rate for each machine is
[2003]
A standard machine tool and an automatic machine tool are being compared for the production of a component. Following data refers to the two machines.The breakeven production batch size above which the automatic machine tool will be economical to use, will be
[2004]
A soldering operation was work-sampled over two days (16 hours) during which an employee soldered 108 joints, actual working time was 90% of the total time and the performance rating was estimated to be 120 percent. If the contract provides allowance of 20 percent of the total time available, the standard time for the operation would be
[2004]
An electronic equipment manufacturer has decided to add a component subassembly operation that can produce 80 units during a regular 8-hour shift.This operation consists of three activities as belowFor line balancing the number of work stations required for the activities M, E and T would respectively be
[2004]
A welding operation is time-studied during which an operator was pace-rated as 120%. The operator took, on an average, 8 minutes for producing the weld-joint. If a total of 10% allowances are at lowed for this operation. The expected standard production rate of the weldjoint (in units per 8 hour day) is
[2005]
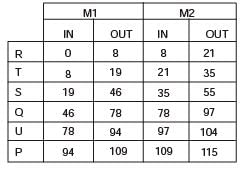
A manufacturing shop processes sheet metal jobs, wherein each job must pass through two machines (M1 and M2, in that order). The processing time (in hours) for these jobs isThe optimal make-span (in hours) of the shop is
[2006]
The table gives details of an assembly line.What is the line efficiency of the assembly line?
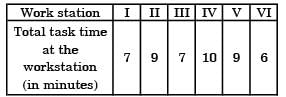
[2006]
Capacities of production of an item over 3 consecutive months in regular time are 100,100 and 80 and in overtime are 20, 20 and 40. The demands over those 3 months are 90, 130 and 110. The cost of production in regular time and overtime are respectively Rs. 20 per item and Rs. 24 per item. Inventory carrying cost is Rs. 2 per item month. The levels of starting and final inventory are nil. Backorder is not permitted. For minimum cost of plan, the level of planned production in overtime in the third month is
[2007]
The Product structure of an assembly P is shown in the figure.Estimated demand for end product P is as follows:Ignore lead times for assembly and subassembly. Production capacity (per week) for component R is the bottleneck operation.Starting with zero inventory, the smallest capacity that will ensure a feasible production plan up to week 6 is
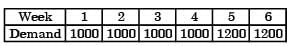
[2008]
Vehicle manufacturing assembly line is an example of
[2010]
The word kanban is most appropriately associated with
[2011 : 1 Mark]
Which one of the following is NOT a decision taken during the aggregate production planning stage?
[2012]
During the development of a product, an entirely new process plan is made based on design logic, examination of geometry and tolerance information. This type of process planning is known as
[2015]
Cylindrical pins of diameter 15±0.020 mm are being produced on a machine. Statistical quality control tests show a mean of 14.995 mm and standard deviation of 0.004 mm. The process capability index Cp is
[2017]


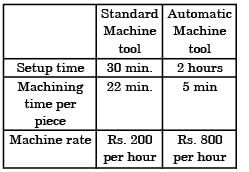
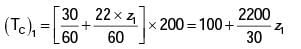 Total cost of z2 component by using Automatic Machine tool,
Total cost of z2 component by using Automatic Machine tool,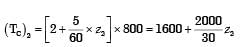 Let break even point be z number of components
Let break even point be z number of components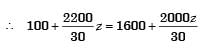




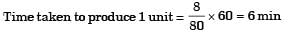 T = 6 min
T = 6 min
 Standard Production rate =
Standard Production rate =