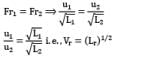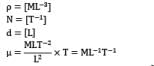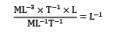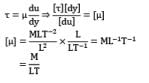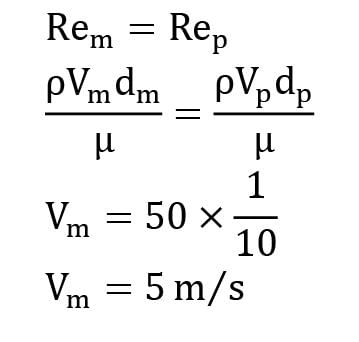Test: Dimensional Analysis & Modeling - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Dimensional Analysis & Modeling
In similitude with gravity force, where equality of Froude number exists, the velocity ratio becomes
where Lr = ratio of linear dimensions of model and prototype.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Consider the following statements:
1. At low Reynolds numbers of any flow, viscous forces dominate over inertial forces. 2. Transition from laminar to turbulent flow occurs over a range of Reynolds number depending on the surface presented to the flow.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
The laminar flow is characterized by Reynolds number which is
Laminar flow between closely spaced parallel plates is governed by the consideration of which one of the following pairs of forces?
The unit of the following property is not m2⁄s
In flow through a pipe, the transition from laminar to turbulent flow does not depend on
In a compressible fluid flow field, the Mach number indicates the ratio of
Weber number is ratio of square root of inertial force to
Assertion (A): In fluid system model studies, a simple scaling-up of measurements made on the model may not yield results accurately corresponding to the prototype.
Reason (R): Surface tension forces may be relatively much more significant in the model than in the prototype.
What are the forces that influence the problem of fluid statics?
The time period of a simple pendulum depends on its effective length l and the local acceleration due to gravity g. What is the number of dimensionless parameters involved?
What is the correct dimensionless group formed with the variables ρdensity, Rotational speed, diameter and μcoefficient of viscosity?
A model of a golf ball is to be studied to determine the effects of the dimples. A sphere 10 times larger in diameter than an actual golf ball is used in the wind tunnel study. What speed should be selected for the model to simulate a prototype speed of 50 m ⁄ s ?