Equilibrium Test (18-12-2016) - IIT JAM MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Equilibrium Test (18-12-2016)
Consider the phase diagram given below:
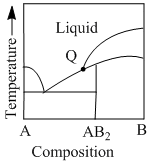
At the intersection point Q has phases that are in equilibrium are

For the following equilibrium: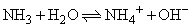 calculate the equilibrium constant, if for the equilibrium,
calculate the equilibrium constant, if for the equilibrium,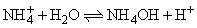
The equilibrium constant is 5.5 × 10-10.
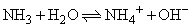 calculate the equilibrium constant, if for the equilibrium,
calculate the equilibrium constant, if for the equilibrium,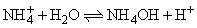
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The elevation in boiling point of a solution of 10 g of a binary electrolyte (molecular mass 100) in 100 g of water is ΔTb. The value of Kb for water is:
For the reaction,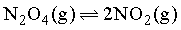 if percentage dissociation of N2O4 are 25%, 50%, 75% and 100%, then the sequence of observed vapour densities will be:
if percentage dissociation of N2O4 are 25%, 50%, 75% and 100%, then the sequence of observed vapour densities will be:
For the reaction, 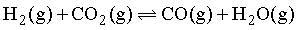 if the initial concentration of [H2] = [CO2] and x mol/litre of H2 is consumed at equilibrium, the correct expression of Kp is:
if the initial concentration of [H2] = [CO2] and x mol/litre of H2 is consumed at equilibrium, the correct expression of Kp is:
H3PO4 is a tribasic acid, it undergoes ionization as:
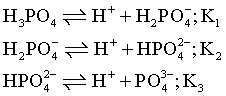
Then, equilibrium constant for the followimg reaction will be:
The equilibrium constant for the reaction is 5. How many moles of CO2 must be added to 1 litre container already containing 3 moles each of CO and H2O to make 2M equilibrium concentration of CO?
A nitrogen–hydrogen mixture initially in the molar ratio of 1:3 reacted equilibrium to form ammonia when 25% of the N2 and H2 had reached. If the total pressure of the system was 21 atm, the partial pressure of ammonia at the equilibrium was:
The freezing point depression constant for water is 1.86°C m–1. If 5 g Na2SO4 is dissolved in 45 g H2O, the freezing point is changed by –3.82°C. Calculate the van't Hoff factor for Na2SO4.
At 25°C, the volue of Pkb (Kb being the dissociation constant as a base) for NH3 in aqueous solution is 4.7. What is the pH of 0.1 M aqueous solution of NH4Cl with 0.01 M NH3 (approxmately):
The solution of CaF2(Ksp = 3.4 × 10–11) in 0.1 M solution of NaF would be:
For the chemical equilibrium can be determined from which one of the following plots?
On adding 0.1 M solution each of Ag+, Ba2+ and Ca2+ in an Na2SO4 solution, the species first precipitated is (Ksp BaSO4 = 10–11, Ksp CaSO4 = 10–6, Ksp Ag2SO4 = 10–5):
Which of the following expression for % ionization of a mono-acidic base (BOH) in aqueous solution at appreciable concentration is correct?
Which of the Following is/are affected by pressure change?
A buffer solution can be prepared from a mixture of?
The equilibrium 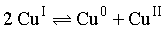 in aqueous medium at 250C shifts towards the left in the presence of:
in aqueous medium at 250C shifts towards the left in the presence of:
The solubility of Pb(OH)2 in water is 6.7x10-6M. The solubility of Pb(OH)2 in a buffer solution of PH=8 is 1.2x10-x what is the value of x
3.1 mole of FeCl3 and 3.2 mole of NH4SCN are added tone litre of water. At equilibrium, 3.0 mol of FeSCN2+ are formed. The equilibrium constant Kc of the reaction,
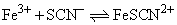 will be:
will be:
The equilibrium of formation of phosgene is represented as:
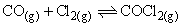
The reaction is carried out in a 500 ml flask. At equilibrium 0.3 mole of phosgene, 0.1 mole of CO and 0.1 mole of Cl2 are present. The equilibrium constant of the reaction is:
SO3(g) is heated in a closed vessel. An equilibrium: 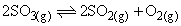 is established. The vapour density of the mixture, in which SO3 is 50% dissociated, is:
is established. The vapour density of the mixture, in which SO3 is 50% dissociated, is:
The dissociation constant of a substituted benzoic acid at 250C is 1.0x10-4. The PH of 0.01M solution of its sodium salt is.
Consider the following reversible system:
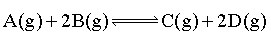 At equilibrium, there are 1.0 mole of A and 2.0 moles of each B,C & D present. If 2.0 mole of B is added further, how many moles of C would be required to be added so that mole of A & D do not change?
At equilibrium, there are 1.0 mole of A and 2.0 moles of each B,C & D present. If 2.0 mole of B is added further, how many moles of C would be required to be added so that mole of A & D do not change?
0.10 mole each of SO2 and SO3 are mixed in a 2.0 dm3 flask at 300K. Equilibrium is attained as
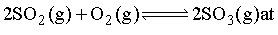
equilibrium pressure is 281.68 kpa. The mole fraction of O2
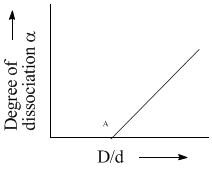
In the Reaction,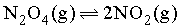 if D and d are the vapour densities at initial stage and at equilibrium then what will be the value of
if D and d are the vapour densities at initial stage and at equilibrium then what will be the value of 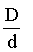 at point A in the following graph?
at point A in the following graph?
The number of degree of freedom of a system consisting of solid sucrose in equilibrium with an aqueous solution of sucrose is:
0.16 g of N2H4 are dissolved in water and the total volume made up to 500 mL. Calculate the percentage of N2H4 that has reacted with water at this dilution. The Kb for N2H4 is 4.0 × 10–6 M:

















